Nestled amidst the towering peaks of the Himalayas, Tibetans and Sherpas perform feats that seem almost superhuman. While most of us would gasp for breath at such dizzying heights, these remarkable people continue their daily activities with ease. Their secret? A unique genetic makeup that has evolved over thousands of years, allowing them to thrive where others struggle. This article explores the fascinating world of high-altitude adaptation and the incredible story of the DNA that makes it possible.
The Perils of High Altitude

At altitudes above 8,000 feet, oxygen levels are significantly reduced, leading to a condition known as hypoxia. For those unaccustomed to such thin air, symptoms can range from mild headaches and dizziness to life-threatening illnesses. The body struggles to deliver enough oxygen to tissues, affecting physical performance and overall health. Yet, for the Tibetans and Sherpas, these heights are home. They traverse these rugged terrains with a grace and endurance that leaves visitors in awe. Their ability to function in such environments is not a mere coincidence but a testament to the power of human adaptation.
Evolutionary Journey to Higher Ground
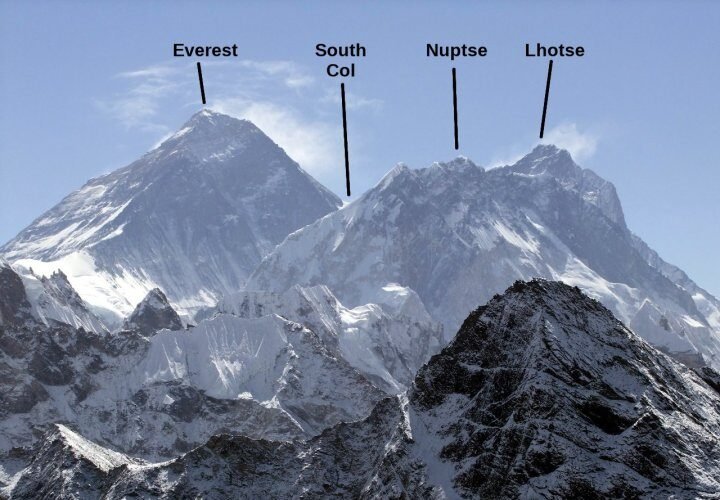

The journey of the Tibetans and Sherpas to high-altitude adaptation is a story of evolution in action. Over thousands of years, these populations have undergone genetic changes that enhance their ability to survive in low-oxygen environments. Unlike other populations who might produce more red blood cells in response to high altitude, Tibetans and Sherpas have developed a more efficient way. Their bodies have evolved to make better use of the oxygen available, reducing the risk of complications such as chronic mountain sickness. This evolutionary journey is a testament to the resilience and adaptability of human beings.
The Role of EPAS1 Gene

