It’s hard not to feel a shiver of excitement when thinking about lightning crackling through a volcanic ash cloud—nature’s fireworks, wild and unpredictable. But what if these electrifying displays on Earth hold secrets to the mysteries of weather on Mars? Scientists are now turning their attention to volcanic lightning, hoping it will unlock answers about the Red Planet’s turbulent past and the powerful forces that shaped its atmosphere. The idea of studying storms on another world through the lens of Earth’s most dramatic eruptions sounds like something from science fiction, but it’s happening right now. Imagine a planet where dust storms rage, volcanoes once towered, and the sky might have been streaked with lightning. The journey to unravel these cosmic weather puzzles has begun, sparking curiosity and igniting new hopes for discoveries that could change what we know about Mars—and maybe even about ourselves.
The Electrifying Phenomenon of Volcanic Lightning
Volcanic lightning is one of nature’s most jaw-dropping sights. Picture a dark ash cloud, churned up from the heart of an erupting volcano, suddenly lit by flashes of electricity. This isn’t the same as a normal thunderstorm; here, the charge builds up as tiny ash particles collide and rub against each other, creating a living, breathing storm inside the plume. For centuries, people have stood in awe of these displays, but only recently have scientists begun to crack the code of how and why these bolts appear. Volcanic lightning is like Earth’s own science experiment, offering clues to the unseen forces at play during an eruption. Some researchers describe it as a “window into chaos,” revealing the raw power and complexity of our planet’s dynamic systems. The phenomenon is not just beautiful—it’s a science puzzle, waiting to be solved.
What Makes Volcanic Lightning Unique?
Unlike the lightning we see in summer thunderstorms, volcanic lightning forms inside clouds filled with ash, gas, and rock fragments. It’s a bit like rubbing a balloon on your hair, but on a scale that could swallow cities. The friction between ash particles creates static electricity, and when enough charge builds up, zap—lightning arcs through the cloud. This unique process means that volcanic lightning can look and behave differently than typical lightning. The bolts might fork in strange directions or light up the sky in hues tinged by volcanic minerals. Each eruption writes its own story in the clouds, making every event a chance to witness something never seen before. Scientists are fascinated by these differences, seeing them as keys to understanding how electricity and weather interact in extreme environments.
How Earth’s Volcanoes Mirror Martian Landscapes
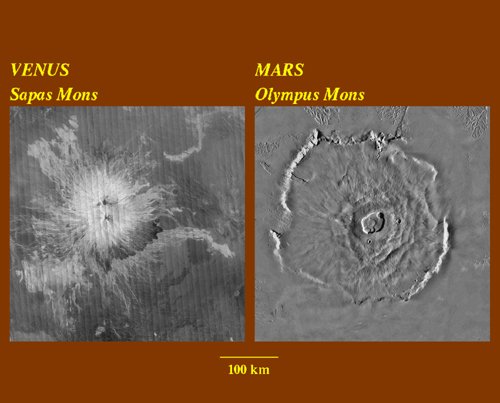
Standing before a volcano like Mount Etna or Eyjafjallajökull, it’s easy to imagine another world. In fact, many of Earth’s volcanic features mirror those found on Mars. The Red Planet boasts massive volcanoes—like Olympus Mons, the tallest in the solar system—that once spewed ash and lava across its surface. The dusty plains and ancient calderas of Mars might have seen eruptions much like those on Earth, complete with turbulent clouds and possibly even lightning. By studying our own volcanoes, scientists can draw comparisons and make educated guesses about what happened on Mars millions of years ago. It’s like piecing together a cosmic jigsaw puzzle, using clues from our backyard to understand a planet millions of miles away.
