Zoonotic diseases, or zoonoses, are infections that are transmitted from animals to humans. Examples like COVID-19, Ebola, and Avian Influenza underscore the significant threat they pose to public health. These diseases can be caused by various pathogens, including bacteria, viruses, and parasites, often with devastating outcomes for human populations. Understanding and preventing these diseases involves recognizing the interplay between humans, animals, and the environment.
The Connection Between Wildlife and Zoonotic Diseases
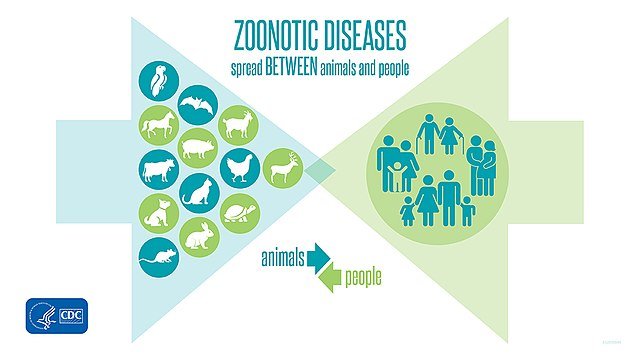
Zoonotic Diseases – Spread BETWEEN animals and people. Image by CDC, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
Wildlife plays a crucial role in the emergence and spread of zoonotic diseases. Many pathogens originate in wild animals and cross over to humans through direct contact or through vectors such as insects. This transmission can stem from habitat destruction, illegal wildlife trade, and closer human-animal interactions. As human activities encroach more closely on natural habitats, there’s an increased risk of novel diseases spilling over from wildlife to humans.
The Role of Wildlife Conservation

Wildlife conservation is pivotal in preventing the spillover of zoonotic diseases. By preserving the natural habitats and ecosystems, conservation efforts reduce human-wildlife interactions, which are often the trigger points for zoonotic diseases. Healthy and robust ecosystems can control disease vectors naturally and reduce the likelihood of pathogens leaping from animals to humans. Conservation also involves protecting biodiversity, which plays a vital role in maintaining the balance of ecosystems.
Habitat Protection as a Preventive Measure

Preserving natural habitats is one of the most effective strategies for preventing zoonotic diseases. When forests and grasslands are destroyed for agriculture or urban development, wild animals are forced into closer contact with humans, increasing the chances of disease transmission. Protected areas and wildlife corridors can help keep animals and humans safely apart while allowing wildlife to thrive in their natural environments.
Biodiversity and Disease Regulation

Biodiversity acts as a natural buffer against disease. A diverse ecosystem can limit the spread of pathogens because it often includes species that are not suitable hosts for diseases, thus interrupting transmission cycles. The dilution effect theory suggests that higher biodiversity leads to lower disease prevalence, as there are more non-host species that dilute the impact and transmission of pathogens. Maintaining species diversity through conservation efforts can be crucial in controlling the spread of zoonotic diseases.
Addressing Illegal Wildlife Trade

Illegal wildlife trade is a critical issue linked to zoonotic disease transmission. The capture, transport, and sale of wild animals bring humans into close contact with potentially infected animals, bypassing the natural barriers that protect us from these pathogens. Enforcing laws against illegal trade, promoting sustainable practices, and raising awareness are essential steps in reducing the risks of disease transmission associated with wildlife trafficking.
Global Cooperation and Policy Initiatives

Wildlife conservation strategies must be supported by robust global cooperation and policy frameworks. International collaborations such as the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species (CITES) and World Health Organization (WHO) initiatives foster sharing of knowledge, resources, and strategies to address the global nature of zoonotic diseases. Strengthening regulations and promoting integrative health approaches that consider the health of humans, animals, and the environment are pivotal for effective prevention strategies.
Community Engagement and Education

Engaging local communities in conservation efforts is vital for sustainable outcomes. Educating communities about the importance of wildlife conservation and the risks of zoonotic diseases can motivate local action and compliance with conservation regulations. Involving communities ensures that conservation strategies are culturally appropriate and economically viable, creating custodians of natural spaces who can effectively aid in preventing disease spillovers.
Conclusion
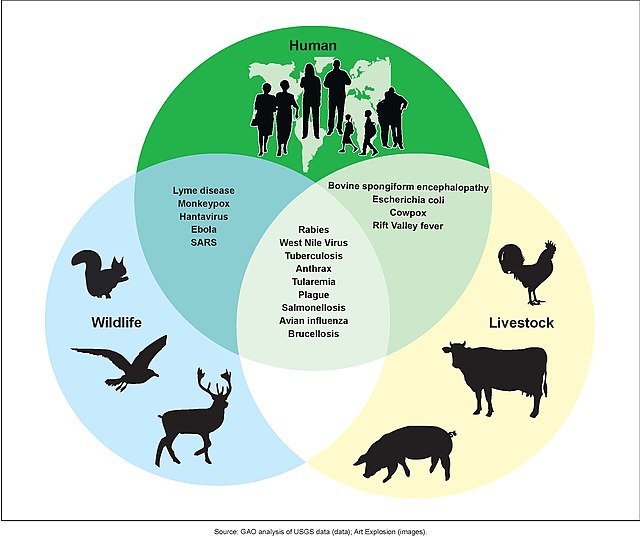
Wildlife conservation is a key factor in preventing zoonotic diseases. From protecting habitats and preserving biodiversity to combating illegal wildlife trade and fostering global cooperation, conservation efforts play an essential role in mitigating the risks of diseases that can have catastrophic impacts on human populations. Promoting an integrated approach that recognizes the interdependencies between human and ecological health is crucial in safeguarding both people and the planet from future pandemics.

Jan loves Wildlife and Animals and is one of the founders of Animals Around The Globe. He holds an MSc in Finance & Economics and is a passionate PADI Open Water Diver. His favorite animals are Mountain Gorillas, Tigers, and Great White Sharks. He lived in South Africa, Germany, the USA, Ireland, Italy, China, and Australia. Before AATG, Jan worked for Google, Axel Springer, BMW and others.




