The story of human evolution is a fascinating tale that spans millions of years, unveiling the intricate journey of our ancestors from australopithecines to modern Homo sapiens. Central to this narrative is the enduring concept of the “missing link”—a popular term capturing the gaps in our understanding of human evolution. As scientists continue to unearth evidence, the quest to piece together this evolutionary puzzle becomes increasingly captivating. But what exactly do we know about our evolutionary lineage so far?
Understanding the Missing Link

The term “missing link” is often used to describe transitional fossils that bridge the gaps between distinct evolutionary stages. In the context of human evolution, it refers to the hypothetical ancestors that connect non-human primates with Homo sapiens. However, the notion of a single “missing link” is misleading. Evolution is not linear but rather a branching tree with numerous forks and sub-branches, representing various hominid species that may have sprung from common ancestors.
The Australopithecines: Early Hominds
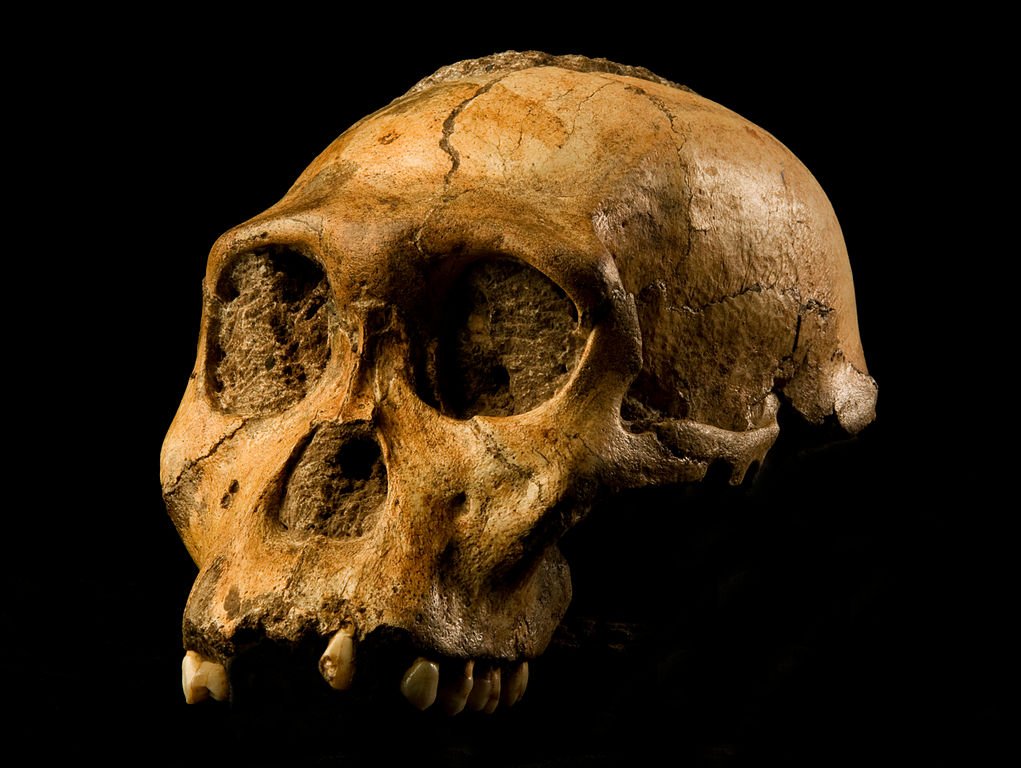
Australopithecines are a pivotal part of human evolution, representing some of the earliest known ancestors with both ape-like and human-like characteristics. Famous specimens such as “Lucy,” a member of the species Australopithecus afarensis, have provided valuable insights into our bipedal past. With features like a small brain and a robust physique, these early hominids illustrate the gradual transition from life in the trees to life on the ground.
Homo habilis: The Tool Maker
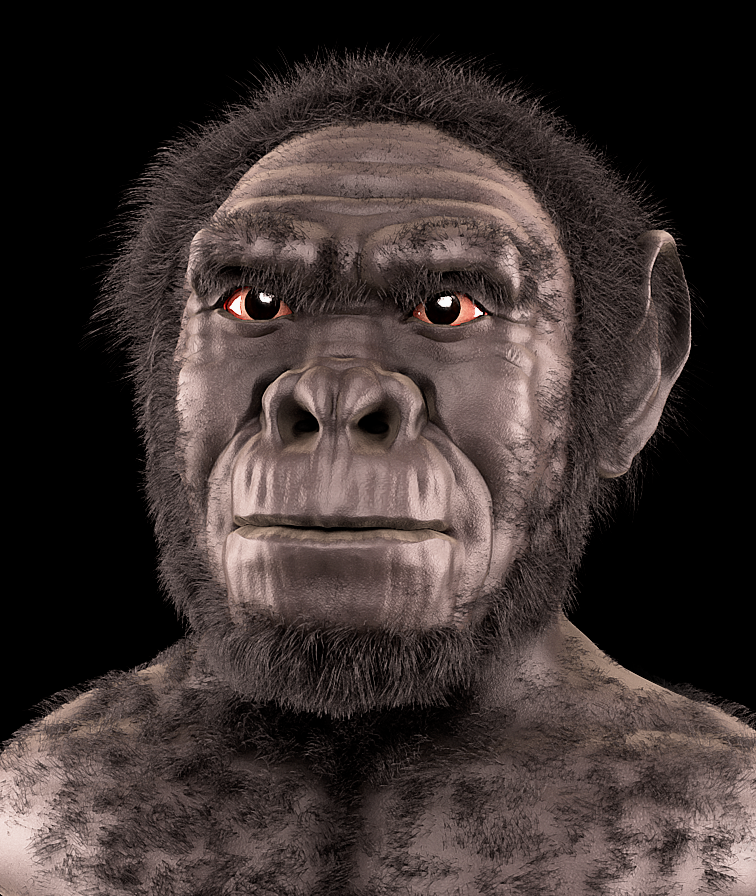

