Oregon, renowned for its lush landscapes and fertile soils, is a leader in America’s wine industry and agricultural sector. However, as wildfires become more frequent and intense, they pose a significant threat to these vital components of the state’s economy. The impact of these fires extends beyond immediate damage, affecting long-term viticulture practices and overall agricultural productivity. This article explores the multifaceted effects of wildfires on Oregon’s thriving wine industry and agricultural economy, aiming to unravel the complexities that vineyards and farms face amidst the rising blaze.
Understanding Oregon’s Wine Industry

Oregon is known for its excellent wines, especially Pinot Noir, which thrives in the state’s cooler climates. The region hosts over 900 wineries and 1,300 vineyards, contributing significantly to the state’s economy and playing a vital role in its cultural identity. Known for sustainable practices, Oregon’s wine producers prize quality and environmental stewardship.
The Rise of Wildfires in the Pacific Northwest

The frequency and severity of wildfires in the Pacific Northwest have increased due to climate change, impacting both forested areas and agricultural lands. Prolonged dry spells, higher temperatures, and reduced snowpack have created conditions ripe for wildfires, threatening Oregon’s vibrant agricultural landscape.
Immediate Threats to Vineyards

Wildfires pose an immediate threat to vineyards, as they can destroy grapevines and infrastructure rapidly. Even if flames do not come into direct contact with the vineyards, smoke exposure can lead to “smoke taint,” a condition that heavily impacts the quality and flavor of wine, leading to significant losses.
Smoke Taint and Its Consequences

Smoke taint occurs when compounds from wildfire smoke infiltrate grape skins, imparting undesirable flavors to the wine, often described as smoky or ashy. This becomes particularly problematic when it comes to delicate wines like Pinot Noir. Addressing smoke taint typically requires costly mitigation measures, straining the resources of winemakers.
Financial Implications for Winemakers

Wildfires result in direct economic losses due to damaged crops and infrastructure, but the long-term financial implications can be just as challenging. Costs associated with smoke taint, reduced yields, and increased insurance premiums add significant financial burdens. Small and medium-sized wineries are particularly vulnerable, facing potential insolvency without adequate support.
Impact on Oregon’s Broader Agricultural Economy

Beyond vineyards, wildfires impact Oregon’s broader agricultural economy, comprising various crops and livestock sectors. Wildfires can lead to burnt fields, water shortages, and reduced air quality, which affect the growth and health of non-grape crops and livestock productivity. This compounds economic losses within the agricultural sector.
Environmental Repercussions

The environmental consequences of wildfires are profound. They decrease soil fertility, promote erosion, and alter water cycles, which are vital to maintaining the health of agricultural lands. Furthermore, wildfires add carbon emissions, contributing further to climate change, which in turn increases the likelihood of future fires.
Adaptation and Resilience Strategies

Many organic and smaller wineries in Oregon are adopting innovative strategies to adapt to the changing climate and increased wildfire risk. This includes installing firebreaks, utilizing smoke-resistant grape varieties, and investing in advanced vineyard management technologies. These measures aim to bolster resilience against future fires and mitigate associated damages.
Role of Government and Institutions

Government support and intervention are critical for the survival and resilience of Oregon’s wine and agricultural industries. Initiatives such as grants, subsidies, and technical assistance play an essential role in helping farmers and winemakers cope with wildfire impacts. Research institutions also contribute by studying smoke taint mitigation techniques and climate-resilient farming practices.
The Role of Insurance

Insurance companies face increasing challenges in providing coverage to wineries and farms in fire-prone areas. While insurance remains an essential tool for managing risks, rising premiums and limited coverage options make it difficult for some producers to remain adequately protected against wildfire-related losses.
Community Collaboration and Education

Community-based efforts improve preparedness and response to wildfire threats. Educational programs inform farmers and winemakers about the latest research and best practices for fire mitigation and recovery. Collaborative networks also strengthen community resilience, ensuring shared resources and knowledge.
Consumer Awareness and Market Dynamics

Consumer awareness about the impact of wildfires on wine quality and agriculture can influence market dynamics. Wineries might use transparent communication strategies to educate consumers and maintain trust, which is essential for sustaining sales even in challenging times.
The Future of Oregon’s Wine Industry

The future of Oregon’s wine industry will likely be defined by adaptation and innovation. As the challenges posed by climate change and wildfires persist, the industry must evolve continuously, integrating sustainable practices that ensure long-term viability.
Conclusion
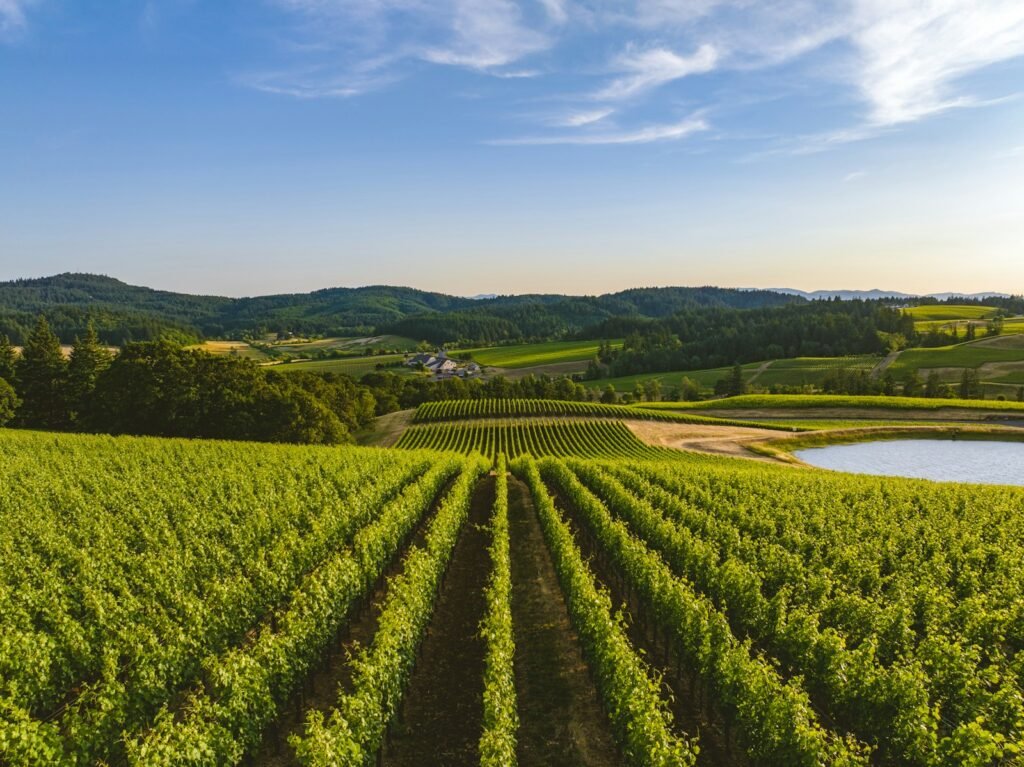

The increase in wildfires presents a formidable challenge to Oregon’s wine industry and its agricultural economy. While the ramifications are significant, the concerted efforts of winemakers, farmers, government bodies, and communities offer hope for resilience and recovery. By fostering innovation, collaboration, and sustainability, Oregon can protect its prestigious wine landscape and broader agricultural achievements, ensuring future generations can continue to savor the fruits of this beloved region.