The universe has always held secrets that seem just beyond our reach, but in the past year, NASA’s cutting-edge laboratories across the United States have been working overtime to unlock mysteries that would have been pure science fiction just decades ago. From potential signs of ancient life on Mars to revolutionary discoveries about black holes that challenge everything we thought we knew about cosmic evolution, American space scientists are pushing the boundaries of human knowledge like never before. These aren’t just academic achievements gathering dust in research papers. Each breakthrough represents a giant leap forward in our understanding of the cosmos and our place within it. Some discoveries might fundamentally change how we think about life beyond Earth, while others are rewriting the textbooks on how the universe itself began. So let’s dive in and explore the ten most jaw-dropping space discoveries that have emerged from NASA’s labs, findings that are reshaping our cosmic perspective one revelation at a time.
Mars Rover Finds “Leopard Spots” That Could Be Ancient Life
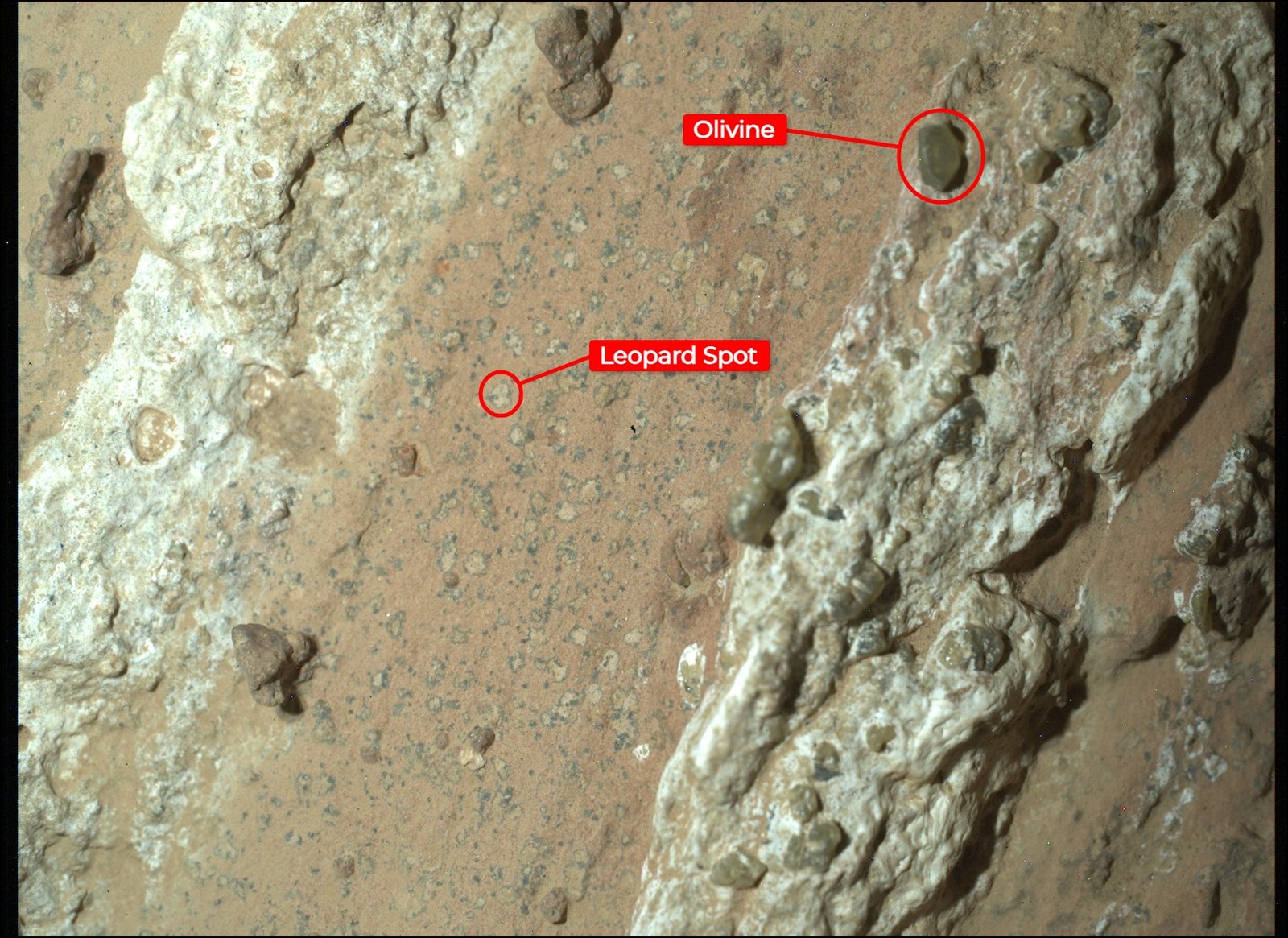

The most tantalizing discovery of the year came from NASA’s Perseverance rover when it discovered potential biosignatures on Mars, marking “the closest we have ever come to discovering life on Mars” according to NASA officials. The breakthrough centers around a rock dubbed “Cheyava Falls” that contains mysterious “leopard spots” patterns that may have formed through chemical reactions known to fuel life.
