CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing technology has emerged as one of the most transformative advancements in medicine and biotechnology. This precise tool allows scientists to make targeted modifications to DNA, offering immense potential for treating genetic disorders, advancing medical research, and addressing global health challenges.
How CRISPR Works: A Closer Look
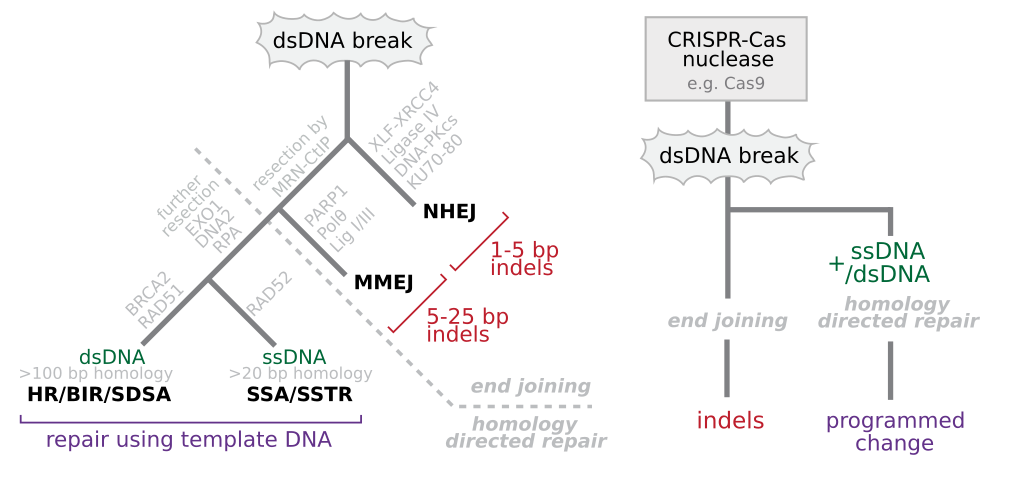
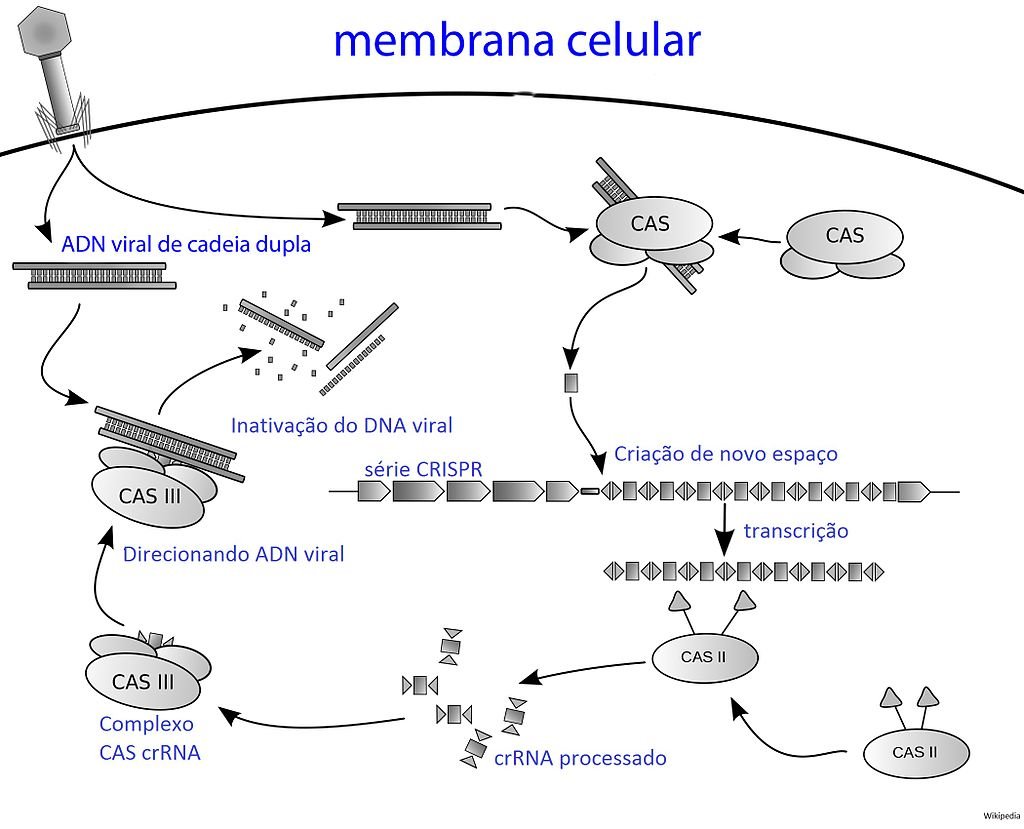
CRISPR-Cas9 acts like molecular scissors, capable of cutting and editing DNA at specific locations. Originally discovered in bacteria as a defense mechanism against viruses, the CRISPR system recognizes the targets specific DNA sequences with precision. This functionality has enabled researchers to alter genetic material in ways that were previously unimaginable.
Applications in Genetic Medicine
CRISPR holds tremendous promise in treating genetic disorders such as cystic fibrosis, sickle cell anemia, and Huntington’s disease. Clinical trials are underway to evaluate how CRISPR can correct defective genes in patients. Additionally, researchers are exploring its potential in cancer therapies, particularly in reprogramming immune cells to target and destroy tumors.
Ethical Considerations and Challenges
While the potential of CRISPR is undeniable, its application raises important ethical concerns. Questions surrounding gene editing in embryos, “designer babies,” and unintended genetic consequences are at the forefront of scientific debates. Regulatory frameworks and ongoing discussions aim to ensure that this technology is used responsibly.
Future Prospects of CRISPR
As researchers continue to refine CRISPR technology, its applications are expanding beyond medicine into agriculture, environmental science, and more. From engineering disease-resistant crops to potentially eliminating diseases like malaria, CRISPR is poised to revolutionize multiple sectors. The possibilities are vast, and ongoing innovation ensures that the technology remains at the cutting edge.
Conclusion
CRISPR gene editing represents a paradigm shift in medicine, offering unparalleled precision and potential in addressing genetic challenges. While ethical considerations must guide its use, the advancements in technology continue to unlock revolutionary possibilities for improving human health and beyond.
Source:





