Australopithecus afarensis is a significant species in the study of human evolution. Often dubbed as one of our earliest ancestors, this species provides crucial insights into the evolutionary journey that led to modern humans. The discovery of an Australopithecus afarensis fossil, famously known as “Lucy,” marked a monumental milestone in the field of paleoanthropology, reshaping our understanding of human origins.
The Remarkable Discovery of Lucy

The discovery of Lucy took place on November 24, 1974, in the Awash Valley of the Afar Triangle, Ethiopia, by the paleoanthropologist Donald Johanson and his team. The name “Lucy” was inspired by the Beatles’ song “Lucy in the Sky with Diamonds,” a favorite among the researchers. Lucy’s skeleton is approximately 40% complete, making it one of the most complete hominin fossils ever found.
Why Lucy Was So Special

Lucy’s skeletal remains offered an unprecedented glimpse into the past. At around 3.2 million years old, her fossil provided evidence of bipedalism, which is the ability to walk upright on two legs, a key characteristic differentiating early hominins from other primates. Before Lucy, the evidence for bipedalism was scant and scattered. Her discovery helped confirm that walking on two legs occurred well before the evolution of larger brains.
Physical Characteristics and Anatomy
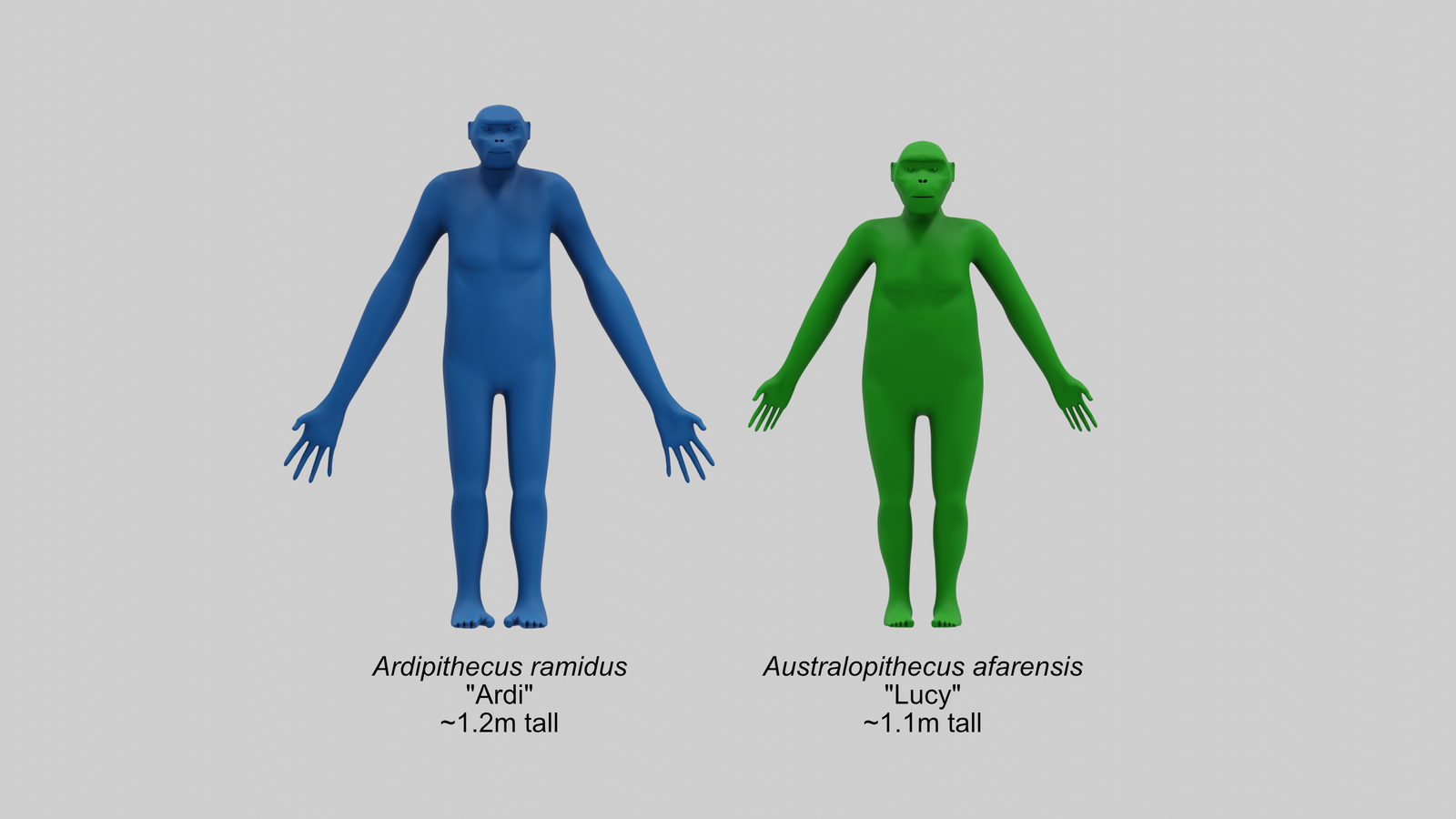
Lucy stood about 3.5 feet tall and weighed around 62 pounds. Her small stature indicates a primitive hominin closely related to both humans and other ape species. One of the defining features of Lucy’s physical structure is the pelvis, shaped to support bipedal locomotion. Her knee joint also suggests she walked upright, although her long arms and fingers indicate she retained the ability for arboreal activity, or tree climbing.
The Impact on Our Understanding of Human Evolution

