Imagine stumbling upon a single fragment of a finger bone in a remote Siberian cave, only to realize it unlocks the story of a mysterious human cousin—one almost lost to time. The tale of the Denisovans is not just another chapter in our human saga; it is a thrilling reminder that our family tree is far more tangled, surprising, and awe-inspiring than we ever imagined. For centuries, their existence remained an unseen whisper, hidden beneath layers of rock and ice. Today, their legacy echoes in our own DNA, challenging everything we thought we knew about who we are and where we come from.
A Cave in the Mountains: The Discovery That Changed Everything
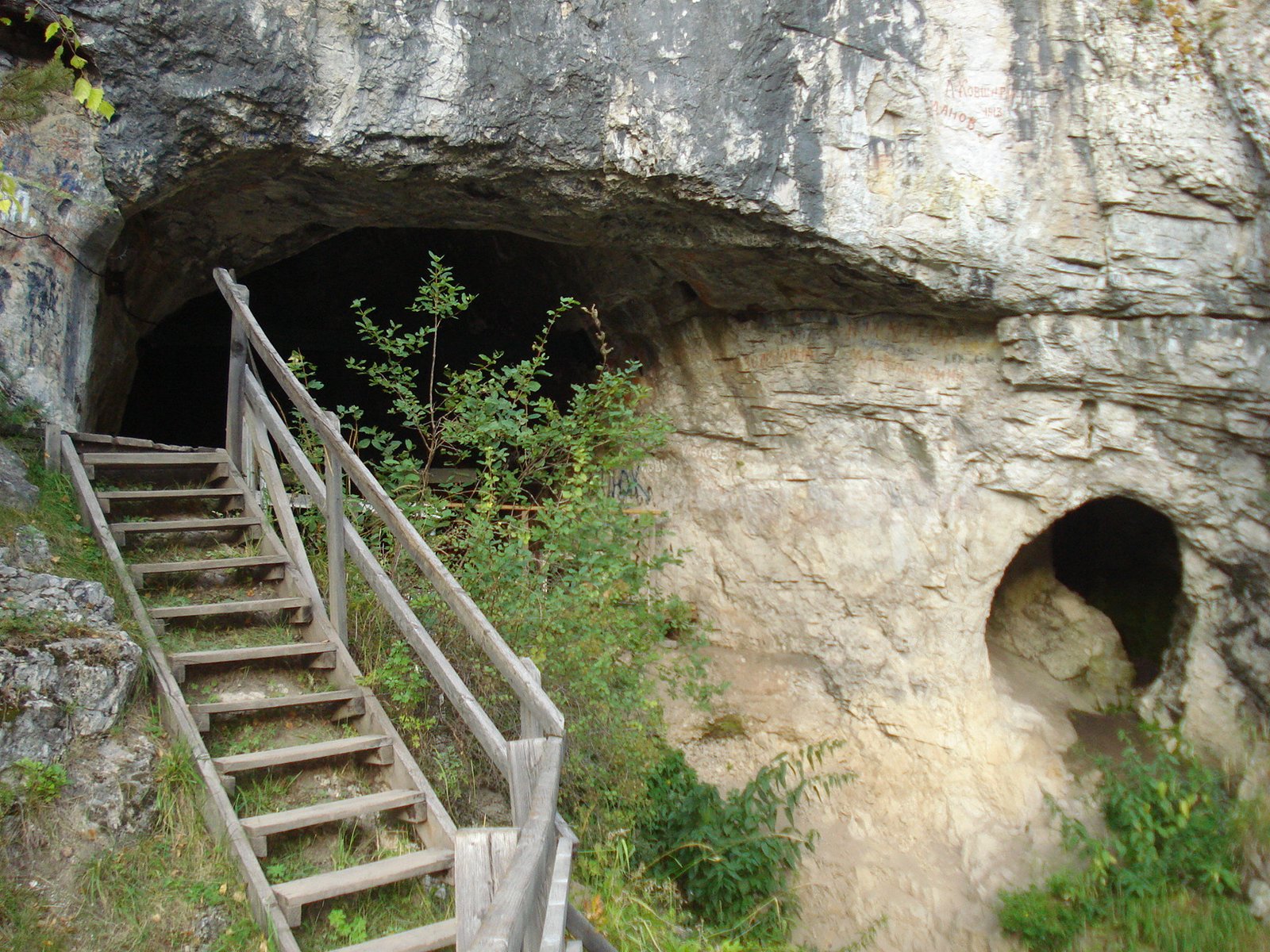

It all began in the chilly darkness of Denisova Cave, nestled in Russia’s Altai Mountains. In 2010, scientists were analyzing DNA from a tiny finger bone found deep within this cave. What they uncovered sent shockwaves through the scientific community. This bone belonged to a previously unknown group of ancient humans, now called the Denisovans. Before this discovery, no one suspected that another close relative to modern humans had once roamed Eurasia. The cave itself became a treasure trove, not just containing this finger bone, but also a few teeth and fragments from other individuals, all painting a picture of a lost people whose story was waiting to be told.