Moving along the evolutionary timeline, Homo habilis emerged around 2.4 million years ago. Nicknamed the “handy man,” this species is widely recognized for its association with the earliest stone tools. The use of tools signifies a monumental leap in cognitive and motor skills, representing a shift toward increased adaptability and innovation in the face of changing environments.
Homo erectus: The Global Wanderer

About 1.9 million years ago, Homo erectus appeared, demonstrating significant advancements in physical and cultural development. Homo erectus is notable for its larger brain size and the capacity for long-distance travel, evident in its widespread presence across Africa, Asia, and even Europe. This migration highlights a key developmental stride in dispersal and adaptation.
Neanderthals and Denisovans: Our Close Cousins
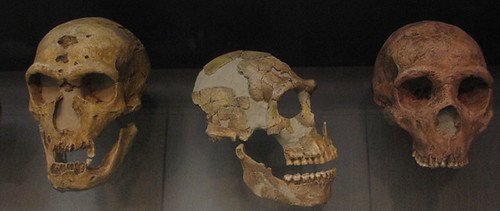
Neanderthals, a robust species known for their adaptability to colder climates, represent another branch in the human evolutionary tree. With evidence of complex social behavior, tool-making, and even symbolic art, Neanderthals challenge preconceived notions of prehistoric “cavemen.” Closely related are the Denisovans, discovered from limited fossil evidence in Siberia, who also contribute to the genetic legacy of modern humans.
Homo sapiens: The Emergence of Modern Humans

