Plants are not just a backdrop to our daily lives; they play a vital role in regulating the Earth’s climate. From the towering trees of rainforests to the humble meadow grasses, plants have a profound impact on the global climate system. This article explores the various ways in which plants contribute to climate control, emphasizing their importance in maintaining our planet’s delicate balance.
Introduction to Plants and Climate Regulation

At first glance, it might seem that plants are passive components of the natural world, simply existing as a food source or providing us with shade on a hot summer day. However, they are key players in the global climatic system. Through processes like photosynthesis, carbon storage, and evapotranspiration, they help regulate atmospheric conditions, influencing weather patterns, temperatures, and even rainfall. Understanding these processes highlights the critical importance of plant life in sustaining a habitable planet.
Photosynthesis: The Earth’s Green Lung

Plants absorb carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere during photosynthesis, the process by which they manufacture food using sunlight. This not only helps reduce excess atmospheric CO2—a significant greenhouse gas—but also produces oxygen as a byproduct, which is essential for the survival of most life forms. Photosynthesis acts as a natural check on global warming and highlights plants’ essential role as nature’s air purifiers.
Carbon Sequestration: Nature’s Storage Units

Through carbon sequestration, plants capture and store atmospheric CO2 in their biomass and the soil. Forests, particularly tropical rainforests, are enormous carbon reservoirs, holding vast amounts of carbon that would otherwise contribute to atmospheric CO2 levels. This storage not only helps mitigate climate change but also underscores the critical importance of conserving and restoring forest ecosystems worldwide.
Evapotranspiration: The Natural Cooling System

Plants release water vapor into the air through a process called evapotranspiration, which has a cooling effect on the environment. This process is not only vital for keeping regional climates stable but also influences global weather patterns by contributing to cloud formation and precipitation. In urban areas, this natural cooling effect is particularly beneficial, helping to counteract the urban heat island effect.
Albedo Effect: Reflecting Solar Energy

Vegetation affects the Earth’s albedo, which is its ability to reflect solar energy back into space. Dense forests and vegetative cover typically have a lower albedo compared to bare surfaces, absorbing more sunlight and retaining heat. However, vegetation still helps moderate temperatures by offsetting the heat through transpiration and shading, thus maintaining a balance.
Influence on Rainfall Patterns
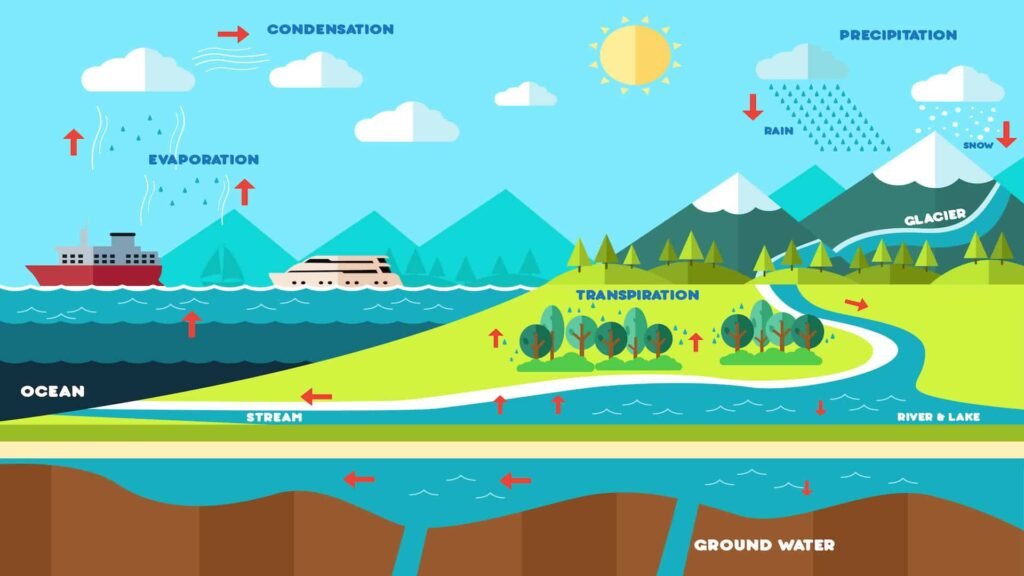
Plants play a crucial role in the water cycle, influencing precipitation patterns. They draw water from the soil and release it into the atmosphere, where it contributes to cloud formation and precipitation. Forests, in particular, are vital for maintaining regional and global precipitation systems, acting as natural regulators of rainfall and reducing the risk of drought.
The Role of Coastal Vegetation
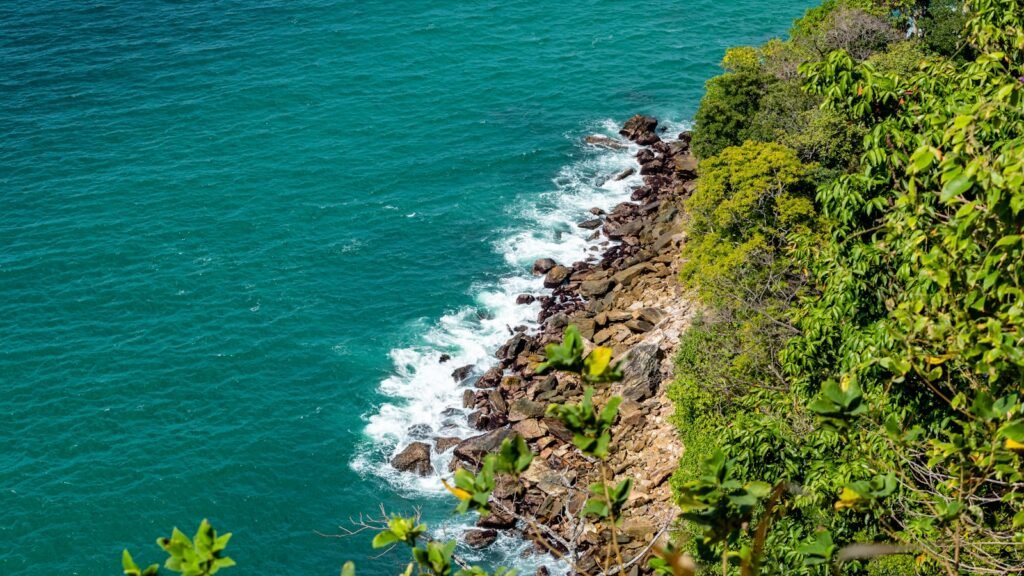

