Human evolution has always been a captivating field that bridges the past with the present. Over the last decade, groundbreaking discoveries have reshaped our understanding of how we, as a species, came to be. As we delve into these revelations, prepare to be amazed by the dynamic and often surprising journey of human evolution.
Unveiling the Mysterious Denisovans

In the past decade, the Denisovans have emerged as one of the most mysterious hominin groups. First discovered from a fragment of a pinky finger bone in a Siberian cave, these ancient relatives of Neanderthals have provided a wealth of genetic information. DNA analysis revealed that Denisovans interbred with ancestors of present-day Asians and Oceanians. This genetic mixing has left traces in the DNA of modern humans, influencing traits such as immune system function. The discovery has opened new doors in understanding human migration and genetic diversity. It reminds us that our lineage is a complex tapestry woven with unexpected threads.
Rewriting History with Homo Naledi
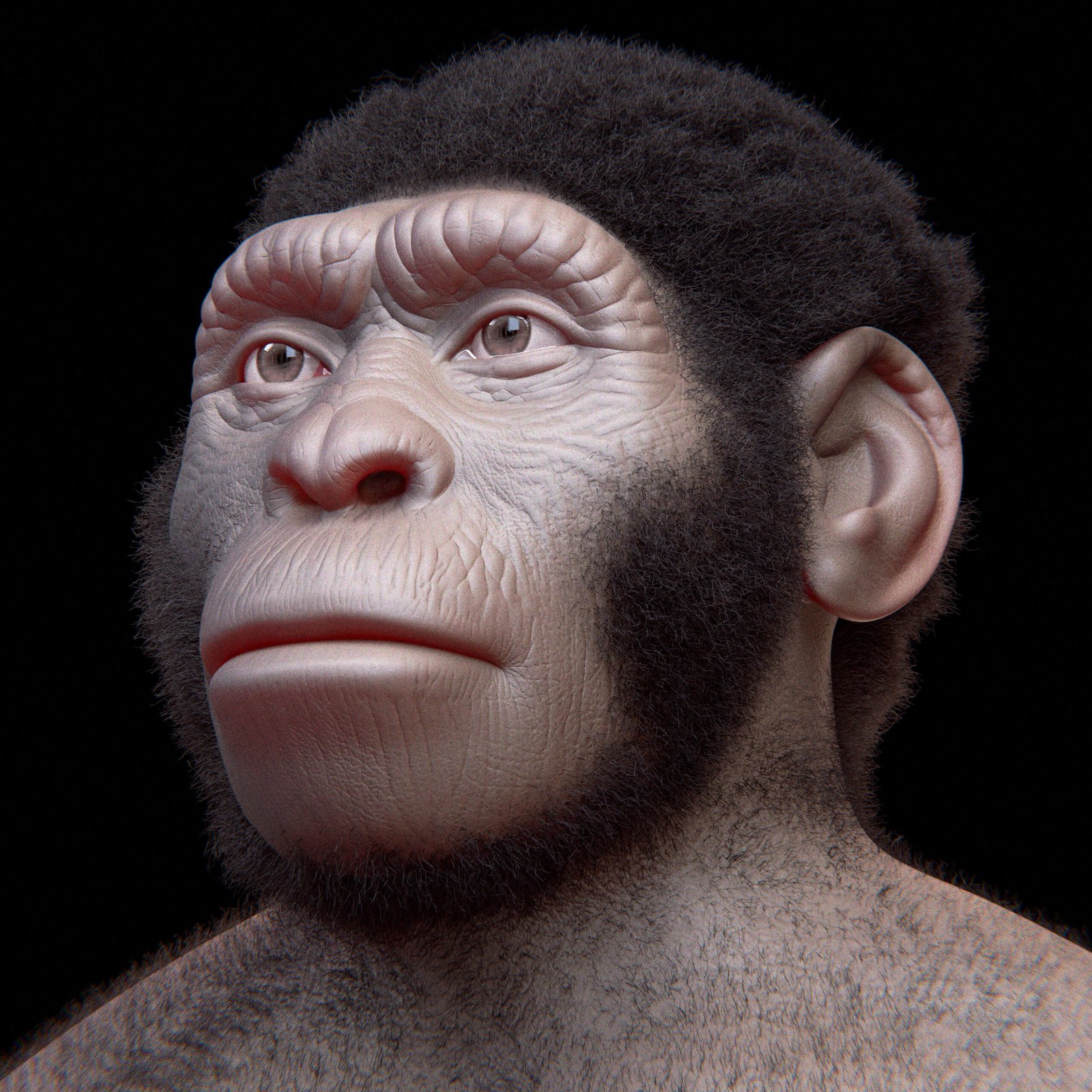

Homo naledi, a previously unknown species, was discovered in the Rising Star cave system in South Africa. This species possessed a curious blend of modern and primitive traits. With a small brain but sophisticated hands, Homo naledi challenges our understanding of what it means to be human. The discovery suggests that multiple hominin species may have coexisted in Africa, each with unique adaptations. It also raises questions about the cognitive capabilities of early hominins. This revelation prompts a reevaluation of the evolutionary tree, highlighting the diversity of our ancestral lineage.
