Imagine a world where the ocean is so cold that most life would freeze within minutes, yet one remarkable creature swims effortlessly through these icy waters—its blood laced with a natural antifreeze. This is not a scene from a science fiction novel, but the daily reality for the Antarctic icefish. These fascinating creatures have adapted in ways that defy belief, rewriting the rules of biology and challenging what we thought we knew about survival in extreme environments. Their story is a testament to the power of evolution and the boundless creativity of nature.
A World of Eternal Winter

The Southern Ocean surrounding Antarctica is one of the harshest places on Earth. Temperatures here can plunge well below the freezing point of freshwater, often hovering around -1.8°C (28.8°F). For most animals, these icy conditions would mean certain death, as their blood and tissues would quickly freeze. Yet, the Antarctic icefish not only survive in this frozen wilderness—they thrive. Their presence in such an inhospitable environment has puzzled scientists for decades and continues to inspire awe among researchers and explorers alike.
Meet the Antarctic Icefish
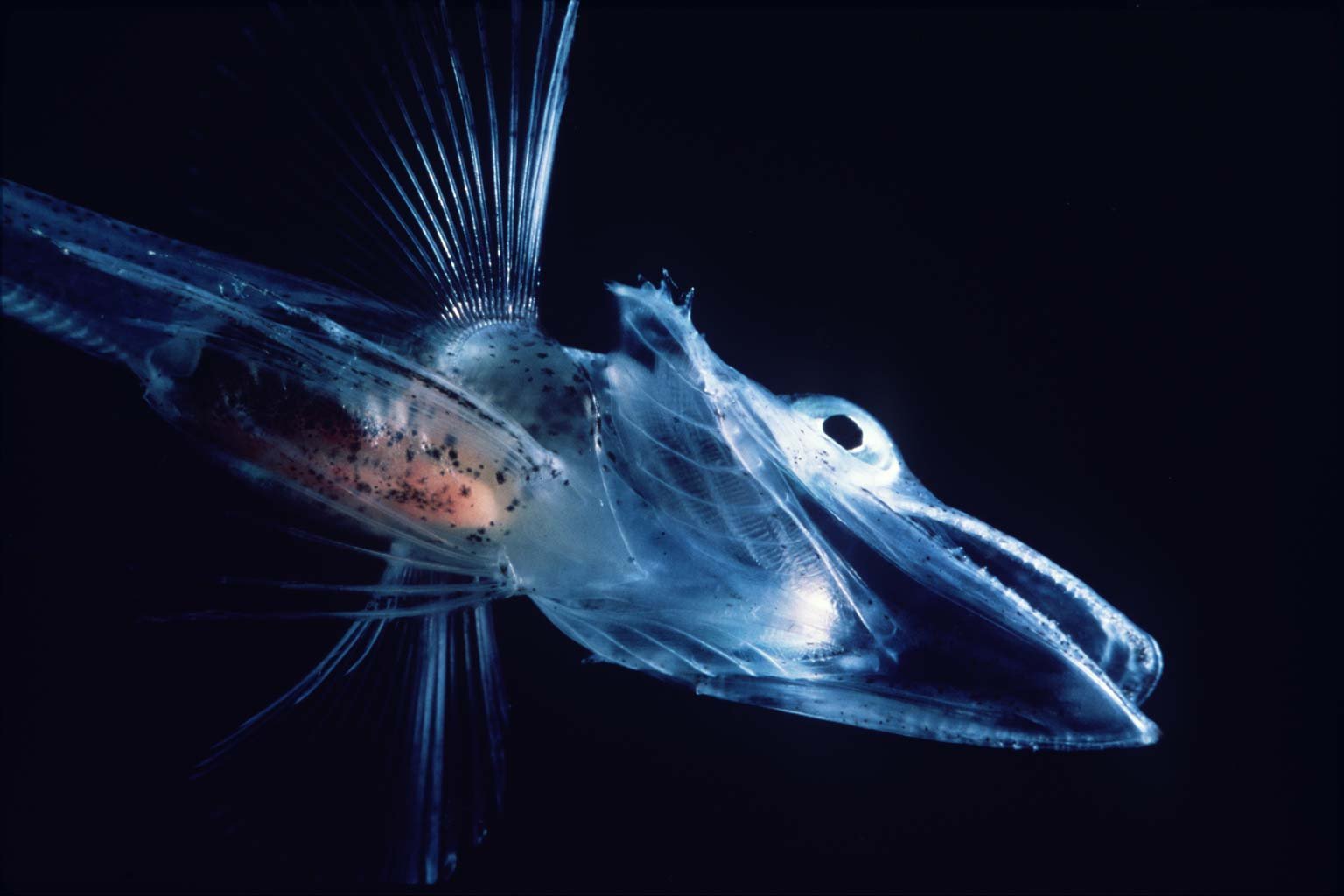