Perseverance came upon Cheyava Falls in July 2024 while exploring the “Bright Angel” formation, a set of rocky outcrops on the northern and southern edges of Neretva Vallis, an ancient river valley measuring a quarter-mile wide that was carved by water rushing into Jezero Crater long ago. The rover’s instruments found that the formation’s sedimentary rocks are composed of clay and silt, which, on Earth, are excellent preservers of past microbial life. Scientists believe the spots on the rock could have been left behind by microbial life if it had used the raw ingredients, the organic carbon, sulfur, and phosphorus, in the rock as an energy source.
James Webb Telescope Discovers “Black Hole Stars” in Early Universe

Astronomers have discovered a new object that could help shed light on mysterious “little red dots” that were first spotted by the James Webb Space Telescope in 2022, with the newfound object, dubbed “the Cliff,” suggesting that the little red dots represent a totally new class of cosmic objects known as a “black hole star”. This newly hypothesized object would essentially be a black hole feeding so rapidly that it lights up the thick cocoon of gas surrounding it, making it glow like a star.
When they were first discovered, little red dots were dubbed “universe breakers” because they seemed too old to exist in the first few billion years of the universe, therefore astronomers looked beyond the standard types of known objects to find an explanation for what they might be. About 70 percent of these objects showed evidence for gas rapidly orbiting 2 million miles per hour – a sign of an accretion disk around a supermassive black hole, suggesting that many little red dots are accreting black holes, also known as active galactic nuclei.
Naked Black Hole Found Floating Alone in Space

A black hole unlike any seen before has been spotted in the early universe – it’s huge and appears to be essentially on its own, with few stars circling it, and the object may represent a whole new class of enormous “naked” black holes that upends the textbook understanding of the young universe. This new black hole, which is as heavy as 50 million suns and is dubbed QSO1, clashes with the old, provisional account of the galaxy formation process, which did not start with black holes.
Black holes were thought to have come along only after a galaxy’s stars gravitationally collapsed into black holes that then merged and grew, but Maiolino and his colleagues described a solitary leviathan with no parent galaxy in sight. Astrophysicists can’t say yet whether these dots are all black holes or not, and in general they’re still confused about the universe’s chaotic childhood, but the telescope’s snapshots suggest a rowdy young cosmos that fabricated big black holes and galaxies both together and independently, or maybe even a universe where black holes were among the first large structures in existence.
Direct Collapse Black Hole Formation Process Discovered

While examining images from the COSMOS-Web survey, two researchers discovered an unusual object that they nicknamed the Infinity Galaxy, displaying a highly unusual shape of two very compact, red nuclei, each surrounded by a ring, giving it the shape of the infinity symbol. Follow-up observations showed that the Infinity Galaxy hosts an active, supermassive black hole, with what is highly unusual being that the black hole is in between the two nuclei, within a vast expanse of gas.