The Surprising Story of Homo Luzonensis
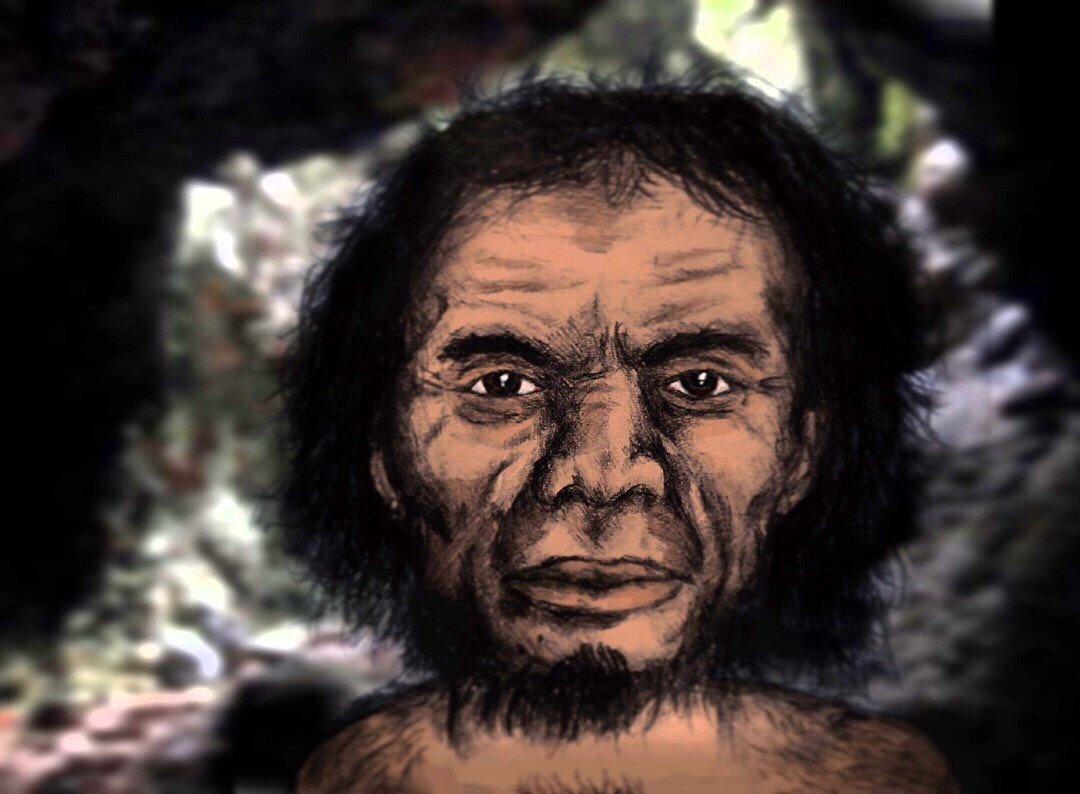

In the Philippines, scientists unearthed a new species named Homo luzonensis. This small-bodied hominin exhibited a mix of ancient and modern features, similar to Homo naledi. The discovery in Luzon Island challenges the conventional view that early humans could not travel across vast water bodies. It suggests that these ancient humans may have had the ability to build rafts or boats, enabling them to reach isolated islands. This finding expands our understanding of human dispersal across Southeast Asia. Homo luzonensis adds another layer of complexity to the evolutionary narrative, emphasizing adaptability and innovation.