Antarctic icefish, also called “white-blooded fish,” belong to the family Channichthyidae. They are found exclusively in the frigid waters off Antarctica. These fish look ghostly, with nearly transparent skin and a pale, ethereal appearance that makes them seem almost otherworldly. Unlike most fish, icefish lack the red pigment hemoglobin in their blood, giving it a milky-white color. This unique trait sets them apart from every other vertebrate on the planet and is a direct result of their adaptation to the Antarctic cold.
The Miracle of Antifreeze Glycoproteins
The secret weapon that allows icefish to survive is a group of molecules known as antifreeze glycoproteins. These remarkable proteins circulate through the fish’s bloodstream, preventing deadly ice crystals from forming inside their bodies. Just like the antifreeze in a car radiator keeps the engine from freezing, these proteins protect the fish’s vital organs from the lethal embrace of the Antarctic chill. Scientists have marveled at this natural invention, which is so effective that it has inspired research into frost-resistant crops and new methods for preserving human tissues.
Why They Don’t Have Red Blood

One of the most surprising facts about icefish is their lack of hemoglobin—the molecule that gives most blood its red color and carries oxygen throughout the body. For a long time, this seemed impossible; after all, how could an animal survive without the main carrier of oxygen? The answer lies in the cold waters themselves. Cold water holds more dissolved oxygen than warm water, making it easier for icefish to absorb enough oxygen directly through their skin and gills, even without hemoglobin. This unusual adaptation is both a blessing and a curse, as it limits the fish to only the coldest, most oxygen-rich waters.
Strange Hearts and Big Blood Vessels
To make up for their lack of hemoglobin, icefish have developed some of the largest hearts in the fish world—sometimes up to four times the size of those in related species. Their hearts pump vast amounts of blood, which is much thinner than normal fish blood, through wide blood vessels. This helps deliver enough oxygen to their organs and muscles. It’s an astonishing example of how life can find a way to adapt, even when it means reengineering the very structure of the body.
Life in Slow Motion
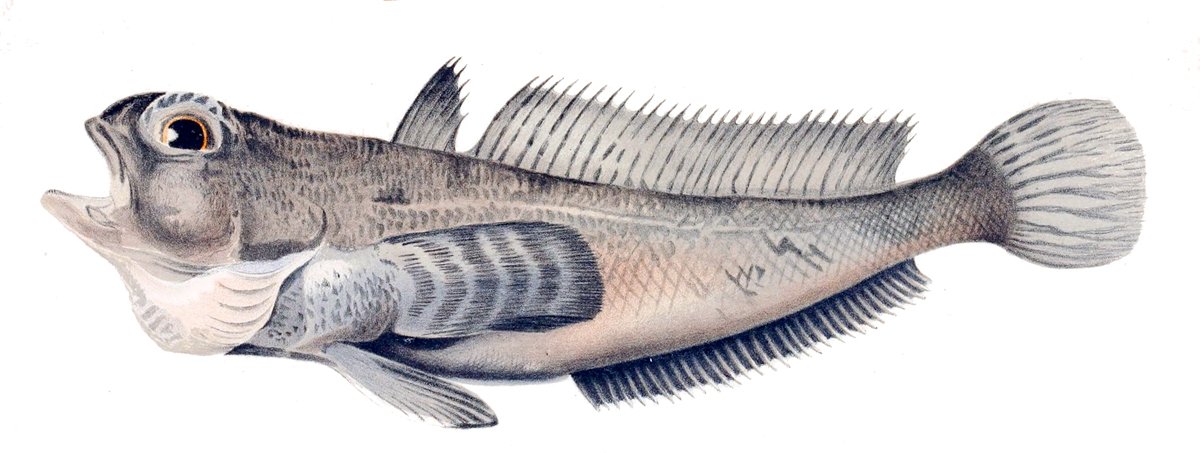
In their cold, slow-motion world, icefish live at a different pace. Their metabolism is sluggish, their movements graceful and unhurried. Growing and reproducing takes longer, but in the frigid Antarctic seas, patience is a survival strategy. Some species can live for decades, quietly gliding through the darkness beneath the ice. This slow lifestyle is a direct result of their extreme environment and unusual biology, proving that sometimes, taking things slow is the key to survival.
A Family of Oddities
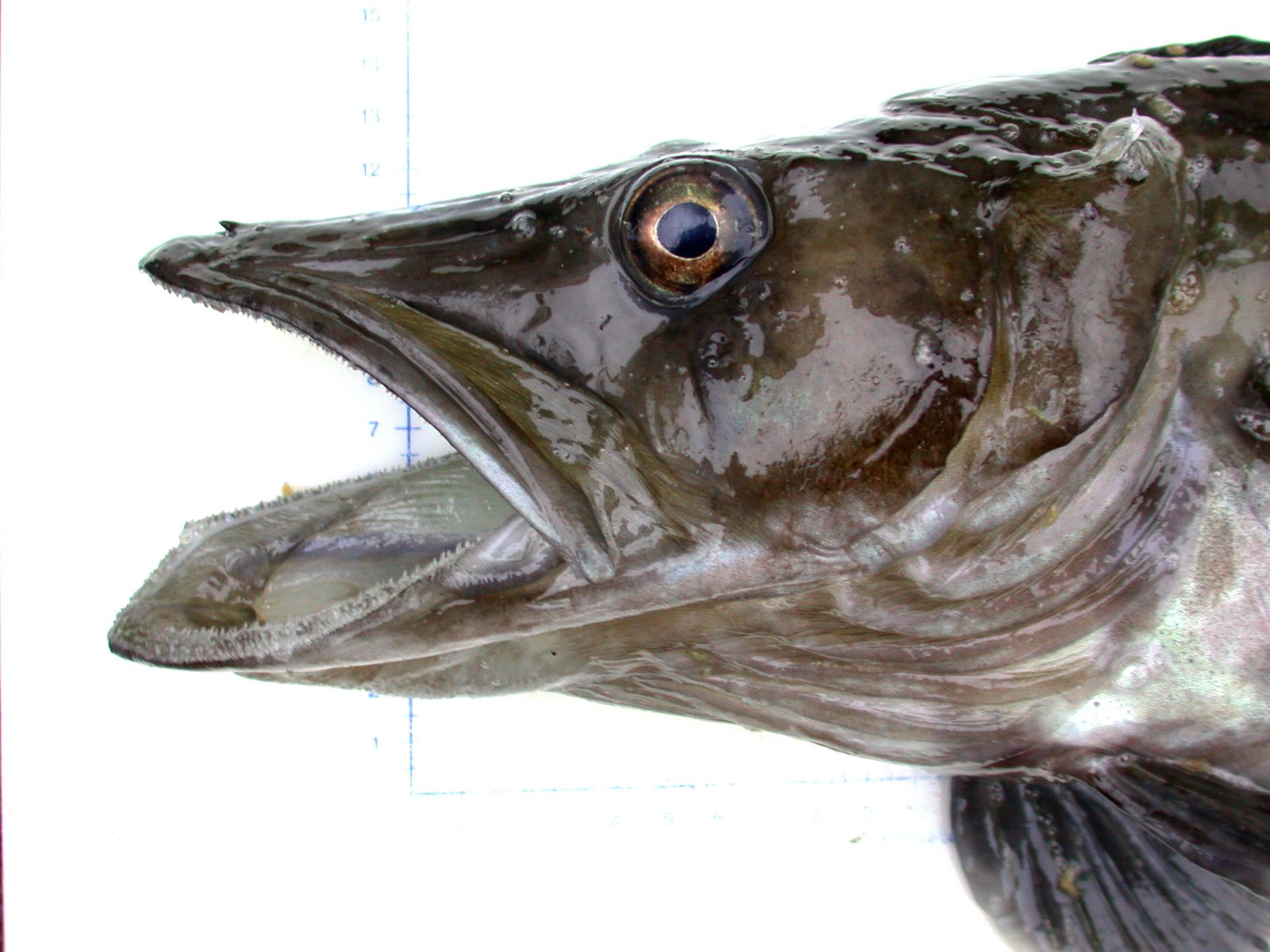

