The Unseen Scope from Orbit (Image Credits: Cdn.mos.cms.futurecdn.net)
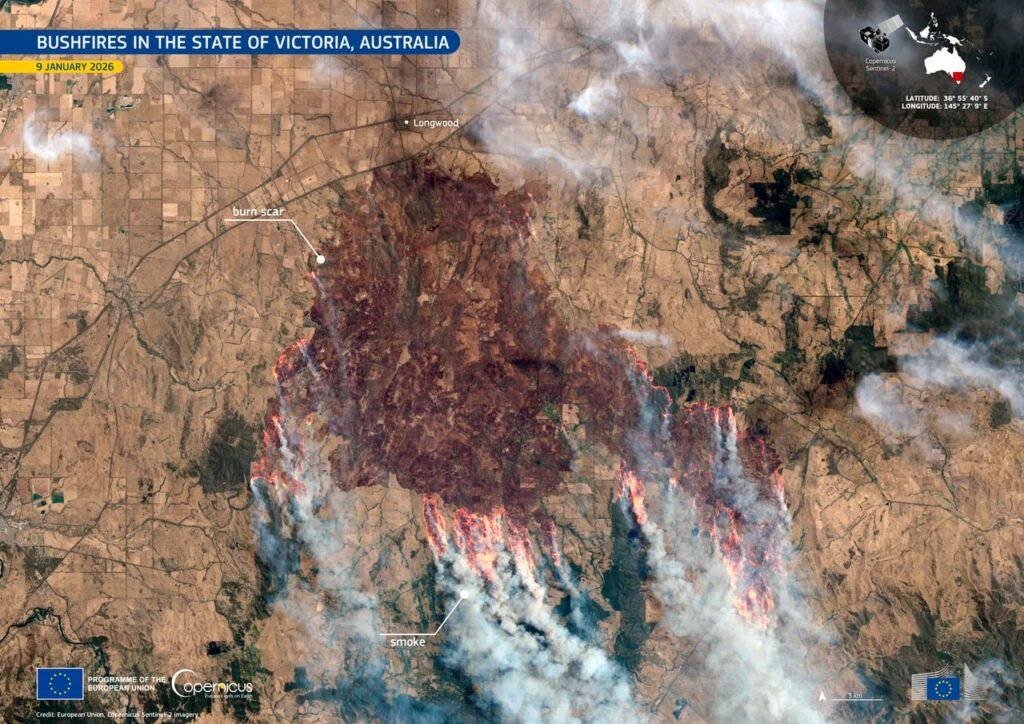
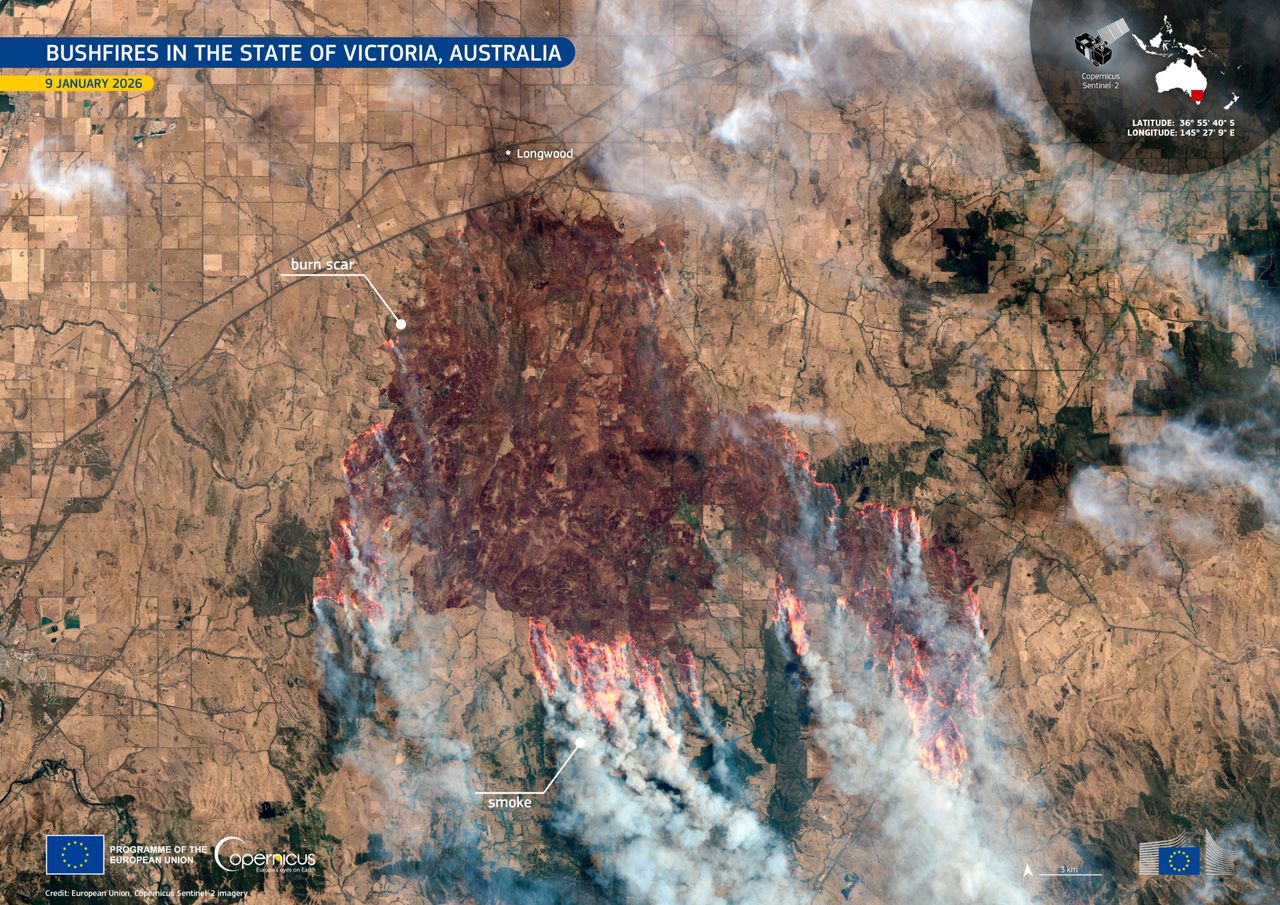
Victoria, Australia – Advanced satellite technology has captured the immense destruction wrought by bushfires sweeping through southeastern regions, offering a bird’s-eye perspective on the crisis unfolding in early 2026.