Coastal vegetation, such as mangroves and salt marshes, acts as a buffer between land and sea, protecting shorelines from erosion while also capturing carbon in sediment layers. These ecosystems are crucial for biodiversity and act as formidable carbon sinks, adding yet another layer to their climate regulatory role.
Impact of Deforestation on Climate

When forests are cleared or degraded, the climate regulation services they provide are significantly diminished. Deforestation contributes to increased atmospheric CO2 levels, reduced rainfall, and heightened temperatures, exacerbating global climate change. The loss of forests shifts the balance, emphasizing the need for conservation and sustainable management of land resources.
The Importance of Reforestation

Reforestation and afforestation are vital strategies in the fight against climate change. Planting trees not only helps restore lost carbon sinks but also revitalizes ecosystems and enhances biodiversity. These efforts contribute significantly to offsetting carbon emissions and mitigating climate impacts, demonstrating the crucial role of proactive environmental stewardship.
Plants as Climate Resilience Builders

By stabilizing ecosystems and supporting biodiversity, plants help build resilience to climate impacts. Healthy ecosystems can better withstand and recover from extreme weather events, such as floods or droughts, protecting human and animal communities alike. The preservation and restoration of plant life are therefore essential components of climate adaptation strategies.
The Future of Plant-Inclusive Climate Strategies

As recognition of the importance of plants in climate regulation grows, more integrated approaches are being developed to incorporate natural solutions into climate policy. Encouraging sustainable agricultural practices, protecting natural ecosystems, and investing in green infrastructure are all essential for leveraging the full climate regulatory potential of plants.
Conclusion: Valuing Our Green Allies

Plants are indispensable allies in the fight against climate change, playing multifaceted roles in regulating Earth’s temperature and maintaining environmental balance. From absorbing carbon dioxide and releasing oxygen to moderating weather patterns and supporting biodiversity, these green champions are central to sustaining life on our planet. As we confront the climate crisis, acknowledging and enhancing the role of plants will be crucial for developing effective strategies and ensuring a sustainable future. By valuing and protecting our green allies, we protect not just the planet’s climatic systems but the very foundation of life itself.