The Hidden Branch: Who Were the Denisovans?
Denisovans were not just another type of Neanderthal or Homo sapiens. Genetic analysis revealed they formed a unique branch of the human family tree, splitting off from Neanderthals around 400,000 to 500,000 years ago. Despite sharing a common ancestor, Denisovans developed their own distinct features and survived in Asia for tens of thousands of years. Unlike Neanderthals, whose remains and tools are scattered across Europe, Denisovan fossils are far rarer, making each discovery a precious puzzle piece. Their existence suggests that human evolution was more like a complex braid than a single straight line.
Fossils and Fragments: Clues from the Distant Past

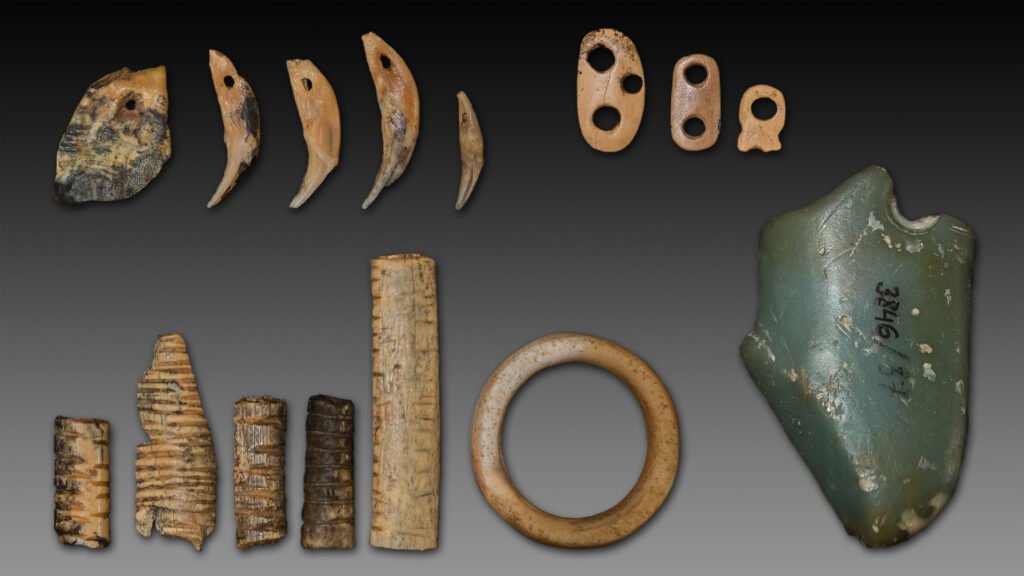
Unlike the plentiful bones left behind by Neanderthals, Denisovan remains are astonishingly scarce. To date, only a handful of teeth, bones, and a jaw have been attributed to Denisovans, many of them found in just one Siberian cave. However, each find offers extraordinary insights. For example, the large molar teeth suggest they may have had robust jaws and a diet that included tough, fibrous foods. The discovery of a Denisovan jawbone on the Tibetan Plateau hints they once survived at high altitudes, braving the cold and thin air long before modern humans did. Every fragment tells a story of resilience and adaptation.
The Power of Ancient DNA: Unlocking Genetic Secrets
What makes Denisovans truly remarkable is not the number of bones left behind, but the secrets hidden within their DNA. Advances in genetic technology allowed scientists to sequence the Denisovan genome, comparing it to that of modern humans and Neanderthals. The results were astonishing. Denisovan DNA revealed a unique genetic signature, confirming they were a distinct group. Even more surprising, traces of their DNA are found in people today—particularly in populations from East Asia, Melanesia, and Australia. This means that long after their bones turned to dust, Denisovans still walk with us, their genes woven into our very being.
Meet Your Distant Cousin: Denisovan DNA in Modern Humans
Perhaps the most shocking twist in the Denisovan story is that many people alive today carry remnants of their DNA. Studies show that up to 6% of the genome in Melanesian populations comes from Denisovans, while people in East and Southeast Asia also carry smaller amounts. This ancient inheritance is not just a fascinating footnote; it has real-world effects. For example, genes inherited from Denisovans help modern Tibetans survive at high altitudes, an adaptation that allows them to thrive in the thin air of the Himalayas. The legacy of the Denisovans lives on, silently shaping our health and abilities.