The team proposes that the black hole formed there via the direct collapse of a gas cloud – a process that may explain some of the incredibly massive black holes Webb has found in the early universe. Astronomers have detected a million-solar-mass black hole that seems to be embedded within this large swath of ionized gas, and they suggest that the black hole might have formed there through a process known as direct collapse. This discovery provides crucial evidence for how supermassive black holes could have formed so early in cosmic history.
Universe May Be Rotating Inside a Black Hole

The James Webb Space Telescope has found perhaps its most profound discovery to date – the uncovered preferred direction for galaxies supports the idea that the universe was born in a black hole. The ten billion dollar telescope has found that the vast majority of deep space and early galaxies it has observed are rotating in the same direction, while around two-thirds of galaxies spin clockwise, the other third rotates counter-clockwise, when in a random universe, scientists would expect to find 50% of galaxies rotating one way, while the other 50% rotate the other way.
“It would be fascinating if our universe had a preferred axis. Such an axis could be naturally explained by the theory that our universe was born on the other side of the event horizon of a black hole existing in some parent universe”. Black holes form from stars or at the centers of galaxies, and most likely globular clusters, which all rotate, meaning black holes also rotate, and the axis of rotation of a black hole would influence a universe created by the black hole, manifesting itself as a preferred axis.
Primordial Black Holes May Have Lit Up the Early Universe

The newly sighted objects don’t merely expand the timeline of galaxy formation back to a much earlier period; they sit in direct conflict with astronomers’ best cosmological models of when stars began to form during the cosmic dawn, so another group of astronomers have put forward a hypothesis to make sense of these puzzling findings, proposing that “primordial” black holes created right after the big bang may have lit up the universe before the first stars.