Neanderthals: More Like Us Than We Thought
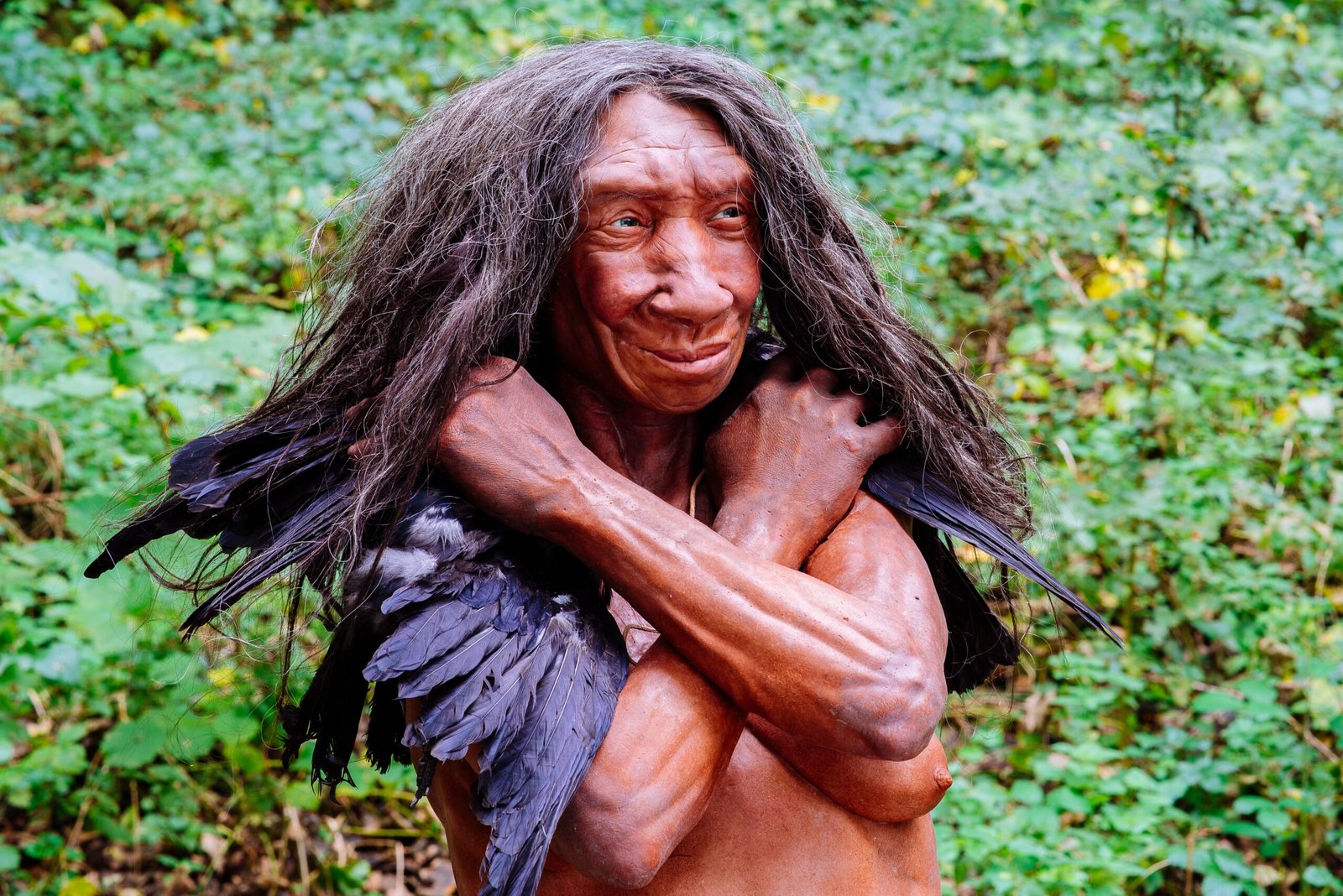

Recent discoveries have painted Neanderthals in a new light, revealing them as beings with complex behaviors and emotions. Evidence shows that Neanderthals created art, used symbolic objects, and even practiced burial rituals. These insights challenge the stereotype of Neanderthals as brutish and unintelligent. Genetic studies have also shown that interbreeding between Neanderthals and modern humans occurred more frequently than previously thought. This genetic exchange has left a lasting impact on the human genome, affecting everything from skin color to disease susceptibility. Such discoveries invite us to reconsider the narrative of human superiority.