The Science Behind Electrical Charges in Ash Clouds
The secret to volcanic lightning lies in the tiny particles that fill the air during an eruption. When a volcano erupts, it blasts ash high into the sky, where those particles collide, break apart, and become charged. It’s similar to shuffling your feet across a carpet and then touching a doorknob—except here, the energy is multiplied by billions of particles. As the charges separate, the ash cloud becomes a giant battery, with electricity building up until it discharges as lightning. Scientists use sensitive instruments to measure these charges and map out how electricity moves through the plume. Understanding this process helps unlock not only the mysteries of volcanic lightning, but also the broader question of how electricity behaves in planetary atmospheres.
Martian Dust Storms: The Red Planet’s Own Fury
Mars is famous for its colossal dust storms, some of which can engulf the entire planet for weeks on end. These storms are more than just a nuisance; they’re a force of nature, shaping the Martian landscape and atmosphere. When wind whips up the fine, iron-rich dust, the particles clash and rub together, much like ash in a volcanic plume. This has led scientists to wonder: could Martian dust storms generate lightning, too? If so, this could have huge implications for everything from weather forecasting on Mars to the safety of future astronauts. By studying volcanic lightning on Earth, researchers hope to predict—and perhaps one day witness—the electrifying spectacle of Martian lightning.
How Lightning Reveals Planetary Weather Patterns
Lightning is more than a flashy light show; it’s a powerful diagnostic tool. On Earth, lightning is a sign of storm intensity, air movement, and the presence of water or ice. By tracking where and how lightning occurs, scientists can map out weather systems and understand their evolution. If similar processes are happening on Mars, studying volcanic lightning could help scientists decode the planet’s atmospheric history. Lightning data can hint at wind speeds, cloud composition, and even the presence of certain minerals. In this way, each bolt of volcanic lightning is like a fingerprint, helping researchers reconstruct the story of planetary weather across time and space.
Why Mars Is the Perfect Testbed for Extreme Weather Studies
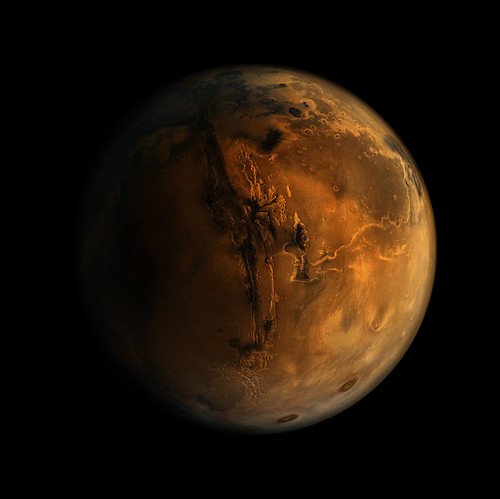

Mars is a planet of extremes—towering volcanoes, sprawling canyons, and dust storms that span continents. Its thin atmosphere and dry conditions make it a natural laboratory for studying weather in its rawest form. Unlike Earth, Mars has no oceans or forests to moderate its climate, so every storm, gust, and flash of lightning is magnified. Scientists relish the chance to test their theories in such a harsh environment. By using data from volcanic lightning on Earth, they can simulate Martian weather in the lab and even design experiments for future Mars missions. The hope is to catch a glimpse of how weather works on worlds vastly different from our own.
Cutting-Edge Tools for Studying Volcanic Lightning
To unravel the mysteries of volcanic lightning, scientists use an array of high-tech gadgets. High-speed cameras capture lightning bolts in stunning detail, revealing patterns invisible to the naked eye. Drones and satellites swoop over erupting volcanoes, collecting data from above the chaos. Ground-based sensors measure electrical fields, ash composition, and even the sound of thunder echoing through the plume. These tools allow researchers to piece together each eruption in three dimensions, building a richer understanding of how lightning forms. The technology is so advanced that some equipment could one day be sent to Mars, ready to catch the first flash of lightning on another planet.
Lessons Learned from Famous Volcanic Eruptions
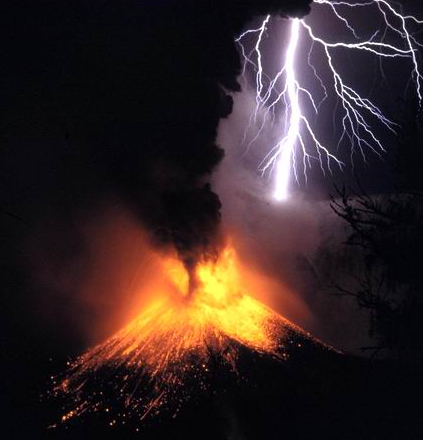

The world has watched in awe as volcanoes like Iceland’s Eyjafjallajökull and Indonesia’s Mount Sinabung erupted, sending ash and lightning into the sky. These real-life laboratories have become testing grounds for scientists eager to observe volcanic lightning up close. Each eruption reveals new patterns—like how the size and shape of ash particles affect electricity, or how weather conditions influence the color and intensity of lightning. By studying these events, scientists are building a library of knowledge that can be applied to other planets. The lessons learned from Earth’s most dramatic eruptions are shaping the future of planetary science.
The Role of Simulations in Understanding Martian Weather
Not all discoveries happen in the field; many begin in the lab. Scientists use powerful computers to simulate volcanic eruptions and dust storms, tweaking variables to mimic Martian conditions. These virtual experiments help researchers predict what kind of lightning might occur on Mars and how it would affect the planet’s atmosphere. Simulations also allow scientists to test new theories and refine their understanding of how ash and dust behave in low-pressure environments. The results guide the design of future missions and even influence how we search for signs of life on Mars.
Challenges of Detecting Lightning on Mars
Catching lightning in action, especially on another planet, is no easy feat. Mars’s thin atmosphere and lack of water mean that any lightning would be fainter and harder to detect than on Earth. Dust storms can block sensors, and the sheer distance from Earth adds another layer of complexity. Despite these challenges, scientists are developing new instruments—like ultra-sensitive microphones and cameras—that can spot even the faintest electrical activity. The hunt for Martian lightning is a game of patience, ingenuity, and dogged curiosity, with every discovery bringing us closer to understanding the Red Planet.
What Martian Lightning Could Mean for Future Exploration
If lightning does occur on Mars, the implications are huge for future explorers. Lightning could pose a risk to spacecraft, rovers, and even human habitats, so understanding it is crucial for safety. On the flip side, electrical activity could also help generate resources, like splitting carbon dioxide for fuel. Understanding how lightning interacts with dust and the Martian surface could help engineers design better equipment and mission protocols. The stakes are high, and every new insight from volcanic lightning on Earth brings us a step closer to safe and successful exploration on Mars.
Could Lightning Help Spark Life on Mars?

One of the most tantalizing questions in science is whether Mars ever supported life. On Earth, lightning is thought to have played a role in creating the building blocks of life, sparking chemical reactions in the atmosphere. If similar processes occurred on Mars, volcanic lightning could have been a catalyst for life’s ingredients. Scientists are now exploring how electrical discharges might interact with Martian minerals and ice, searching for clues to ancient biology. The idea that a flash of lightning could have lit the spark of life on another planet is both thrilling and humbling.
Analog Missions: Rehearsing for Mars Here on Earth

Scientists don’t have to wait for a mission to Mars to start learning. Every year, teams conduct “analog missions” on Earth, simulating Martian conditions in places like the Atacama Desert or Iceland’s volcanic fields. By studying volcanic lightning in these remote, Mars-like environments, researchers prepare for the challenges of planetary exploration. These missions help test new instruments, train astronauts, and refine scientific methods. It’s a hands-on, boots-in-the-dust approach that bridges the gap between Earth and Mars.
Collaboration Across Disciplines: The Power of Teamwork

Understanding volcanic lightning and Martian weather isn’t a job for one scientist alone. It takes a team—geologists, meteorologists, engineers, and even astronauts—all working together. By combining their expertise, these teams can see connections that might otherwise be missed. For example, geologists might notice patterns in ash deposits, while engineers design sensors to pick up faint signals. This spirit of collaboration is driving innovation and pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in planetary science.