There are more than a dozen species of Antarctic icefish, each with its own strange adaptations. Some have elongated bodies, others sport strange fins or bizarre faces. Yet all share the hallmark features of the group: white blood, antifreeze proteins, and a ghostly appearance. These evolutionary oddities are living proof that when life is pushed to the edge, it can respond with astonishing creativity.
Predators and Survival Tactics
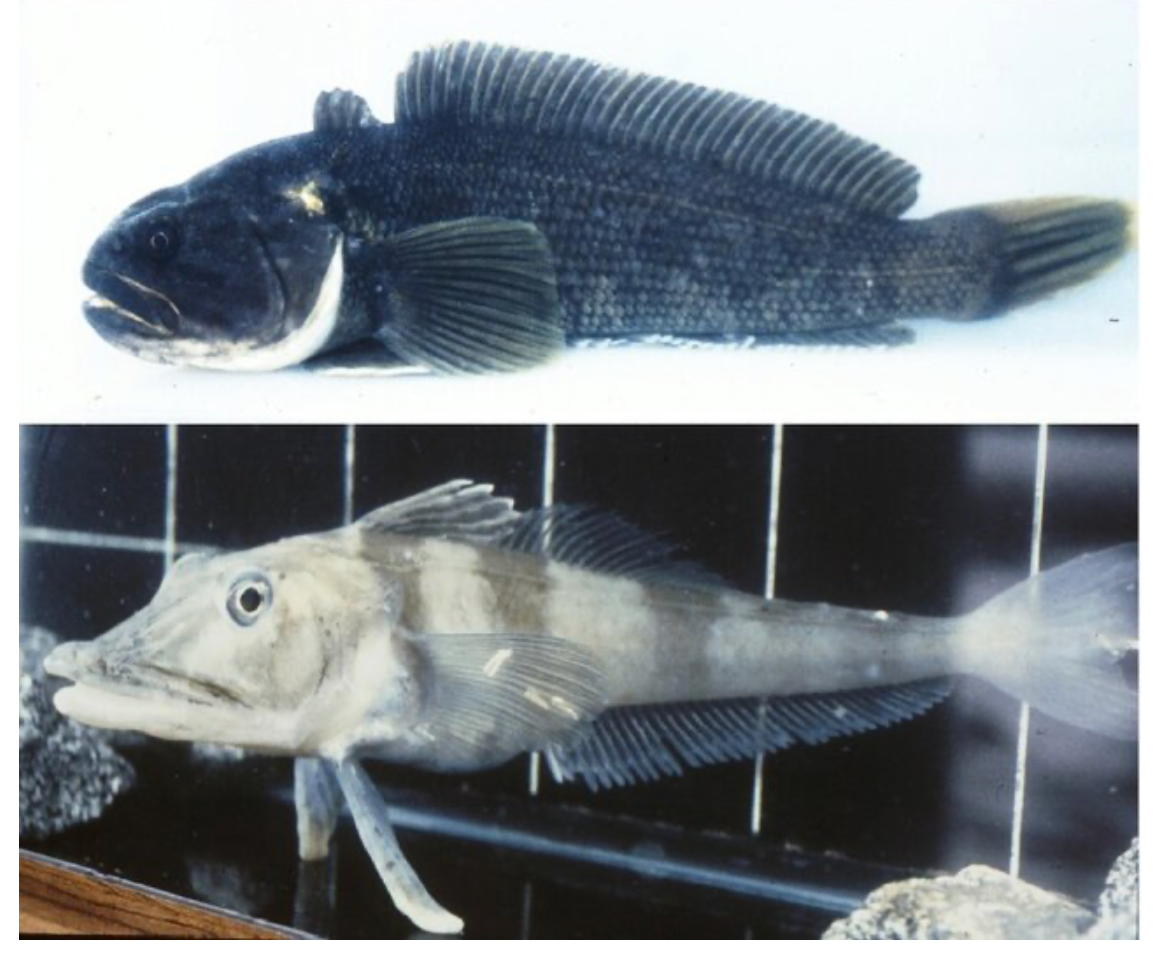