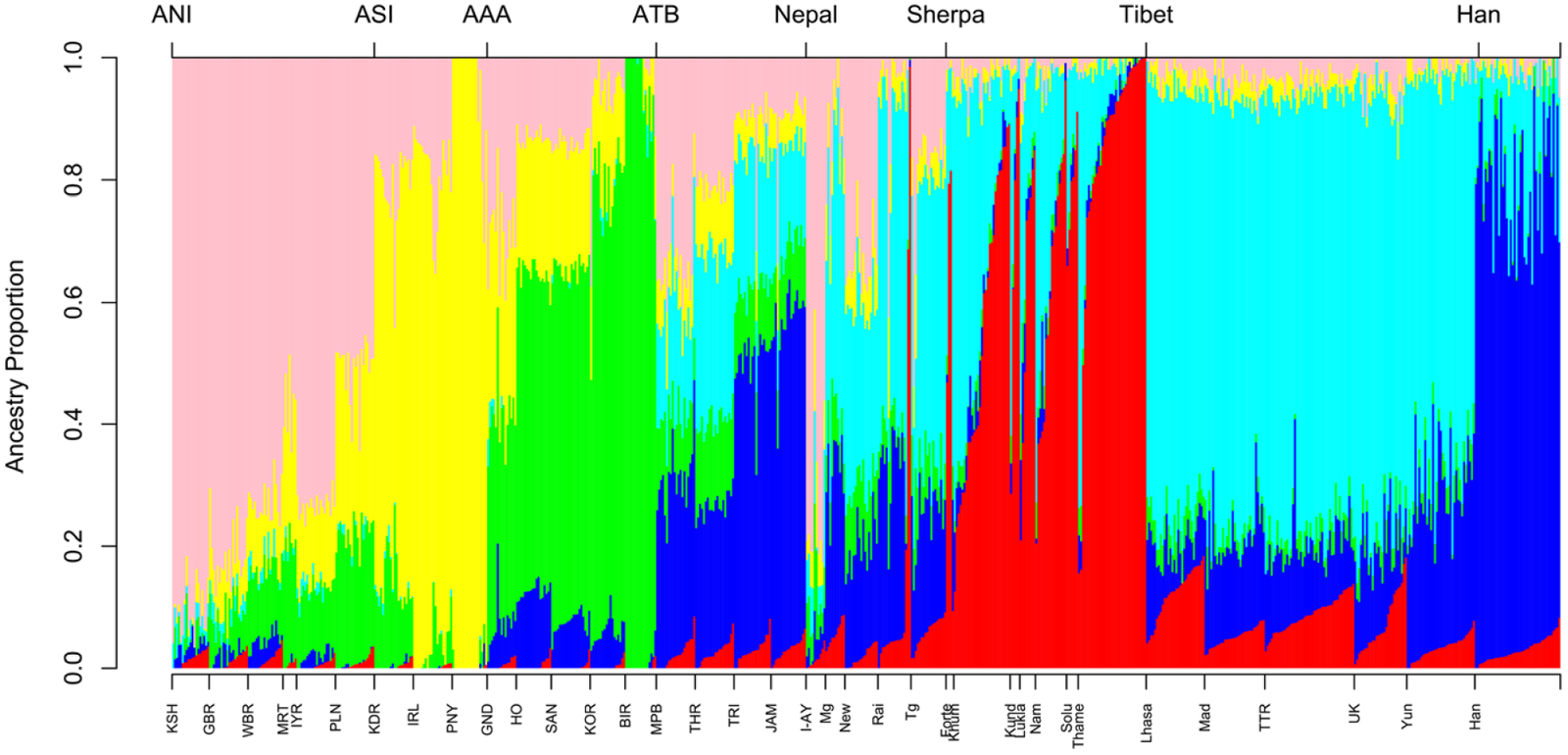
Central to the high-altitude adaptation of Tibetans and Sherpas is a gene known as EPAS1. Often referred to as the “super athlete gene,” EPAS1 plays a crucial role in regulating the body’s response to low oxygen levels. Research has shown that Tibetans possess a unique variant of this gene, which is thought to have been acquired through ancient interbreeding with a now-extinct human species known as the Denisovans. This genetic inheritance enables their bodies to utilize oxygen more efficiently, minimizing the physiological stresses associated with high altitude. The EPAS1 gene is a perfect example of how genetics can shape human capabilities in extraordinary ways.
Cardiovascular Efficiency
Beyond genetic mutations, Tibetans and Sherpas exhibit remarkable cardiovascular efficiency. Their hearts and lungs are adapted to work seamlessly in low-oxygen conditions. Studies have found that they have larger lung capacities and higher blood flow rates, allowing for greater oxygen uptake and delivery to tissues. This adaptation is akin to an athlete’s training, where the body becomes finely tuned to perform under specific conditions. For the Sherpas, this means they can carry heavy loads across treacherous mountain passes with ease, a skill that has earned them a reputation as the ultimate high-altitude guides.
Metabolic Adaptations

Metabolism plays a pivotal role in how the body responds to high-altitude stress. Tibetans and Sherpas have adapted to utilize energy more efficiently, ensuring that their bodies function optimally despite the lack of oxygen. Research suggests that these populations have a higher resting metabolism, which allows them to maintain body temperature and energy levels in the harsh Himalayan climate. This metabolic adaptation is crucial for survival and is a key factor in their extraordinary endurance. It’s a bit like having a finely tuned engine that runs smoothly even in the toughest conditions.
Generations of Cultural Knowledge
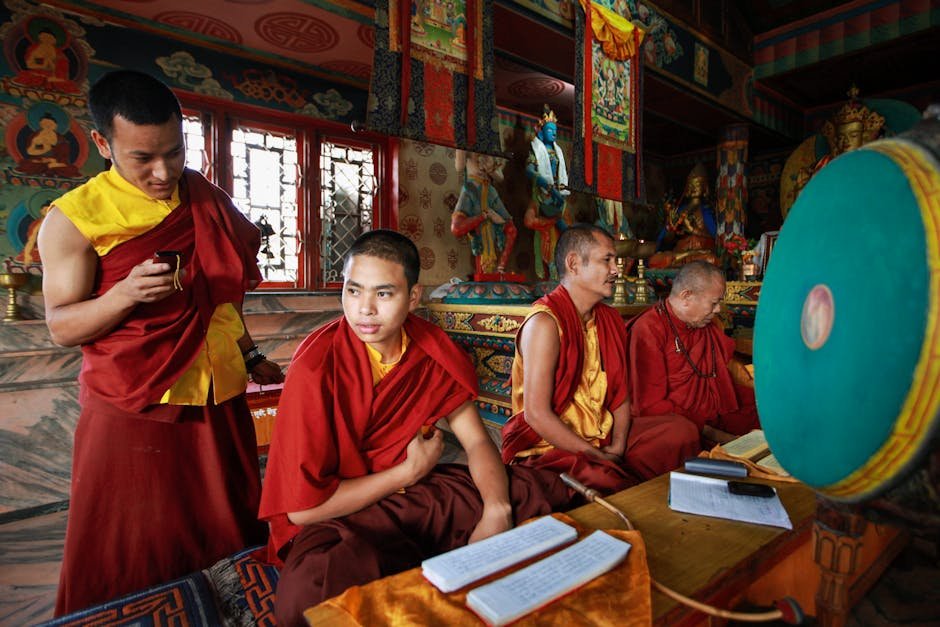