What We’ve Learned So Far—and What’s Next
Every discovery about volcanic lightning adds a piece to the puzzle of Mars. Scientists have learned that electrical activity plays a big role in shaping weather, both on Earth and potentially on Mars. They’ve also developed new tools and techniques that could one day be used on the Red Planet. The next big leap could come from a dedicated Mars mission equipped to hunt for lightning, or from breakthroughs in lab simulations here on Earth. The journey is ongoing, and the future is wide open.
The Emotional Impact of Exploring the Unknown
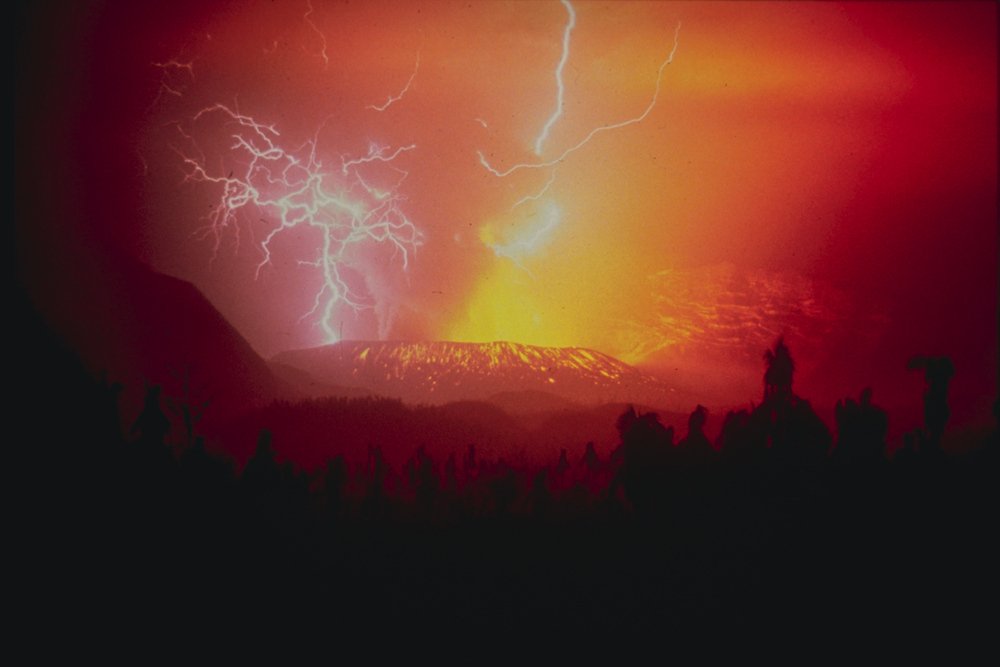

There’s something deeply moving about standing at the edge of a volcano, feeling the rumble beneath your feet and watching lightning flicker in the ash. It reminds us of how small we are—and how big our questions can be. Studying volcanic lightning isn’t just about science; it’s about curiosity, courage, and the thrill of discovery. The search for Martian weather touches something primal in us: the desire to know what lies beyond the horizon, and what secrets the universe might still hold.