The Unseen Scope from Orbit
Weather satellites orbiting Earth have compiled hundreds of images that stitch together a comprehensive picture of the blazes. These observations, gathered over recent days, highlight the rapid spread and intensity of the fires in Victoria. Fire fronts stretch across vast landscapes, turning green expanses into charred terrain almost overnight.
One particularly striking visualization comes from the Copernicus Sentinel-2 mission, which scanned the area on January 15. The imagery reveals smoke plumes billowing outward, obscuring parts of the continent and underscoring the fires’ ferocity. Such data not only documents the event but also aids ground teams in real-time decision-making.
Experts note that these orbital snapshots provide a level of detail impossible from the ground. Thermal sensors detect hotspots invisible to the naked eye, allowing for precise mapping of affected zones. This technology has become indispensable during Australia’s fire seasons.
Victoria’s Fires: A Monumental Challenge
The bushfires in Victoria have engulfed more than 404,000 hectares since igniting earlier this month, an area exceeding five times the size of Singapore. Multiple blazes, fueled by dry conditions and strong winds, have forced evacuations and strained emergency resources. Communities in the Gippsland region and surrounding areas faced the brunt of the initial outbreaks.
Satellite composites show the fires’ evolution from scattered hotspots to interconnected infernos. By January 14, the smoke had spread far enough to blanket southeastern Australia in a hazy shroud. This visual evidence emphasizes the urgency of containment efforts amid predictions of heightened fire risk for the summer.
Authorities reported that the season’s outlook, issued by the Australasian Fire Authorities Council in late 2025, had warned of elevated dangers in southwestern and central Victoria. The current events align with those forecasts, prompting widespread preparedness campaigns.
National Implications and Smoke’s Far Reach
Beyond Victoria, the bushfires contribute to a broader pattern across Australia during the 2025-26 season. Similar incidents have flared in Queensland, the Northern Territory, and South Australia, though Victoria’s remain the most destructive to date. Satellite data from polar-orbiting platforms illuminates these widespread threats, comparing fire brightness to urban lights at night.
Smoke from the southeastern blazes has drifted across the continent, impacting air quality in major cities. Observations from geostationary satellites track these plumes, revealing their path toward coastal and inland populations. Such monitoring helps forecast health risks and visibility issues for travelers.
- Key fire zones: Gippsland, central Victoria, and parts of New South Wales.
- Area burned: Over 404,000 hectares in Victoria alone.
- Smoke coverage: Extending to southeastern Australia and beyond.
- Technological aids: Copernicus Sentinel-2 and weather satellites for thermal imaging.
- Risk outlook: Heightened through summer, per AFAC predictions.
Advancing Fire Management Through Space Tech
Satellites play a pivotal role in modern disaster response, integrating data with ground reports for comprehensive strategies. In this season, agencies have leveraged multi-day imagery to predict fire growth and allocate resources efficiently. The Barkly bushfire in the Northern Territory, for instance, has burned over 2 million acres, demonstrating the tool’s value nationwide.
Collaboration between international space programs enhances these efforts. The European Union’s Copernicus initiative, alongside NASA’s contributions, provides free access to high-resolution images. This global partnership ensures that remote areas receive timely attention, potentially saving lives and property.
Still, challenges persist. Dense smoke can obscure satellite views, requiring cross-verification with other sensors. Ongoing research aims to refine these systems for even greater accuracy in dynamic environments like Australia’s varied terrain.
Key Takeaways
- Satellite imagery has documented over 404,000 hectares burned in Victoria, highlighting the fires’ unprecedented scale.
- Smoke plumes from the blazes are visible across southeastern Australia, affecting air quality and visibility.
- Technologies like Copernicus Sentinel-2 enable real-time tracking, supporting faster emergency responses.
As the 2026 bushfire season intensifies, these orbital insights remind us of nature’s power and humanity’s ingenuity in confronting it. The vivid depictions from space serve as a call to action for better preparedness and environmental stewardship. What steps can communities take to mitigate future risks? Share your thoughts in the comments below.