The James Webb Space Telescope, which launched in 2021, has spotted hundreds of strange black holes and galaxies in the early universe, revealing a chaotic first billion years of cosmic history. These primordial black holes would represent a completely different formation mechanism than the stellar collapse process we understand today. Instead of forming from dying stars, they would have condensed directly from the extreme density fluctuations present in the moments following the Big Bang, potentially explaining how such massive black holes existed so early in cosmic history.
Potential Moon-Forming Disk Discovered Around Exoplanet
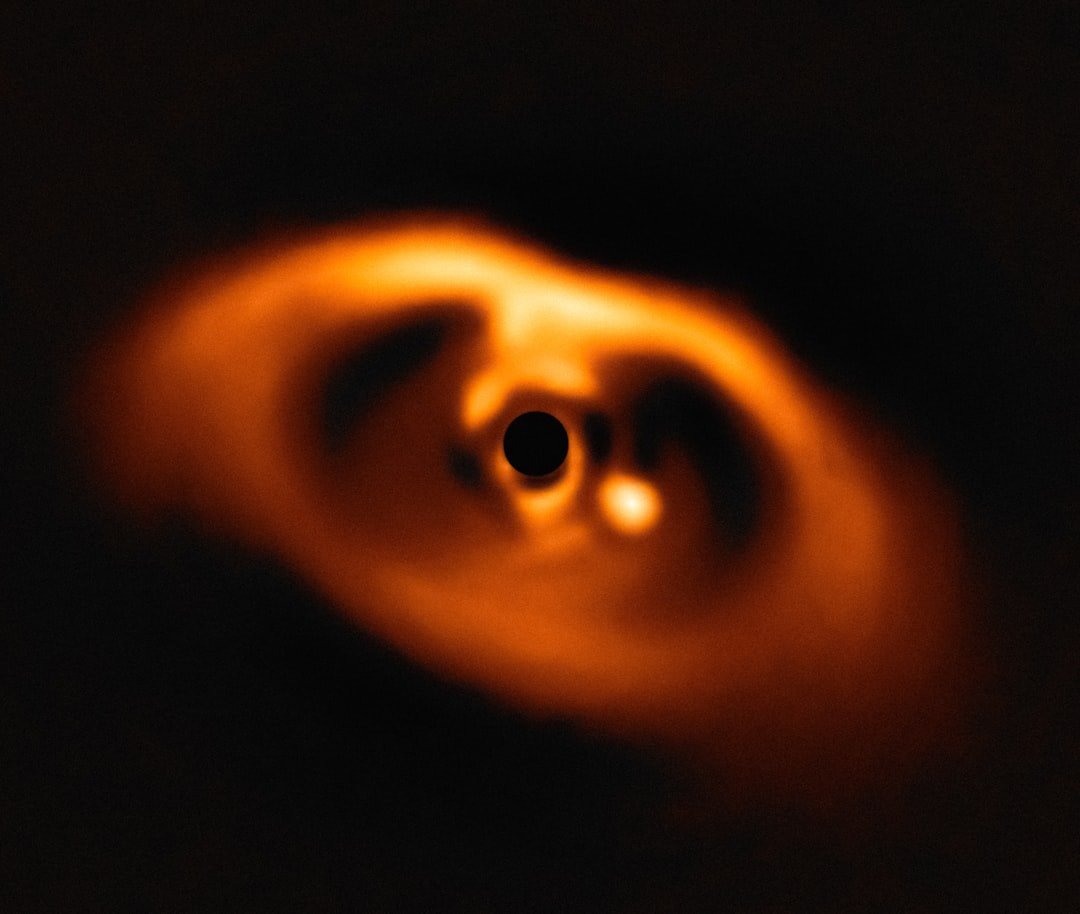
NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope has provided the first direct measurements of the chemical and physical properties of a potential moon-forming disk encircling a large exoplanet, with the carbon-rich disk surrounding the world called CT Cha b, which is located 625 light-years away. Spectroscopic data from NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope suggests the disk contains the raw materials for moon formation: diacetylene, hydrogen cyanide, propyne, acetylene, ethane, carbon dioxide, and benzene.
This represents the first time scientists have been able to directly observe and analyze the composition of a circumplanetary disk – the type of structure from which moons are believed to form. The discovery provides unprecedented insight into how moon systems develop around giant planets, offering a window into processes that occurred in our own solar system billions of years ago. The detection of organic molecules in the disk also raises intriguing questions about the potential for complex chemistry in such environments.
Earth’s Global Electric Field Finally Detected
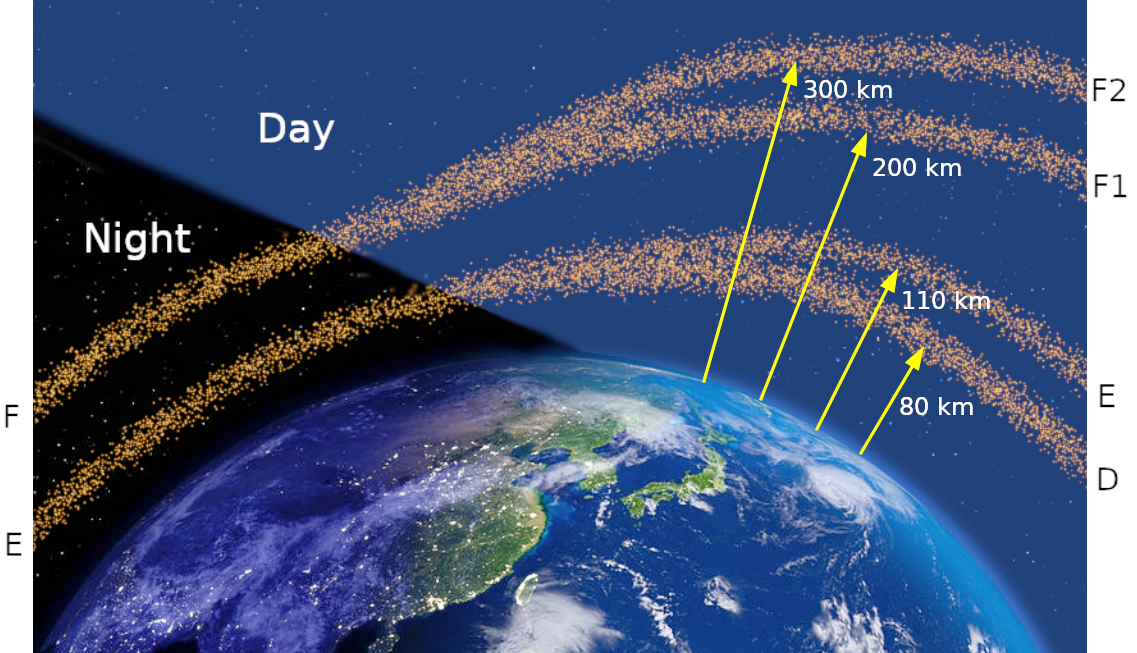
Scientists announced findings from a sounding rocket launched in 2022 that confirmed the existence of a long-sought global electric field at Earth. This breakthrough discovery represents the confirmation of a theoretical phenomenon that scientists had been trying to detect for decades. The global electric field plays a crucial role in atmospheric dynamics and may help explain how particles escape from Earth’s atmosphere into space.
