Since its successful launch on December 25, 2021, the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) has been captivating scientists and space enthusiasts alike. As the most powerful telescope ever launched into space, JWST is set to revolutionize our understanding of the universe. From peering back in time to revealing the secrets of distant galaxies, the telescope promises to unlock mysteries that have puzzled astronomers for decades. Let’s delve into the various ways JWST is reshaping our perception of the cosmos.
Introduction: The Genesis of Webb

The James Webb Space Telescope, named after NASA’s second administrator, was conceived to push the boundaries of astronomical observations. Unlike its predecessor, the Hubble Space Telescope, JWST operates primarily in the infrared spectrum, which allows it to peer through cosmic dust clouds and gain insights into the early universe. Its innovative design and capabilities mark a significant leap forward in our quest to understand the cosmos.
Peering Back in Time

One of JWST’s main objectives is to explore the era of “cosmic dawn,” the time when the first stars and galaxies formed. By observing the universe’s early days, scientists can gather information about its formation and evolution. Infrared technology allows JWST to detect light that has been stretched into infrared wavelengths due to the expanding universe, essentially allowing us to look back over 13 billion years in time.
Exploring the First Galaxies and Stars

The ability to observe the first galaxies and stars is a crucial aspect of JWST’s mission. Understanding the birth and maturation of these ancient structures provides insights into galaxy formation and evolution. JWST’s infrared sensitivity plays a critical role in capturing data on these faint objects, which are key to comprehending the universe’s formative years.
Unveiling the Mysteries of Exoplanets
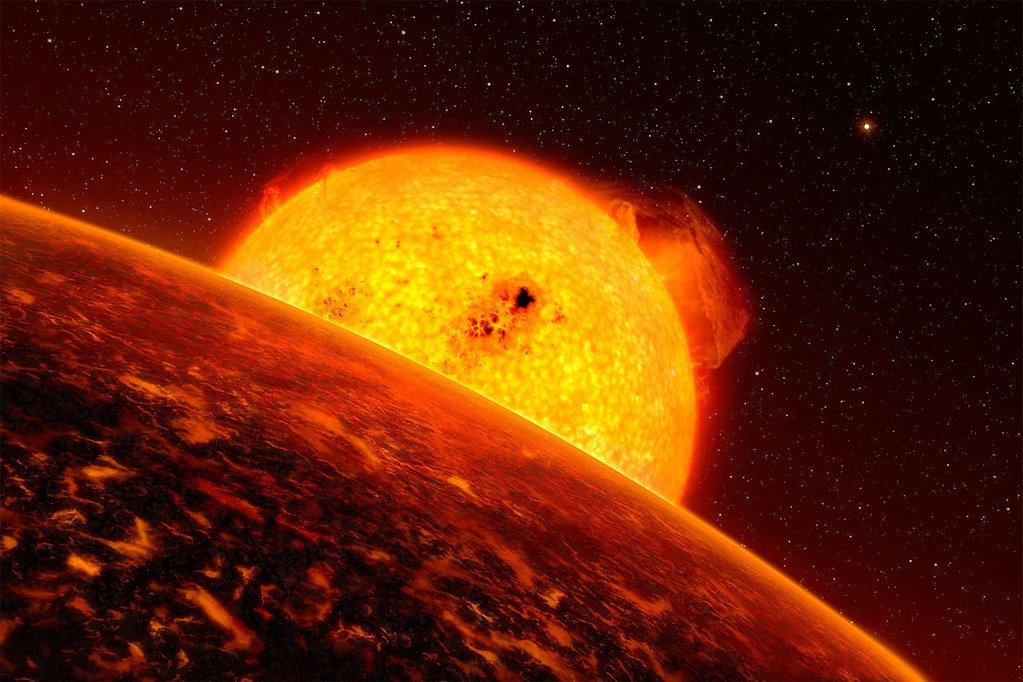

Another remarkable capability of the James Webb Telescope is its potential to study exoplanets—planets outside our solar system. With its advanced instruments, JWST can analyze the atmospheres of exoplanets, searching for signs of habitability or even life. By investigating atmospheric compositions, temperatures, and chemical profiles, JWST will provide deeper insights into these distant worlds and the possibility of life beyond Earth.
Shedding Light on Star and Planet Formation

JWST’s ability to penetrate dense nebulae and star-forming regions will transform our understanding of how stars and planets form. Its infrared vision can peer through obscuring dust clouds and capture images of embryonic stars and protoplanetary disks, offering an unprecedented view of these formative processes. This will improve our understanding of solar system formation and the diverse architectures of planetary systems.
Contributing to Our Knowledge of Black Holes

Black holes, some of the most enigmatic objects in the universe, are another focus of JWST’s mission. The telescope is designed to study the environments surrounding these cosmic giants, including their interactions with nearby stars and the impact of their intense gravitational fields. By observing the infrared radiation emitted by material as it gets sucked into black holes, JWST will help unravel the complex dynamics near these powerful objects.
Deciphering the Universe’s Expansion