Even in the icy depths, danger lurks. Icefish must watch out for predators like seals and larger fish. To avoid becoming a meal, many icefish rely on camouflage, blending in with the silvery light filtering down through the ice. Some species bury themselves in the soft seabed, while others use stealth and slow movements to avoid detection. Their transparent bodies are not just a quirk of evolution—they’re a clever survival tool in a world where every advantage counts.
Reproduction in the Deep Freeze

Reproducing in the Antarctic is no easy task. Icefish lay their eggs in nests on the sea floor, where the parents often guard them for months. The cold water slows development, so it can take a long time for the eggs to hatch. This parental care is unusual among fish and helps ensure that the young survive in a world where the odds are stacked against them. Watching over their eggs, icefish parents show a level of dedication that’s rare in the animal kingdom.
What the Icefish Can Teach Us
The story of the Antarctic icefish is more than just a tale of survival—it’s a source of inspiration for scientists and innovators. The antifreeze proteins discovered in these fish are being studied for their potential in medicine, food preservation, and even ice cream production. Their unique biology could help unlock new ways to protect human organs during transplant or make crops more resistant to frost. The humble icefish, swimming unseen in the shadows of the Antarctic, might just hold the key to breakthroughs that could change our lives.
The Unseen Victims of Climate Change

As the climate warms, the icy realm of the Antarctic is changing. For icefish, rising temperatures pose a grave threat, as their delicate adaptations make them vulnerable to even small shifts in their environment. If the waters warm too much, these remarkable fish may lose their edge, struggling to survive in a world they were never built for. Their plight is a stark reminder of the interconnectedness of all life and the urgent need to protect the fragile ecosystems at the ends of the Earth.
The Antarctic icefish, with its antifreeze blood and ghostly form, stands as a symbol of nature’s power to adapt and endure against the odds. In their story, we find wonder, warning, and a deep sense of curiosity—a reminder that even in the coldest, darkest places, life finds a way. What other secrets might be hidden beneath the ice, waiting to amaze and inspire us?