The discovery has significant implications for understanding planetary atmospheres throughout the solar system and beyond. This electric field influences the behavior of charged particles in our atmosphere and contributes to processes that allow some atmospheric gases to escape to space. Understanding this mechanism could be vital for comprehending why some planets retain their atmospheres while others, like Mars, have lost much of theirs over geological time.
Solar Maximum Period Officially Declared
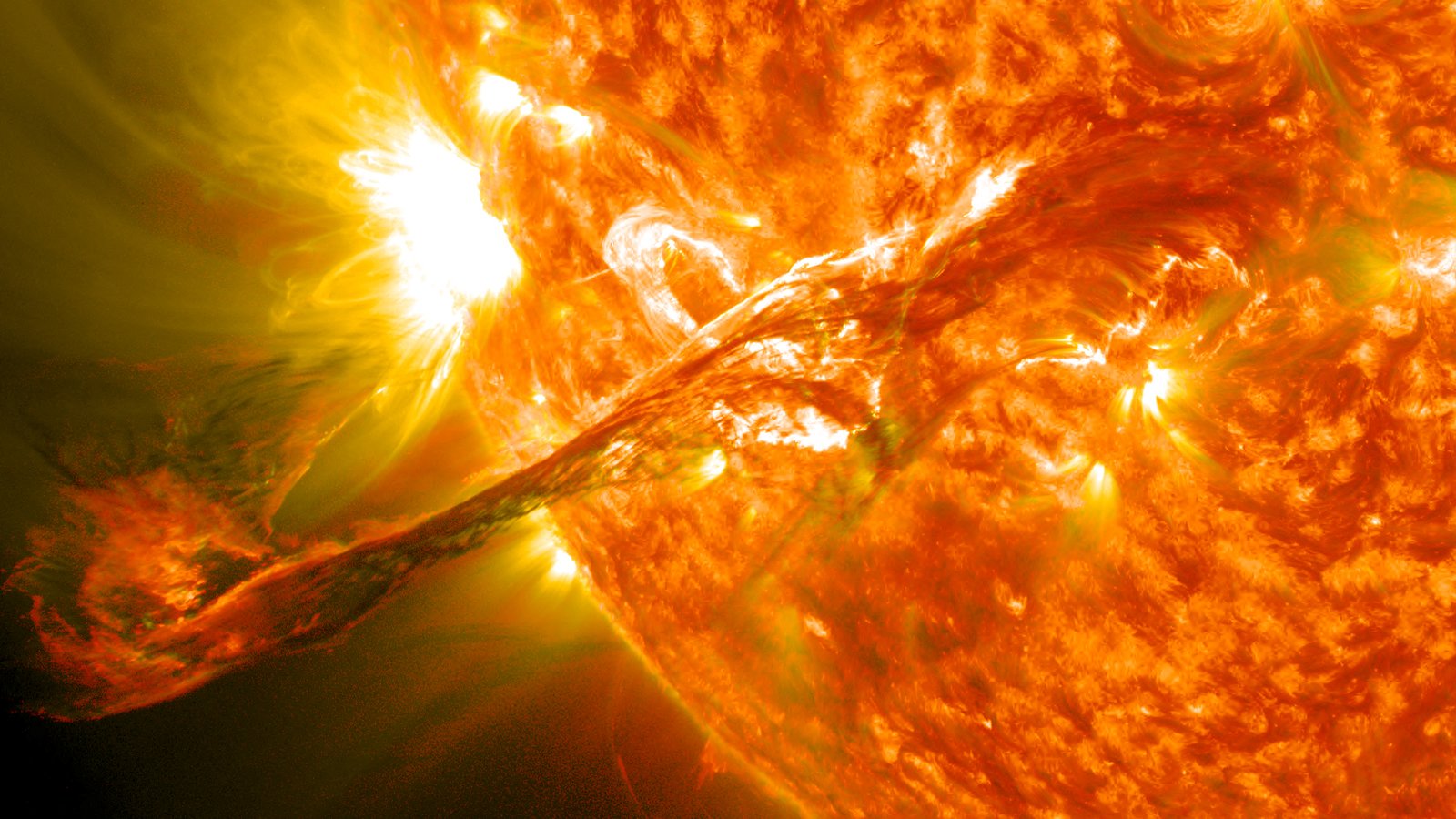

NASA and partners declared that the Sun reached solar maximum in 2024, a period of heightened solar activity when space weather becomes more frequent. The announcement came after careful analysis of solar activity patterns and magnetic field behavior. During solar maximum, the Sun’s magnetic field becomes more complex and unstable, leading to increased numbers of solar flares, coronal mass ejections, and other energetic phenomena.
This declaration has important implications for space missions, satellite operations, and even technology here on Earth. Enhanced solar activity can disrupt communications, damage sensitive electronics on spacecraft, and create beautiful auroral displays at lower latitudes than usual. NASA’s fleet of solar monitoring spacecraft has been closely tracking this activity, providing unprecedented data about our star’s behavior during this active phase of its roughly eleven-year cycle.