JWST is poised to contribute significantly to our understanding of the universe’s expansion. By studying distant supernovae and galaxies, it will offer precise measurements of cosmic distances, aiding in the determination of the universe’s expansion rate. This research will provide crucial data to understand the nature of dark energy, the mysterious force driving this expansion.
Expanding Our Understanding of Cosmic Dust

Cosmic dust, though often overlooked, is vital to our understanding of the universe. The particles play a crucial role in star formation, planetary evolution, and the chemical enrichment of galaxies. JWST’s advanced capabilities allow it to study these minuscule particles in greater detail, presenting opportunities to learn about their composition, distribution, and impact on the cosmic environment.
Revealing the Lifecycle of Stars

JWST offers a unique opportunity to study the life cycles of stars, from their birth within stellar nurseries to their eventual deaths. By capturing images and data on star-forming regions and remnants like supernovae, JWST is unveiling the various stages of stellar evolution, providing a more comprehensive understanding of how stars, including our own sun, transform over time.
Collaborating Across International Frontiers
JWST represents a collaborative effort among NASA, the European Space Agency (ESA), and the Canadian Space Agency (CSA). This international partnership exemplifies the spirit of cooperation in scientific exploration, bringing together bright minds and cutting-edge technology from around the world. The collective expertise and resources of these agencies foster innovations that propel our understanding of the universe.
Stimulating Technological Advancements
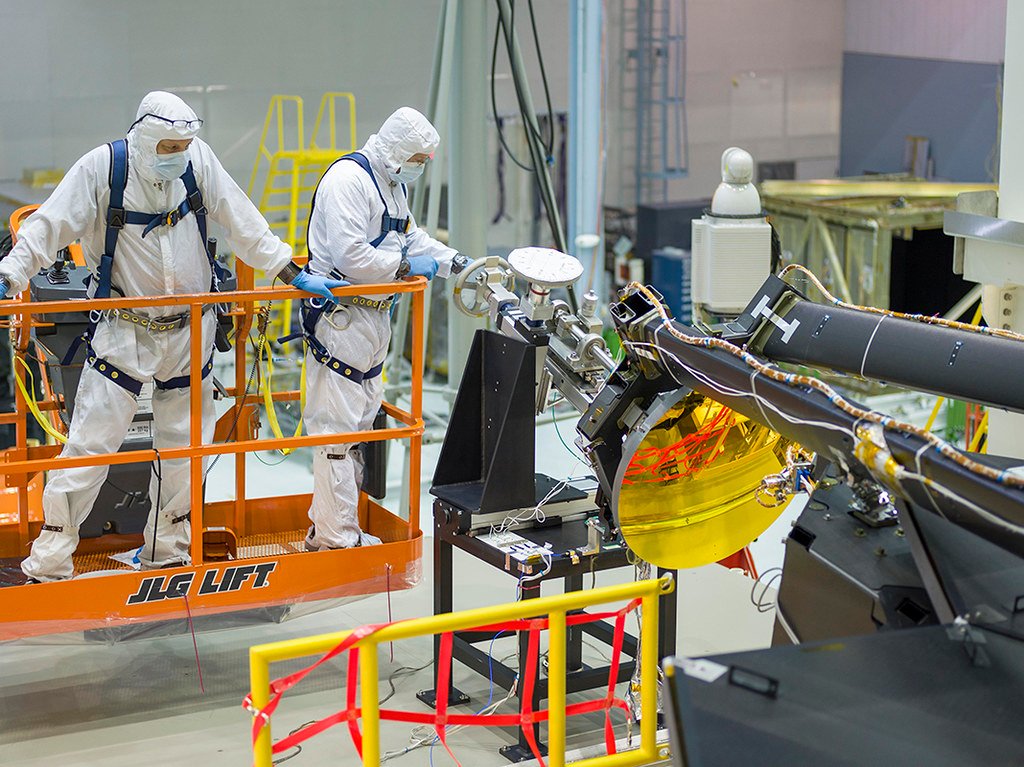

The development of JWST has pushed the boundaries of technology, resulting in significant advancements applicable beyond astronomy. Innovations in materials science, cryogenics, and optics developed for JWST have transferable benefits to other fields, including medical imaging and communications. The technological prowess underlying JWST’s design highlights the interconnectedness of scientific exploration and technological progress.
Inspiring Future Generations

The awe-inspiring discoveries made possible by JWST have the power to captivate and inspire future generations of scientists and explorers. By expanding our knowledge of the universe, the telescope ignites curiosity and wonder, encouraging young minds to embark on their own scientific journeys. The continued exploration of space fuels imagination and fosters a deep appreciation for the vastness and intricacy of the cosmos.
Conclusion: A New Era of Discovery

The James Webb Space Telescope is not just a scientific marvel; it is a beacon of exploration and discovery. By uncovering the universe’s secrets and transforming our understanding of the cosmos, JWST holds the promise of a new era in astronomy. As it continues its mission, the telescope inspires us to push the boundaries of our knowledge and pursue the answers to fundamental questions about our place in the universe. The discoveries ahead are bound to be as vast as the universe itself, offering insights that could forever alter our understanding of space and time.