Bringing the Public Along for the Ride
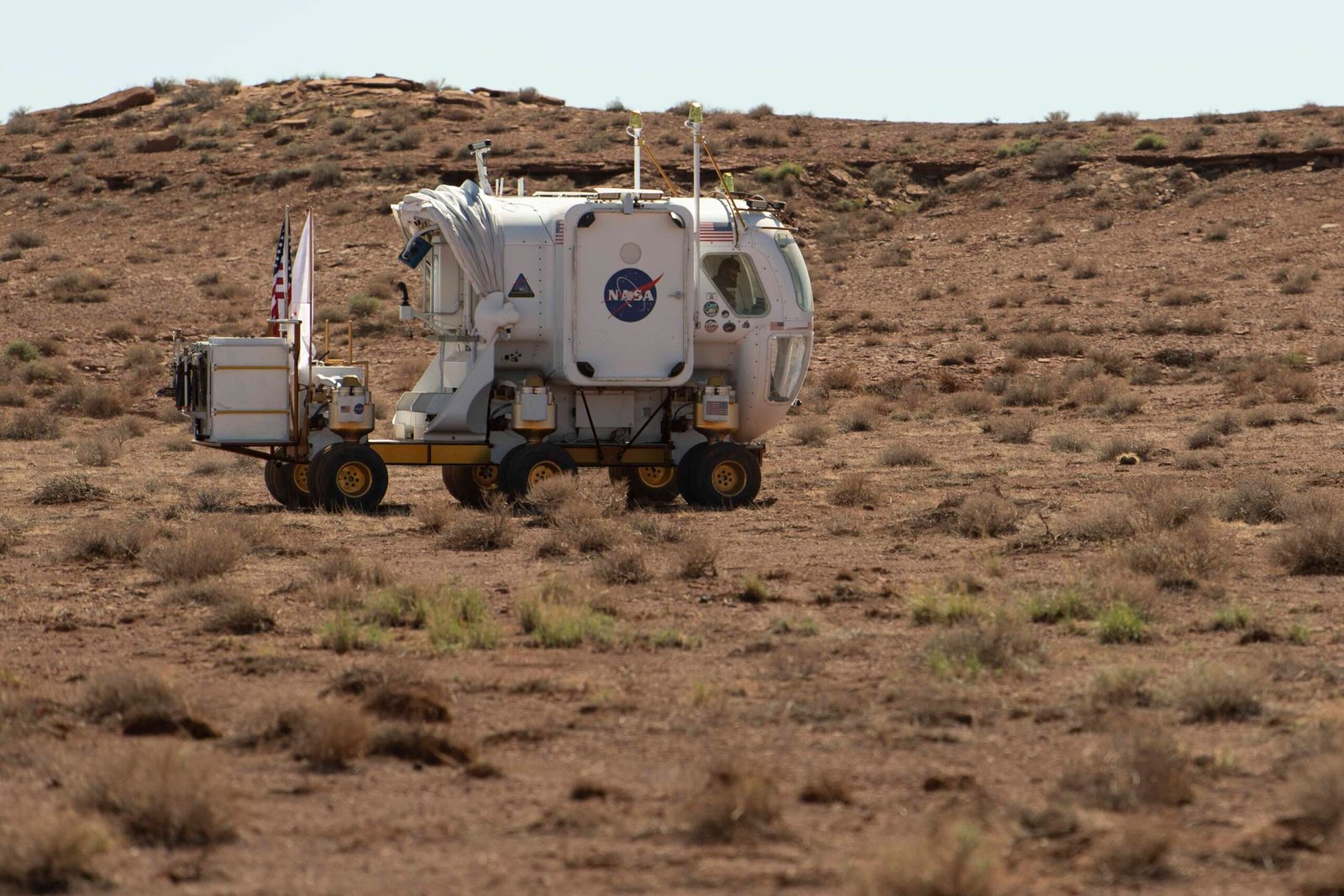

Science is at its best when everyone gets to join in. Through live-streamed eruptions, interactive maps, and citizen science projects, researchers are inviting the public to be part of the adventure. Schoolchildren can watch volcanic lightning from thousands of miles away, while amateur astronomers hunt for signs of storms on Mars. This open-door approach is sparking new interest in planetary science and inspiring the next generation of explorers.
A Future Lit by Lightning: Where Curiosity Leads
The study of volcanic lightning is more than a quest for knowledge; it’s a reminder of the electrifying power of curiosity. Every flash in the sky, whether on Earth or Mars, is a beacon guiding us forward. As scientists continue to dig deeper, build better tools, and dream bigger, one thing is clear: the universe still has plenty of surprises in store. Who knows what the next bolt of inspiration will reveal?