Tracing Human Migration Through Ancient DNA
Advancements in ancient DNA analysis have revolutionized our understanding of human migration patterns. Scientists can now extract and analyze DNA from ancient bones with unprecedented accuracy. This has allowed researchers to trace the movement of early humans across continents, revealing complex migration routes and interactions. Studies have shown that early humans migrated out of Africa in multiple waves, each wave contributing to the genetic makeup of modern populations. These insights provide a more nuanced understanding of how human societies evolved and adapted to new environments. The story of human migration is one of resilience and adaptability.
The Enigma of the Red Deer Cave People
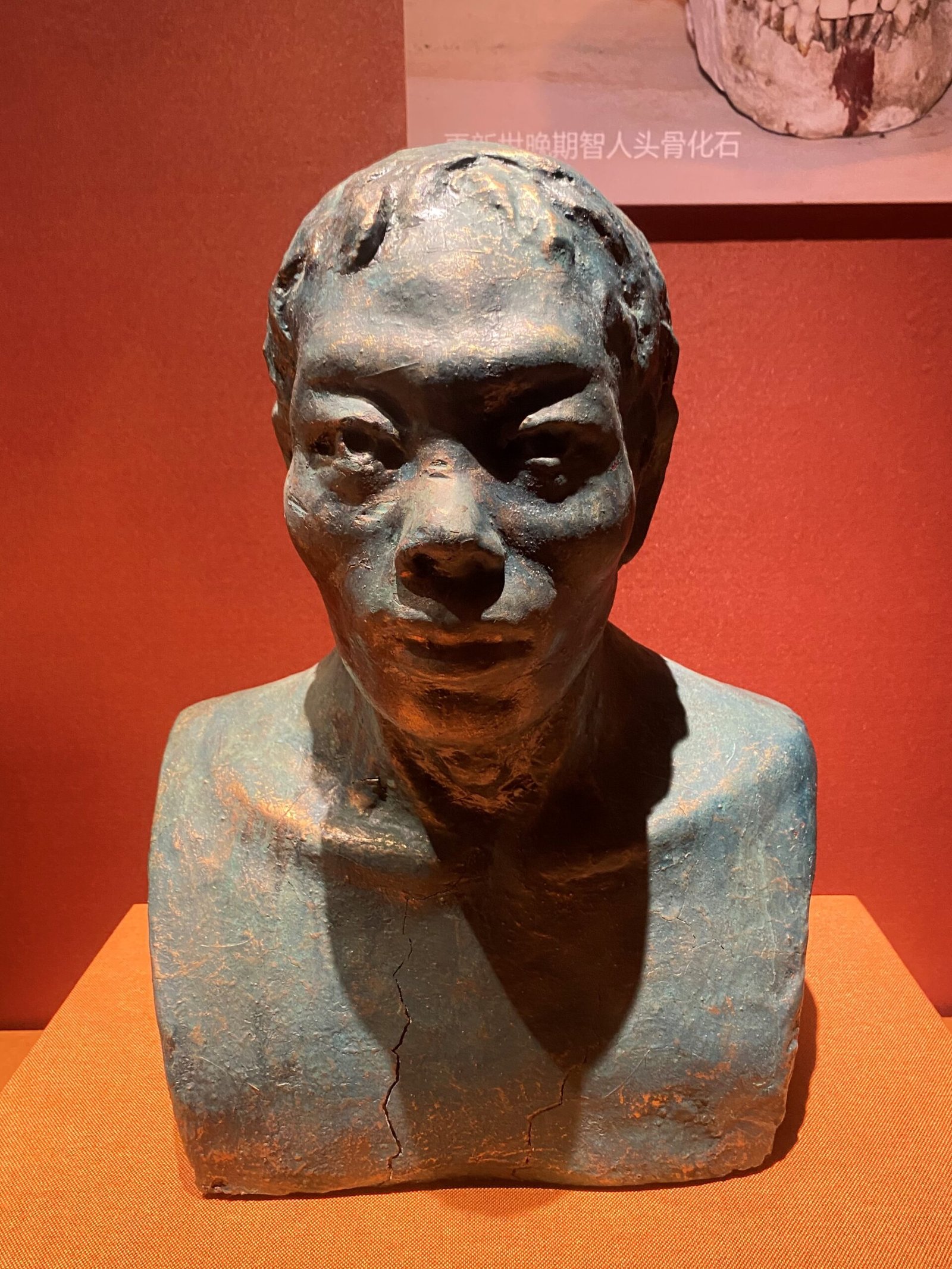

The discovery of the Red Deer Cave People in China has added another piece to the puzzle of human evolution. These ancient humans, who lived around 14,000 years ago, display a mix of archaic and modern features. The uniqueness of their skeletal remains has sparked debates among scientists about their place in the human family tree. Some researchers speculate that they may represent a distinct branch of humanity that survived much longer than other archaic humans. The Red Deer Cave People challenge the conventional timeline of human evolution, suggesting the possibility of undiscovered hominin species.
The Role of Climate in Human Evolution

