Imagine waking up one day in a world that feels eerily familiar and yet, unsettlingly artificial. This mind-bending scenario is at the heart of the Boltzmann Brain hypothesis—a concept that challenges our foundational understanding of reality itself. The question it poses is both simple and profound: Could everything we perceive as the universe be an elaborate illusion, a mere flicker of consciousness in the vast cosmic landscape? This hypothesis ventures into the murky waters of physics, philosophy, and cosmology, inviting us to question the very fabric of existence.
The Origins of the Boltzmann Brain
The Boltzmann Brain hypothesis is named after Ludwig Boltzmann, an Austrian physicist whose work in statistical mechanics laid the groundwork for our understanding of thermodynamics. Boltzmann proposed that the universe is in a state of entropy, constantly moving towards disorder. In this vast entropic sea, random fluctuations could theoretically produce self-aware entities—or “Boltzmann Brains”—that momentarily perceive a coherent reality. While Boltzmann himself never explicitly formulated this idea, it emerges naturally from his theories. The hypothesis suggests that it’s statistically more likely for a single brain to spontaneously appear in the void than for an entire universe to exist as we know it. This idea challenges our conventional understanding of the cosmos and our place within it.
Understanding Entropy and Random Fluctuations
Entropy is a measure of disorder within a system, often associated with the second law of thermodynamics, which states that the total entropy of an isolated system can never decrease over time. In simple terms, systems tend to evolve towards a state of maximum disorder. However, within this chaotic progression, random fluctuations can occur, leading to temporary decreases in entropy. Imagine stirring a cup of coffee and observing the swirling patterns—each swirl is a transient fluctuation in an otherwise predictable process. The Boltzmann Brain hypothesis leverages these fluctuations, suggesting that given infinite time, a random arrangement of particles could spontaneously form a conscious brain. Although this may sound improbable, in a universe that exists eternally, even the most unlikely events become possible.
Cosmological Implications
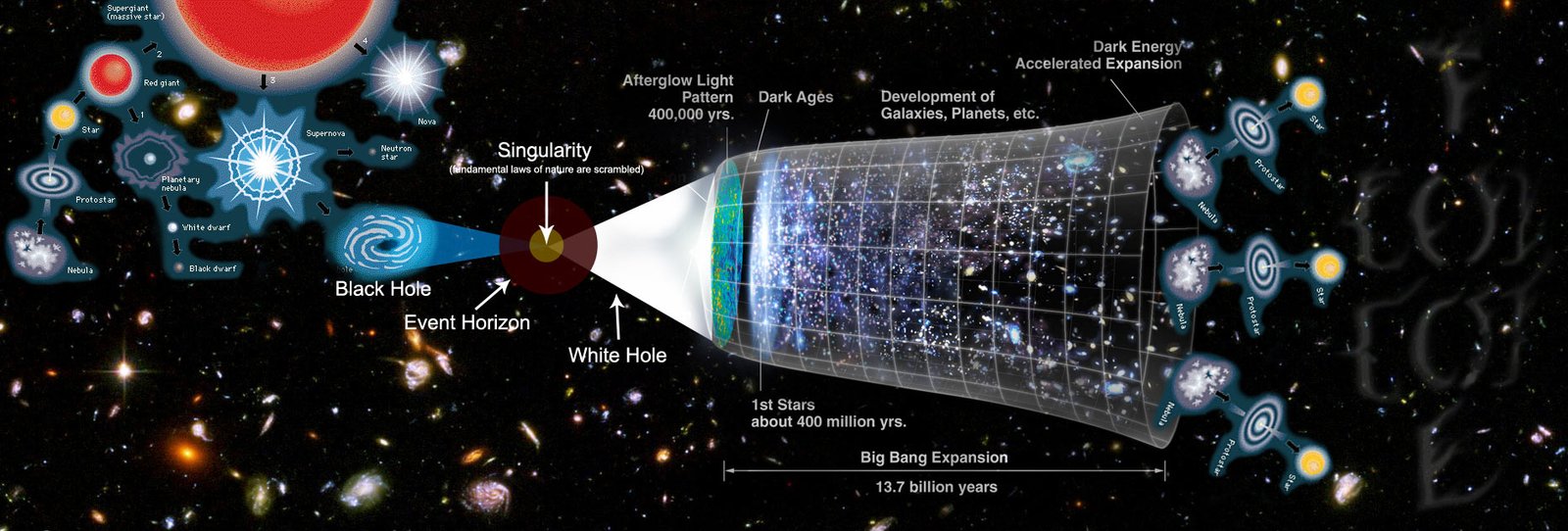
If the Boltzmann Brain hypothesis holds any truth, it poses significant implications for our understanding of the universe. It suggests that the vast cosmos we observe might be a rare exception rather than the rule. Our universe, with its structured galaxies and complex life forms, could be a fleeting anomaly within a chaotic multiverse. For cosmologists, this raises questions about the nature of reality and the assumptions underpinning our scientific models. Could the universe be a temporary construct, destined to dissolve back into entropy? The notion challenges the very foundation of cosmological theories, urging scientists to consider alternative explanations for the universe’s existence.