Before Lucy’s discovery, much of our understanding of early human ancestors was fragmented and speculative. Lucy provided concrete evidence to support the hypothesis that bipedalism preceded other evolutionary developments, challenging previously held notions that increased brain size was the initial driving force in human evolution. Lucy’s find bridged a gap between modern humans and earlier, more primitive species, marking her as a pivotal link in the evolutionary chain.
Lucy’s Place in the Hominin Family Tree
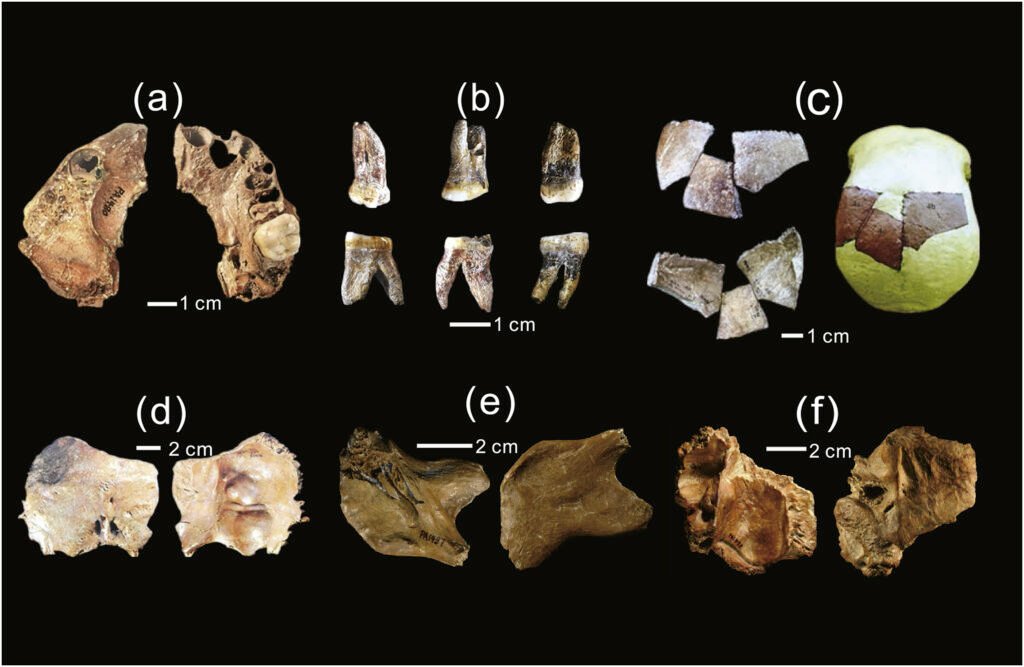
Australopithecus afarensis, represented by Lucy, fits into a complex network of hominin species that showcases the intricate path of evolution. While Lucy is not considered a direct ancestor of Homo sapiens, her species shares a common ancestor with ours, offering vital clues about the evolutionary path our own lineage took.
Technological Advances and Further Discoveries

Since the discovery of Lucy, technological advances and ongoing fossil discoveries have continued to expand our understanding of human evolution. Genetic analyses, advanced imaging techniques, and new methodologies in fossil dating enable scientists to build more detailed evolutionary timelines. Additional Australopithecus afarensis remains have been found, broadening the knowledge about the species and their way of life.
Conclusion: A Lasting Legacy

The discovery of Lucy fundamentally shifted the landscape of paleoanthropology and human evolutionary studies. Her uncovering not only underscores the complexity of our ancestry but also ignites the curiosity to further explore the roots of humanity. Lucy continues to be a symbol of the enduring quest to understand where we come from, highlighting the intrinsic link we share with our ancient predecessors.




