Jupiter’s Cyclonic Polar Dance (Image Credits: Cdn.mos.cms.futurecdn.net)
Researchers studying the wild polar atmospheres of Jupiter and Saturn have uncovered patterns that illuminate the hidden dynamics deep within these massive planets.
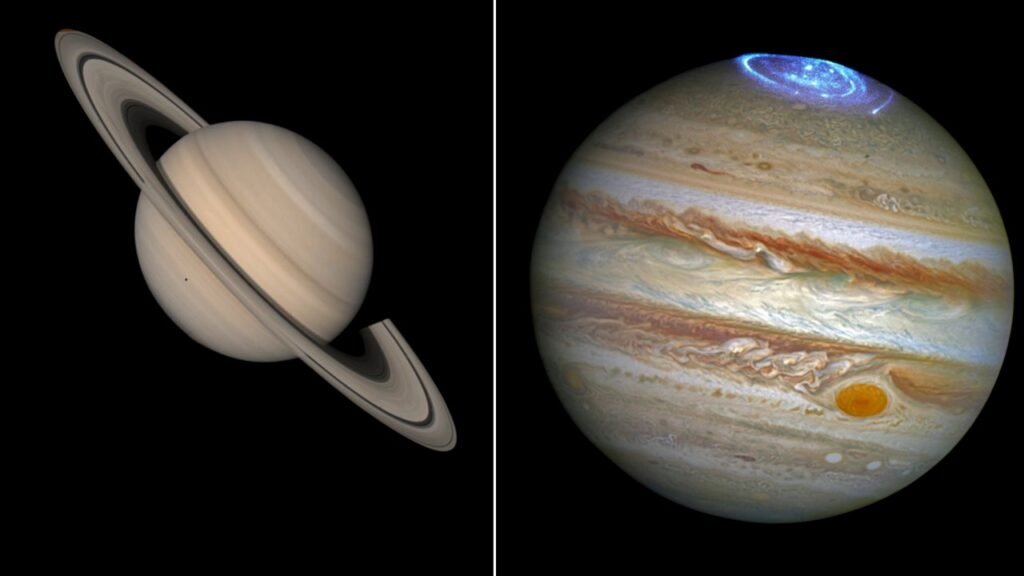
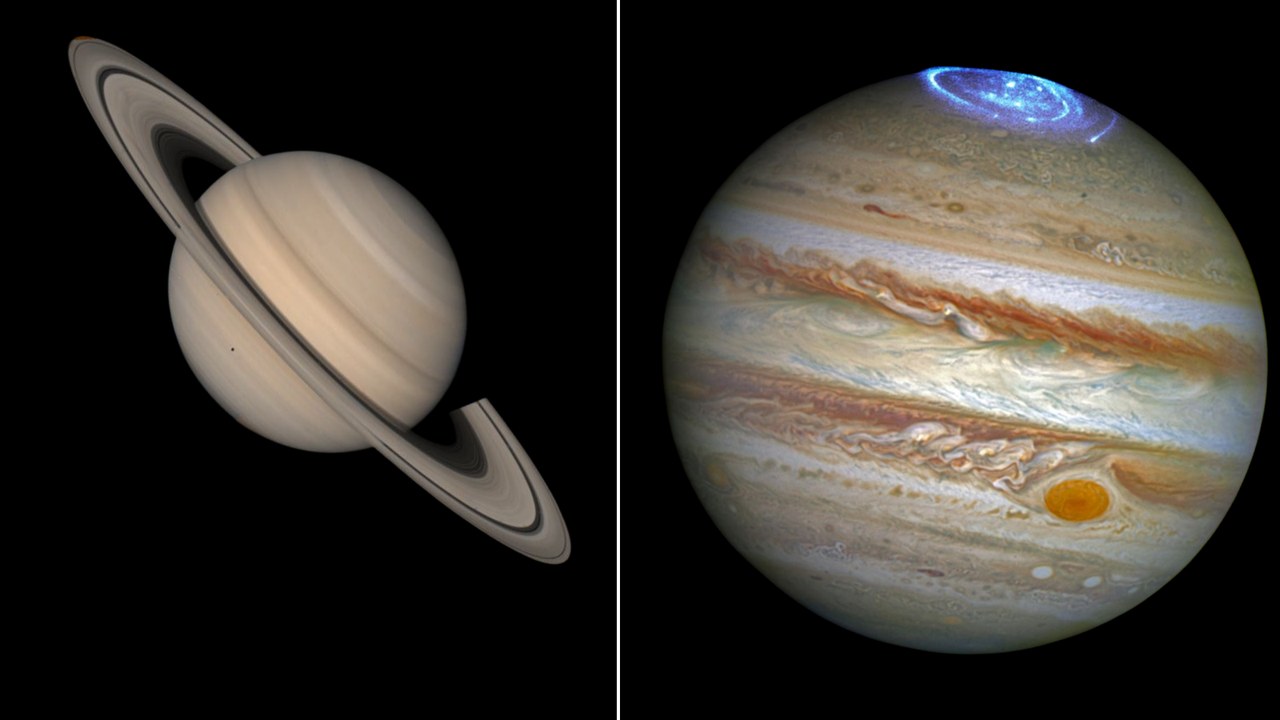
Jupiter’s Cyclonic Polar Dance
At Jupiter’s north and south poles, missions revealed clusters of powerful cyclones arranged in geometric precision. These storms, each larger than Earth, rotate without merging, defying typical atmospheric behavior. Observations from spacecraft showed eight vortices surrounding each pole, packed tightly together.
Such stability puzzled scientists initially. The arrangement suggested strong underlying forces at work. These polar features emerged prominently in data collected over years of close study. The cyclones’ persistence hinted at influences from the planet’s rapid rotation and deep interior flows.
Saturn’s Enigmatic Hexagon
Saturn displayed its own polar oddity: a massive hexagonal storm encircling the north pole. This six-sided jet stream, spanning 20,000 miles across, stood out in images from past flybys. Winds there reached speeds of 200 miles per hour, creating a waveform that repeated around the hexagon.
Unlike fleeting Earth weather, this structure endured for decades. Researchers linked it to interactions between atmospheric waves and the planet’s spin. The hexagon’s depth extended far below the clouds, connecting surface chaos to subsurface layers. Such longevity pointed to stable interior processes sustaining it.
Bridging Atmospheres to Cores