Philosophical Perspectives
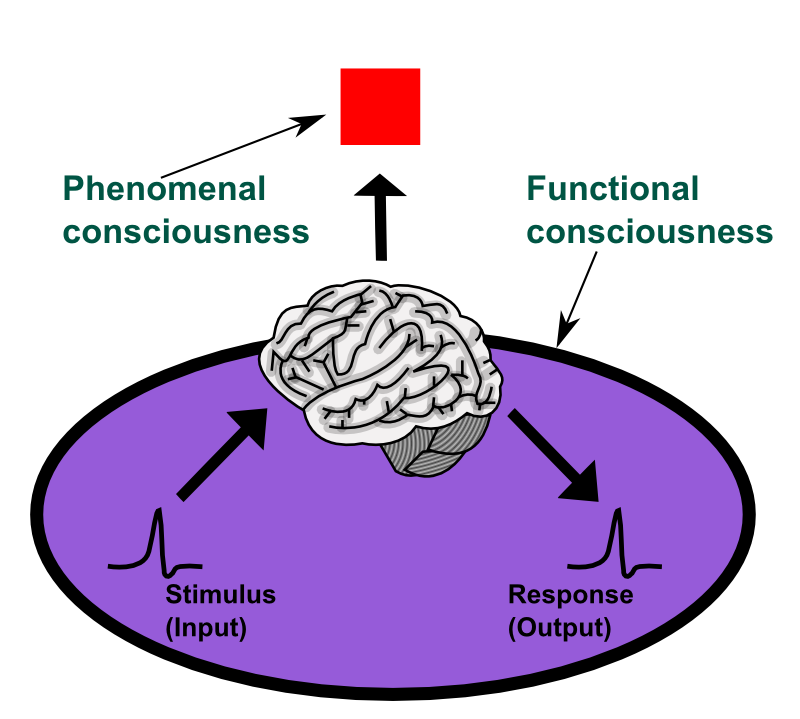
The Boltzmann Brain hypothesis also invites philosophical exploration, touching upon age-old questions about reality and consciousness. If our perceptions are merely transient illusions, what does this mean for our understanding of self and existence? Philosophers have long grappled with the nature of reality, from Plato’s allegory of the cave to Descartes’ meditations on doubt. The Boltzmann Brain adds a modern twist to these discussions, suggesting that our perceived universe might be a fleeting figment of a cosmic imagination. It challenges us to question the reliability of our senses and the nature of consciousness itself, blurring the line between reality and illusion.
The Role of Probability
Probability plays a crucial role in the Boltzmann Brain hypothesis. In an infinite universe, every possible event, no matter how improbable, is bound to occur eventually. This includes the spontaneous formation of a conscious brain amidst the cosmic chaos. The probability of such an event is vanishingly small, yet not zero. This raises intriguing questions about the likelihood of our universe being a genuine construct versus a temporary fluctuation. If Boltzmann Brains are more probable than a structured universe, then the reality we perceive might be an exception to the cosmic norm. Understanding probability in this context challenges our intuition and forces us to reconsider the nature of existence itself.
Criticisms and Counterarguments
Despite its intriguing premise, the Boltzmann Brain hypothesis faces several criticisms. Critics argue that it leads to paradoxes and contradictions, undermining the foundations of scientific inquiry. If our universe is a random fluctuation, then the laws of physics themselves could be illusions, making scientific exploration meaningless. Additionally, the hypothesis relies on assumptions about the infinite nature of the universe, which remain speculative. Some physicists propose that the likelihood of Boltzmann Brains appearing is negligible compared to the formation of structured universes. These counterarguments highlight the complexity of the hypothesis and the challenges in reconciling it with established scientific principles.