Europa Clipper Successfully Launches Toward Jupiter’s Moon
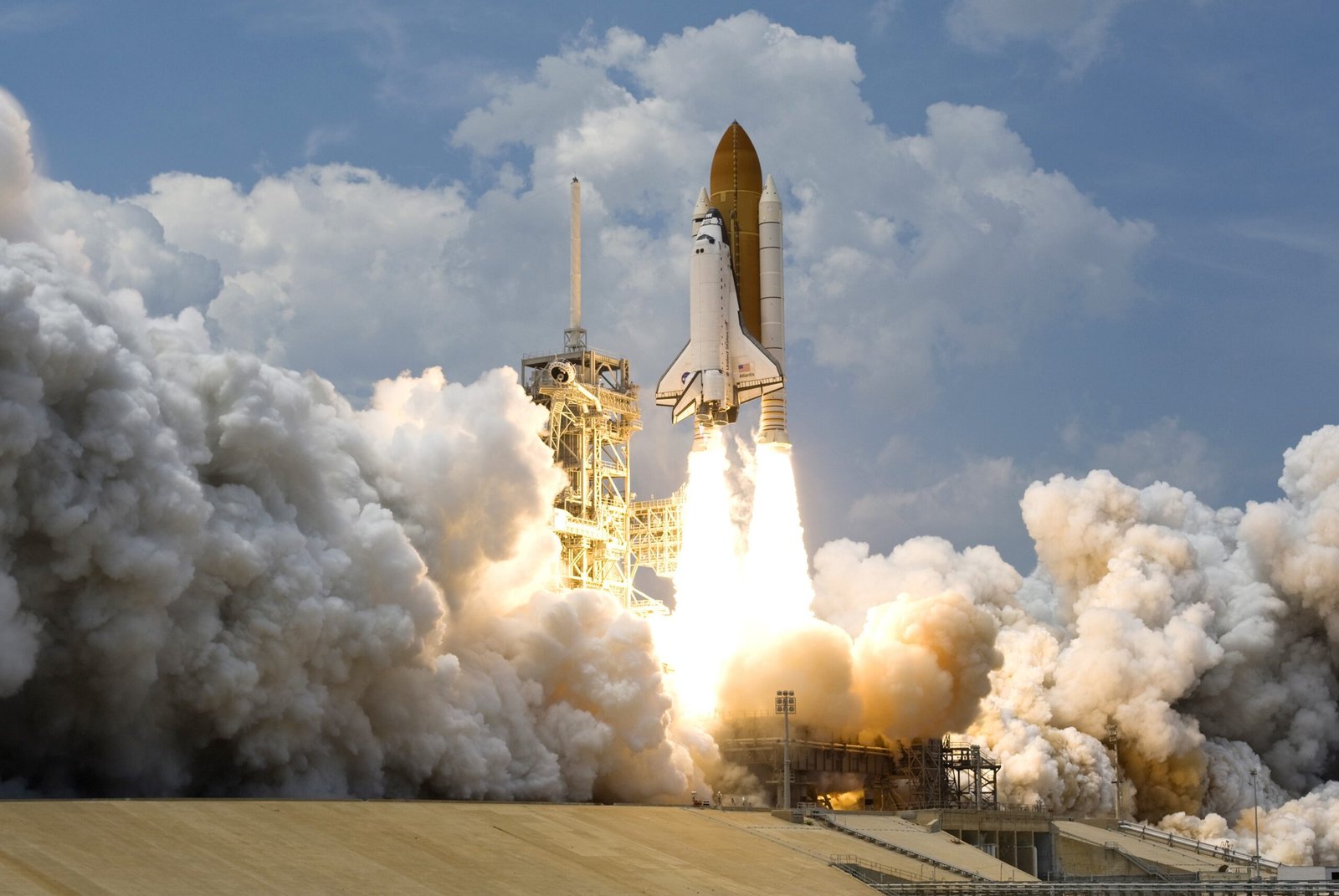

A SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket carrying NASA’s Europa Clipper spacecraft lifted off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on October 14, 2024, with the spacecraft planning to fly by Mars in February 2025, then back by Earth in December 2026, using the gravity of each planet to increase its momentum, and with help of these “gravity assists,” Europa Clipper will achieve the velocity needed to reach Jupiter in April 2030.
Europa Clipper represents one of the most ambitious missions ever launched to study a potentially habitable world beyond Earth. The spacecraft carries a suite of sophisticated instruments designed to investigate Europa’s subsurface ocean, which scientists believe may contain more water than all of Earth’s oceans combined. The mission will conduct detailed reconnaissance of Europa’s ice shell and subsurface ocean, assessing the moon’s potential for harboring conditions suitable for life as we know it.
Conclusion

These ten groundbreaking discoveries from NASA’s laboratories represent more than just scientific achievements – they’re fundamentally changing how we understand our place in the cosmos. From potential biosignatures on Mars that could answer the age-old question “Are we alone?” to revolutionary insights about black holes that suggest our entire universe might exist within one, these findings are reshaping our cosmic perspective in ways we never imagined possible. What makes these discoveries even more remarkable is that they’re just the beginning. With missions like Europa Clipper now en route to Jupiter and the James Webb Space Telescope continuing to peer deeper into space and time than ever before, we’re living through what might be the most exciting era of space discovery in human history. Each revelation opens up new questions and possibilities, reminding us that the universe still holds countless secrets waiting to be uncovered. What do you think about these incredible discoveries? Could we really be living inside a black hole, or do you find the potential signs of life on Mars more compelling? Tell us in the comments.

Jan loves Wildlife and Animals and is one of the founders of Animals Around The Globe. He holds an MSc in Finance & Economics and is a passionate PADI Open Water Diver. His favorite animals are Mountain Gorillas, Tigers, and Great White Sharks. He lived in South Africa, Germany, the USA, Ireland, Italy, China, and Australia. Before AATG, Jan worked for Google, Axel Springer, BMW and others.