Denisovan Tools and Culture: More Than Mere Survivors
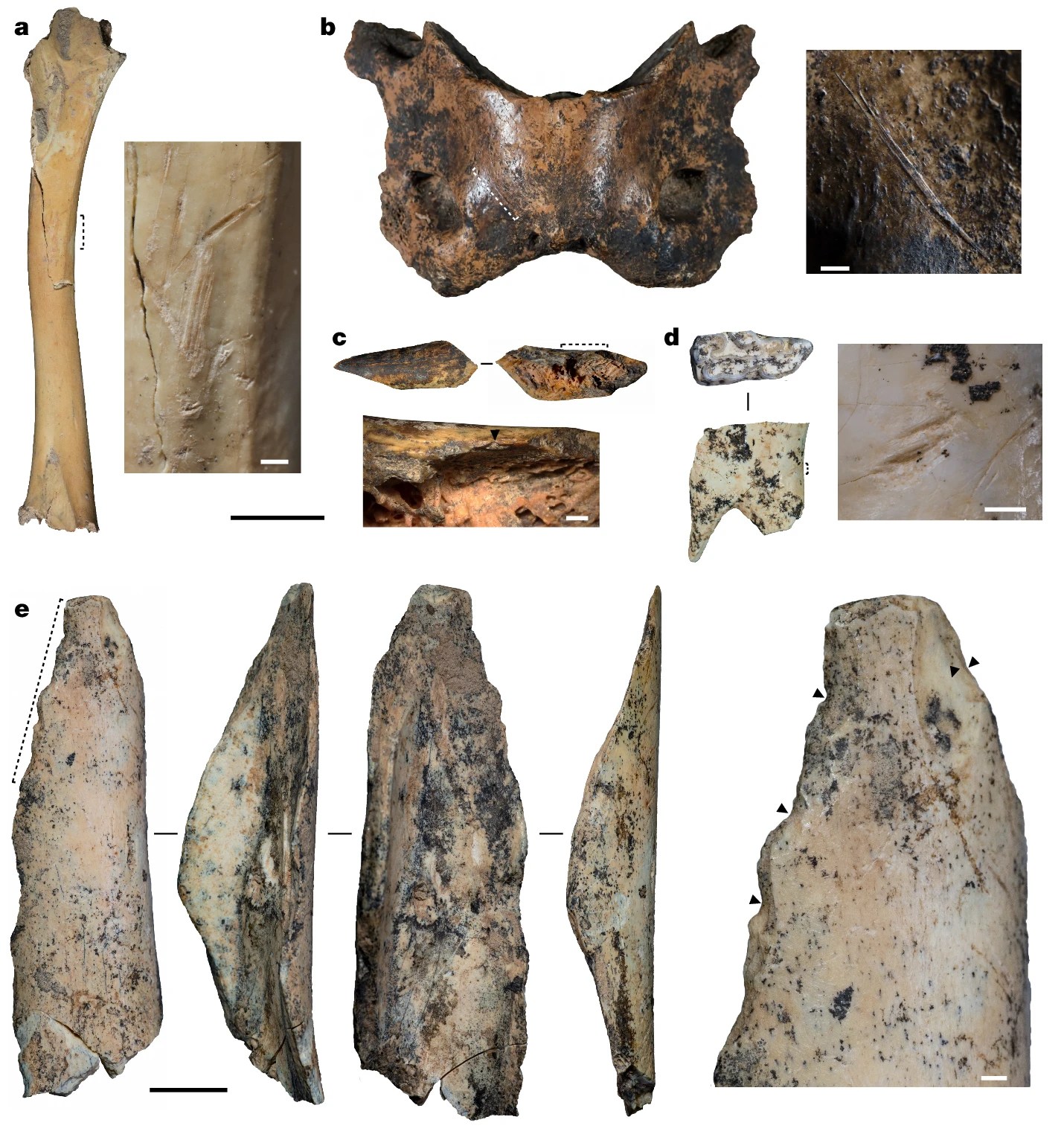

Although Denisovan bones are rare, evidence suggests they were skilled toolmakers and resourceful survivors. Archaeological finds in Denisova Cave include sophisticated stone tools and ornaments made of bone, ivory, and even ostrich eggshells. Some artifacts, like a delicately carved bracelet, hint at a sense of artistry and community. These discoveries challenge the stereotype of ancient humans as simple or primitive. Instead, Denisovans appear as creative, adaptable people who made the most of their harsh and unpredictable world.