These polar phenomena serve as natural laboratories for probing planetary interiors. Turbulent polar regions amplify signals from deep convection currents. Scientists model how heat and material rise from metallic hydrogen layers, fueling the storms above.
Key observations include:
- Jupiter’s poles host rigidly packed cyclones that resist disruption.
- Saturn’s hexagon waves propagate from interactions with zonal jets.
- Both planets show polar downwelling, where air sinks toward interiors.
- Temperatures at poles run hotter than expected, suggesting internal heat sources.
- Lightning and chemical signatures trace vertical mixing from depths.
Implications for Giant Planet Science
Understanding these weather extremes refines models of gas giant formation and evolution. Polar dynamics reveal how magnetic fields interact with fluid interiors. For Jupiter, the findings confirmed a fuzzy core rather than a solid one. Saturn’s patterns supported theories of helium rain altering deep compositions.
Future missions will build on this foundation. Enhanced simulations now incorporate polar data to predict interior states. These insights extend to exoplanets, aiding searches for habitable worlds.
Key Takeaways
- Polar storms provide direct windows into convection and heat transport.
- Geometric stability challenges and refines atmospheric theories.
- Observations enhance models of core structures and magnetic dynamos.
The polar mysteries of Jupiter and Saturn remind us how surface spectacles reveal profound depths. What aspects of these gas giants intrigue you most? Share your thoughts in the comments.




