The story of mammals is a fascinating tale of adaptation and survival, tracing back to the time of dinosaurs. The mammalian lineage has undergone significant transformations since its earliest ancestors emerged hundreds of millions of years ago. Fossils, the remnants of ancient life embedded in Earth’s crust, provide us with vital clues about this evolutionary journey. This article delves into what these fossils reveal about the evolution of mammals, detailing how they developed the traits that define them today.
The Ancestors
Long before mammals as we know them roamed the Earth, their ancient ancestors existed as small, reptile-like creatures. These synapsids, often referred to as “mammal-like reptiles,” were characterized by a single temporal opening on each side of the skull. Fossil evidence shows that by the late Permian period, around 260 million years ago, these creatures were already diversifying into various forms, setting the stage for the mammalian evolution that would follow.
Triassic Transformations
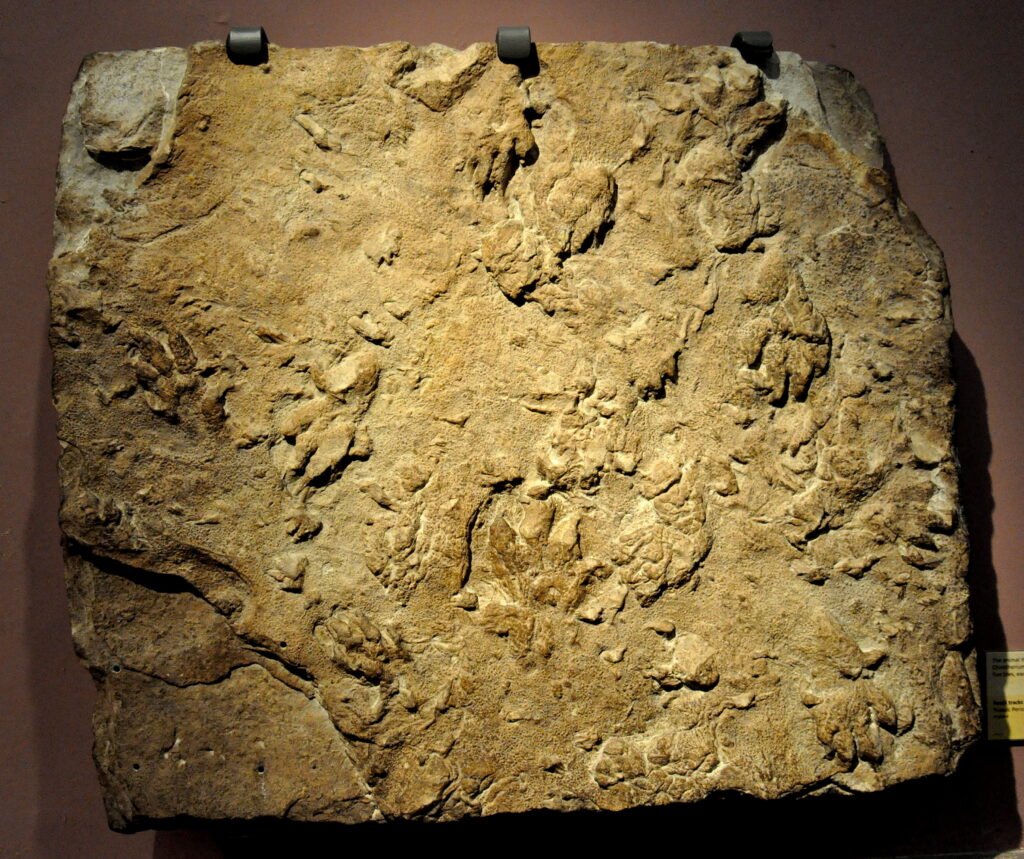

The Triassic period marked a crucial turning point in mammalian evolution. As the dinosaurs emerged, so did the first true mammals. These early mammals, evolving from their synapsid ancestors, were small, nocturnal creatures that managed to survive and thrive in the shadows of the gigantic dinosaurs. Fossils from this period, such as those of Morganucodon, provide crucial insights into these early adaptive strategies.
Jurassic Diversification
During the Jurassic period, mammals began to diversify and fill various ecological niches. The fossil record reveals the development of different mammalian lineages adapting to specific diets and habitats. Notable discoveries, such as the Castorocauda, a semi-aquatic mammal, highlight how early mammals ventured into novel environments, showcasing their versatile survival strategies even amidst the dominance of dinosaurs.
Cretaceous Developments

The Cretaceous period witnessed further diversification of mammals. Despite living under the shadow of formidable predators, mammals continued to evolve, developing characteristics that would become defining traits. Fossils from this period, such as those of multituberculates, illustrate mammals’ ability to exploit different ecological roles, including herbivory and insectivory, thereby enhancing their adaptability and resilience.
The End-Cretaceous Extinction

The catastrophic event that marked the end of the Cretaceous period, around 66 million years ago, led to the extinction of the dinosaurs and opened up a plethora of ecological opportunities for mammals. The fossil record post-dating this event shows an extraordinary increase in mammalian diversity and size, indicating a significant evolutionary expansion as mammals moved to occupy habitats vacated by the dinosaurs.
The Cenozoic Era
With the dawn of the Cenozoic Era, often referred to as the “Age of Mammals,” mammals rapidly diversified into a wide array of forms, sizes, and ecological niches. Fossils from this era illustrate a remarkable evolutionary burst, in which mammals evolved into the diverse array of species we see today, from tiny bats to enormous whales. This era highlights the versatility and adaptability of mammals in a changing world.
Understanding Mammalian Traits

Fossils are a treasure trove of information on how mammals developed their unique traits, such as endothermy (warm-bloodedness), fur, and live births. Features like the differentiation of teeth suggest dietary adaptations, while the structure of ear bones provides evidence for improved hearing capabilities. These adaptations likely played a significant role in helping mammals survive and evolve through various environmental challenges.
The Role of Technological Advancements in Fossil Research

Recent technological advances have significantly enhanced our understanding of mammalian evolution. Techniques like CT scanning and genetic analysis allow paleontologists to examine fossils in unprecedented detail, uncovering new aspects of their anatomy and evolutionary significance. These technologies have helped uncover previously unknown species, thereby filling gaps in the mammalian evolutionary tree.
The Ongoing Saga of Mammalian Evolution

The story of mammals is an unfolding narrative of resilience and innovation. Fossils provide an indispensable record of this journey, allowing us to piece together how mammals adapted to various environments and challenges over millions of years. Even today, the study of these ancient remains continues to yield new discoveries, offering fresh insights into the evolution of mammals and reminding us of the ever-changing tapestry of life on Earth.

Jan loves Wildlife and Animals and is one of the founders of Animals Around The Globe. He holds an MSc in Finance & Economics and is a passionate PADI Open Water Diver. His favorite animals are Mountain Gorillas, Tigers, and Great White Sharks. He lived in South Africa, Germany, the USA, Ireland, Italy, China, and Australia. Before AATG, Jan worked for Google, Axel Springer, BMW and others.