Denisovans and Neanderthals: A Complicated Relationship

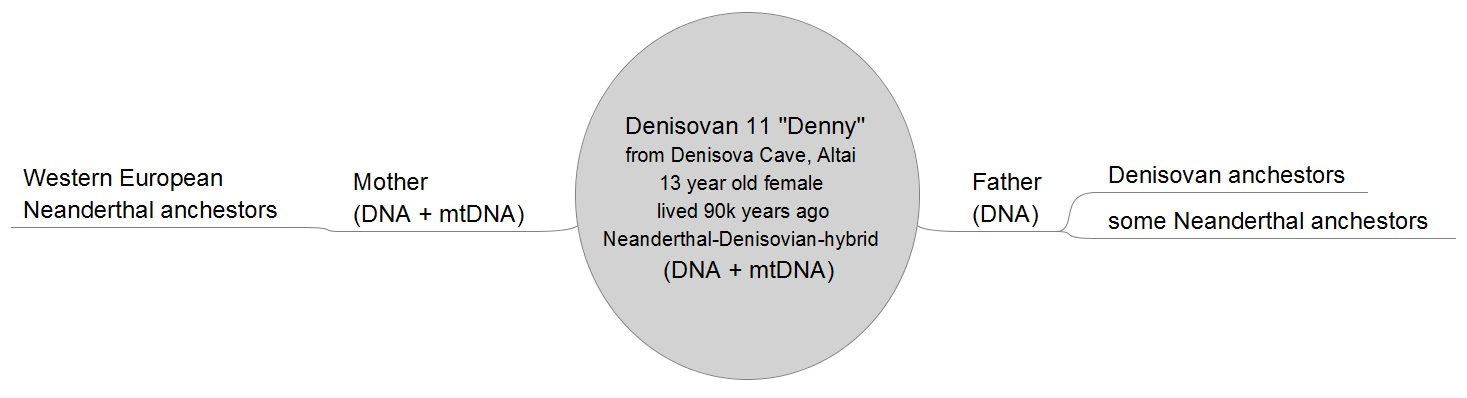
The relationship between Denisovans and Neanderthals was more than just distant kinship. Genetic evidence shows that these two groups interbred multiple times, sharing genes and perhaps even living side by side in some regions. Incredibly, the bone of a young girl found in Denisova Cave revealed she was the direct offspring of a Neanderthal mother and a Denisovan father—the first known first-generation hybrid in human history. This discovery paints a picture of ancient Eurasia as a crossroads where different human species met, mingled, and sometimes merged.
Denisovans in the High Himalayas: Masters of Extreme Environments
One of the most astonishing discoveries about the Denisovans is their ability to survive in high-altitude environments long before modern humans attempted it. The 160,000-year-old Denisovan jawbone found on the Tibetan Plateau suggests they thrived where oxygen is scarce and temperatures plunge. Modern Tibetans inherit a gene variant from Denisovans that helps them process oxygen efficiently at high altitudes. Their success in such extreme environments is a testament to human adaptability and the surprising ways our ancestors shaped the world we live in today.
The Mystery of Denisovan Appearance: What Did They Look Like?
Despite genetic breakthroughs, the physical appearance of Denisovans remains largely a mystery. With only a few bone fragments and teeth, scientists must rely on genetics and imagination to reconstruct their faces. Some evidence hints at robust jaws, large teeth, and perhaps a sturdy, powerful frame. Recent studies using DNA have attempted to predict Denisovan features, suggesting differences from both Neanderthals and modern humans. The truth, however, is that much about their looks remains hidden, leaving us to wonder what it would be like to meet a Denisovan face to face.
The Vanishing Act: Why Did the Denisovans Disappear?
The fate of the Denisovans is one of the greatest puzzles in human history. Despite their adaptability and resilience, they vanished from the fossil record around 50,000 years ago. The causes of their disappearance are still debated. Climate change, competition with modern humans, or merging with other groups through interbreeding might all have played a role. Their extinction serves as a poignant reminder that survival is never guaranteed, even for the most resourceful of species. Yet their genetic legacy endures, a silent testament to their lasting impact.
The Ongoing Search: What More Will We Learn?
The story of the Denisovans is far from complete. Each new fossil, tool, or strand of DNA adds another layer of intrigue to their tale. Scientists continue to explore caves and sift through sediments, hoping to uncover more about where Denisovans lived, how they interacted with others, and what daily life was like. As technology advances, the possibility of new discoveries grows ever stronger. The search for our forgotten ancestors is a journey filled with mystery, excitement, and the promise of rewriting our understanding of what it means to be human.