Homo sapiens, our own species, first appeared approximately 300,000 years ago in Africa. Characterized by a highly developed brain, ability for abstract thought, and elaborate language, modern humans have since spread across the globe. The genetic diversity found within Homo sapiens today is a testament to the adaptability and resilience of our species.
Genomics and the Insights It Provides
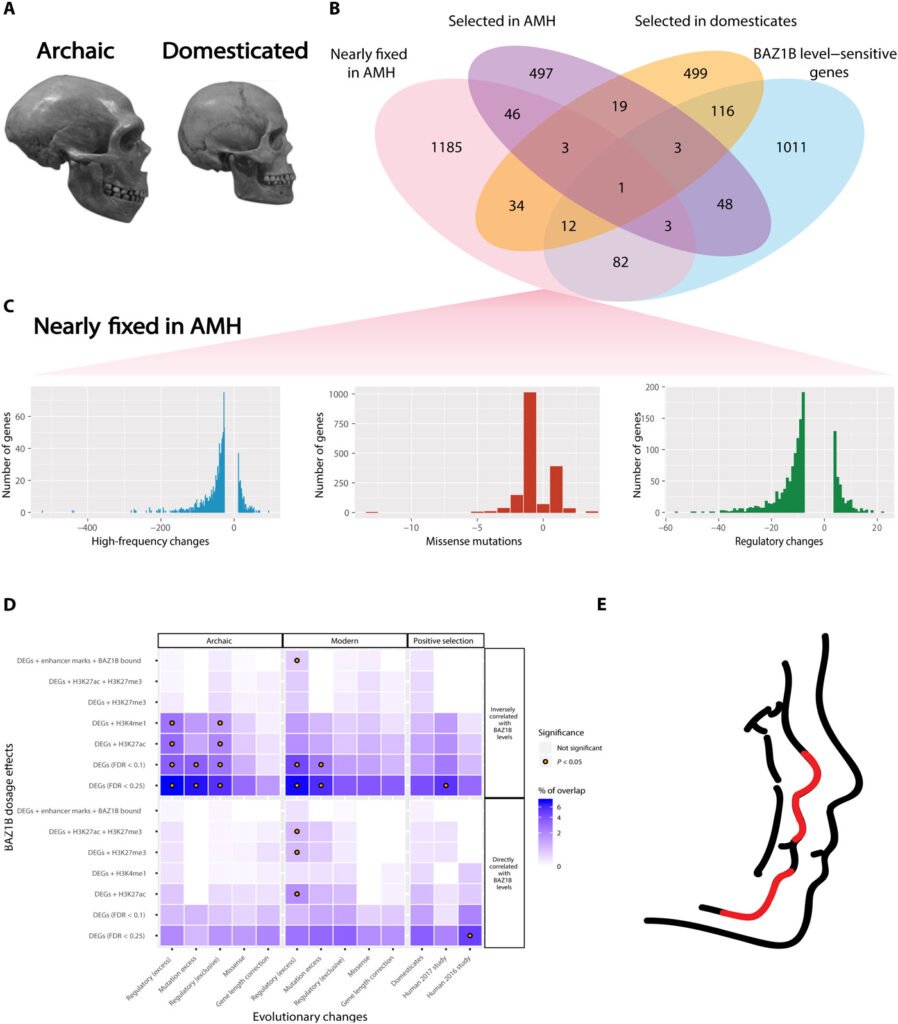
The study of ancient DNA has revolutionized our understanding of human evolution, providing insights into genetic relationships between species. Genomics allows scientists to trace ancestry lines, revealing interbreeding events between Neanderthals, Denisovans, and early modern humans. This genetic mixing paints a complex picture of past interactions and migrations.
Piecing Together the Fossil Record
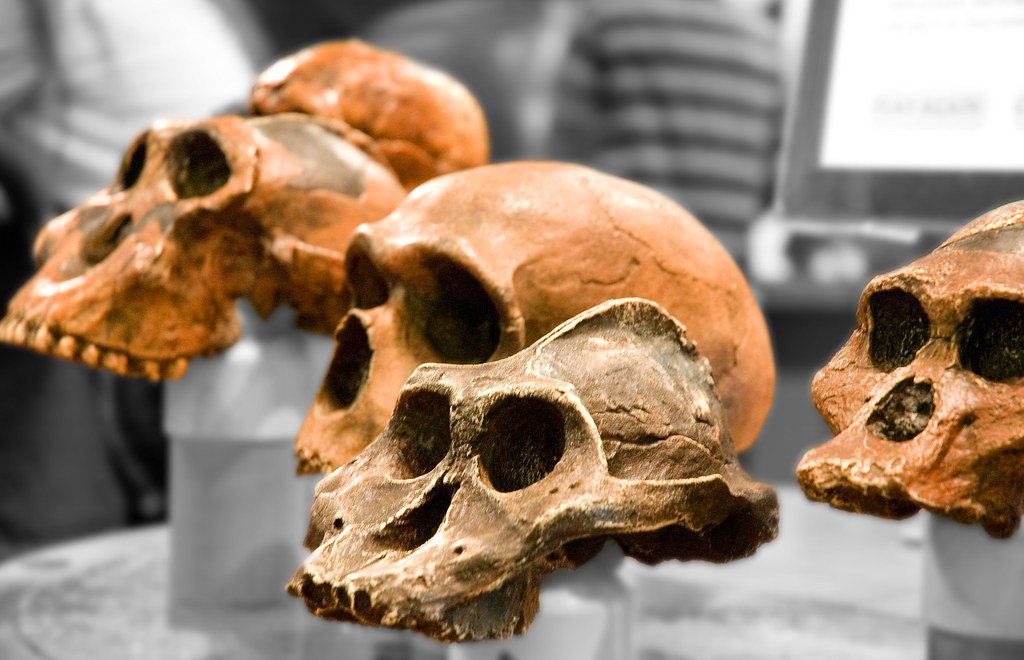

The fossil record, while incomplete, continues to be a primary source of information for evolutionary studies. Each new discovery, whether it’s a bone fragment or a complete skeleton, adds pieces to the complex puzzle of human ancestry. Researchers use these fossils to infer behavior, appearance, and ecological interactions of ancestral species.
Challenges in Human Evolutionary Research

Understanding human evolution is fraught with challenges, including the scarcity of fossils, preservation issues, and dating reliability. Additionally, interpreting fossil evidence inherently involves a degree of speculation. Advances in technology and methodologies are crucial in overcoming these obstacles, allowing for more precise reconstructions of our evolutionary history.
The Ongoing Quest for Knowledge

The quest to understand human origins is ongoing, with each discovery prompting new questions and hypotheses. Continuous exploration efforts and advances in interdisciplinary research fields promise to fill gaps in our knowledge and provide a clearer picture of our evolutionary past.
Conclusion: The Unfolding Story of Our Origins

The mystery of the missing link represents not a singular gap but multiple open questions within the grand narrative of human evolution. As research progresses, discoveries from fossils, genetic studies, and new technologies continually reshape our understanding of where we come from. This unfolding story of human origins is not just a scientific pursuit but also a profound exploration of what it means to be human.