While genetic adaptations are vital, cultural knowledge passed down through generations also plays a significant role in the survival of Tibetans and Sherpas at high altitudes. Traditional practices, such as specific breathing techniques and dietary habits, complement their genetic makeup, helping them thrive. These cultural adaptations are interwoven with their daily lives and reflect a deep understanding of their environment. The integration of genetic and cultural adaptations is a powerful example of how humans can conquer even the most challenging landscapes.
The Sherpa Legacy
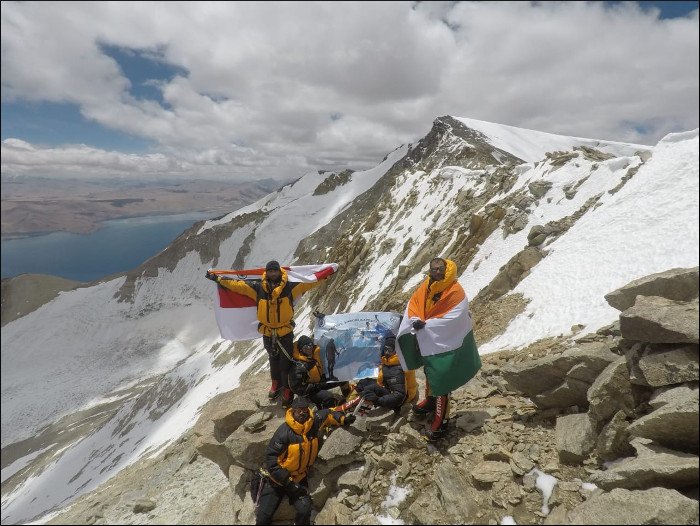

Sherpas are renowned worldwide for their mountaineering prowess, often accompanying climbers on expeditions to the world’s highest peaks. Their ability to navigate treacherous terrains and manage the challenges of extreme altitude is legendary. This legacy is built on both their genetic advantages and their cultural heritage. The Sherpa community’s skills have become invaluable to adventurers seeking to conquer the Himalayas. Their legacy is a testament to the strength of human adaptation and the enduring spirit of exploration.
Challenges and Modern Science

Despite their remarkable adaptations, Tibetans and Sherpas face challenges in an ever-changing world. Climate change and modernization threaten their traditional ways of life, and the influx of tourism brings both opportunities and pressures. Modern science continues to study these populations, seeking to understand the genetic secrets that could offer insights into human health and resilience. The knowledge gained from studying high-altitude adaptations has the potential to impact medical research and help those suffering from conditions related to low oxygen levels.
The Broader Implications

The study of high-altitude superhumans like the Tibetans and Sherpas has far-reaching implications. Understanding their genetic adaptations could lead to breakthroughs in medicine, particularly for conditions that involve oxygen deprivation, such as chronic lung diseases and heart conditions. Their story also highlights the incredible capacity of the human body to adapt to extreme environments, offering hope and inspiration for future generations. The lessons learned from the Himalayas can be applied to challenges faced by people worldwide.
Unraveling the Mysteries of Human Potential

The DNA of high-altitude superhumans is a testament to the boundless potential of human evolution. As science continues to unravel the mysteries of our genetic makeup, the story of Tibetans and Sherpas serves as a reminder of our incredible adaptability. Their journey from ancient ancestors to modern-day mountaineers is a powerful narrative of survival and innovation. By understanding their adaptations, we gain insights into the resilience of the human spirit and the possibilities of genetic evolution. The secrets of the Himalayas may hold the key to unlocking new frontiers in human health and endurance.