Climate change has played a pivotal role in shaping human evolution. Fluctuating climates over millions of years have influenced the development of various human traits. For instance, the expansion of grasslands may have prompted early humans to walk upright, freeing their hands for tool use. Climate shifts also drove migration, pushing humans to adapt to new environments. These environmental pressures led to the development of traits like larger brains and complex social behaviors. Understanding the interplay between climate and evolution offers valuable insights into how humans have adapted to changing conditions. It underscores the importance of adaptability in our evolutionary history.
Revelations from the Atapuerca Site
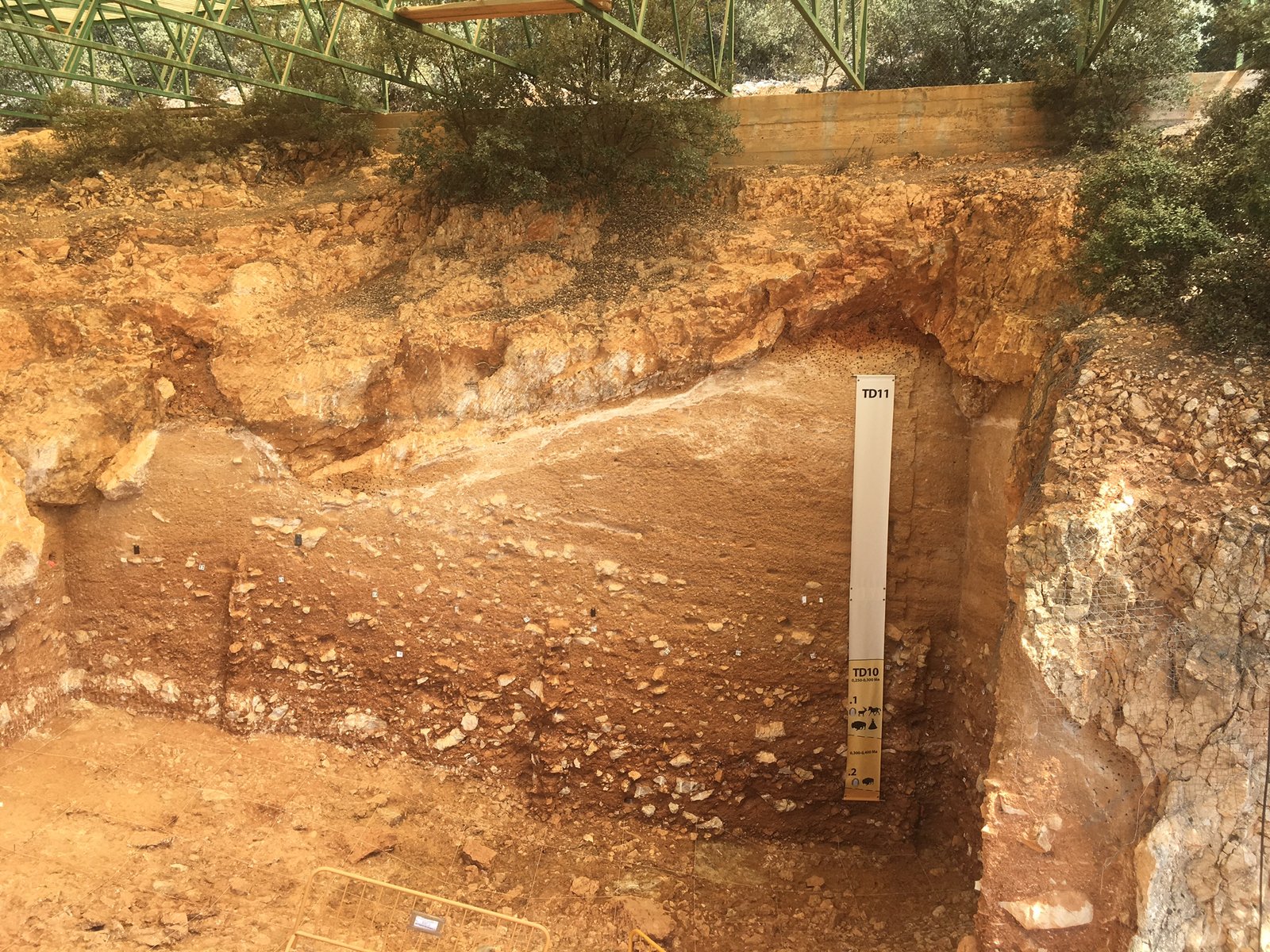

The Atapuerca site in Spain has continued to yield remarkable discoveries, providing a window into the lives of early humans. Fossils found here belong to a species known as Homo antecessor, one of the earliest known European hominins. These remains offer clues about the diet, social structures, and behaviors of ancient human populations. The site has also revealed evidence of cannibalism, highlighting the harsh realities faced by early humans. Atapuerca’s findings contribute to our understanding of the evolution of modern human traits and behaviors. The ongoing research at this site promises to unlock more secrets of our past.
Understanding the Evolution of Human Intelligence
The evolution of human intelligence is a topic of endless fascination. Recent discoveries have shed light on the development of cognitive abilities in early humans. Fossil evidence suggests that brain size alone does not account for human intelligence. Instead, the organization and connectivity of the brain played a crucial role. Studies of ancient tools and artifacts indicate that early humans possessed problem-solving skills and social intelligence. These findings highlight the importance of culture and communication in the evolution of our species. Understanding the roots of human intelligence offers insights into what makes us uniquely human.
The Future of Human Evolution Studies
As technology advances, the field of human evolution is poised for exciting developments. Techniques such as 3D imaging and artificial intelligence are transforming the way scientists study ancient remains. These tools allow for more detailed analyses and reconstructions of early human life. The integration of interdisciplinary approaches, combining genetics, archaeology, and anthropology, promises to deepen our understanding of human evolution. The future holds the potential for even more astonishing discoveries that will continue to shape our perception of humanity’s past. As we look to the future, the quest to unravel the mysteries of human evolution remains as compelling as ever.