The Multiverse Theory
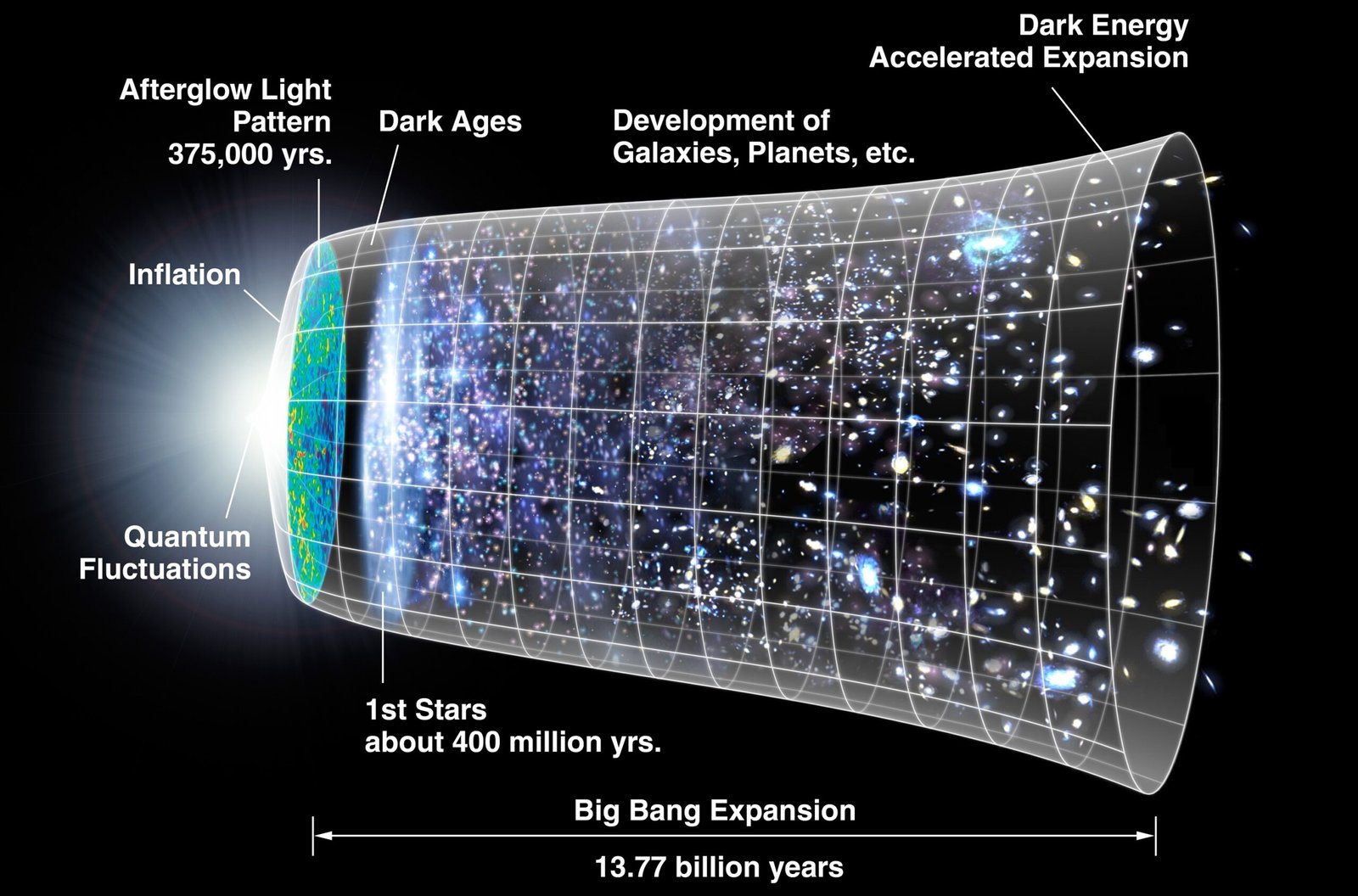
The concept of Boltzmann Brains is often discussed in the context of the multiverse theory—a hypothesis suggesting the existence of multiple, parallel universes. In such a multiverse, each universe could have different physical laws and constants. The Boltzmann Brain hypothesis aligns with this view, proposing that our universe might be one of many, each with varying degrees of entropy and structure. This perspective broadens our understanding of the cosmos, suggesting that our universe is just one possibility among countless others. While the multiverse theory remains speculative, it offers a framework for exploring the implications of Boltzmann Brains within a broader cosmic landscape.
Thinking Beyond Human Experience
The Boltzmann Brain hypothesis challenges us to think beyond human experience and consider the universe from a broader perspective. It invites us to question the assumptions underlying our understanding of reality and explore the limits of human perception. This requires a willingness to embrace uncertainty and contemplate the unknown. By examining the hypothesis, we expand our intellectual horizons and engage with the mysteries of the cosmos. It encourages us to explore new frontiers of thought and consider possibilities beyond our immediate comprehension, fostering a deeper appreciation for the complexity of the universe.
Implications for Science and Society
The exploration of the Boltzmann Brain hypothesis has broader implications for science and society. It challenges scientists to refine their models and consider alternative explanations for the universe’s existence. This process of questioning and exploration is fundamental to scientific progress, driving innovation and discovery. For society, the hypothesis encourages a deeper reflection on the nature of reality and our place within the cosmos. It invites individuals to contemplate the mysteries of existence and engage with philosophical questions that transcend the boundaries of science. By embracing the unknown, we foster a culture of curiosity and wonder, inspiring future generations to explore the frontiers of knowledge.
A Universe of Possibilities
The Boltzmann Brain hypothesis opens the door to a universe of possibilities, challenging us to reconsider our understanding of reality and the cosmos. It invites us to embrace the mysteries of existence and explore the boundaries of human thought. While the hypothesis remains speculative, it serves as a catalyst for intellectual exploration and philosophical inquiry. By engaging with these ideas, we enrich our understanding of the universe and our place within it. As we continue to explore the frontiers of science and philosophy, the Boltzmann Brain hypothesis reminds us that the universe is a vast, enigmatic tapestry, waiting to be unraveled by curious minds.




