Space travel, once the exclusive dream of sci-fi enthusiasts and visionaries, has become a symbol of human ingenuity and determination. As we witness the rise of commercial spaceflight and plan for missions to Mars, it’s crucial to look back and appreciate the pioneering efforts that paved the way for these modern marvels. The first space missions pushed the boundaries of what was possible, laying the groundwork for today’s advancements. Through triumphs and failures alike, they charted the unknown and inspired generations to come.
Early Endeavors in Space Exploration

The inception of space exploration traces back to the mid-20th century, during the height of the Cold War. In 1957, the Soviet Union launched Sputnik 1, the first artificial satellite, marking humanity’s first successful foray beyond Earth. This achievement set the stage for an era of rapid technological advancement, spurred by intense competition between superpowers.
The Space Race and its Impact

The fierce rivalry known as the Space Race drove innovation at an unprecedented pace. The Soviet Union and the United States each aimed to outdo the other in space achievements. The U.S. responded to Sputnik with Explorer 1 in 1958, and the subsequent Apollo program sought to push the boundaries even further, culminating in the historic Apollo 11 moon landing in 1969.
Engineering Marvels: Developing New Technologies
To operate in the harsh environment of space, engineers developed groundbreaking technologies. Among these were powerful rockets, guidance and navigation systems, and life-support systems that could sustain humans in space. Many of these technologies, including miniaturized computers and advanced materials, have since been adapted for a range of applications on Earth.
The Role of Unmanned Missions

Before humans could safely travel to space, unmanned missions provided crucial data. Probes like Luna, Vostok, and NASA’s Ranger series explored the Moon and nearby planets. These missions tested new technologies, gathered knowledge, and evaluated conditions in outer space, providing vital information that would inform all future human endeavors.
The First Journeys with Life: Animals in Space

Animals were the first Earthlings to experience life beyond our atmosphere. The Soviet Union’s Laika, a dog, and the United States’ chimpanzees, such as Ham, provided insight into the biological effects of space travel. Their contributions were invaluable, offering data that helped shape human spaceflight safety protocols.
Pioneering Human Spaceflight

Yuri Gagarin’s milestone 1961 journey aboard Vostok 1 marked the first time a human ventured into space, orbiting Earth and returning safely. This feat was followed by Alan Shepard’s suborbital flight a month later, as the United States worked toward longer missions and eventual moon exploration.
Lessons from Apollo Missions

The Apollo missions were a testament to human capability and resilience. They overcame numerous obstacles, from hardware malfunctions to human error, illustrating the importance of meticulous preparation and adaptability. These missions also led to the development of critical emergency procedures that continue to protect astronauts today.
The Legacy of Skylab and Space Stations

NASA’s Skylab, launched in the 1970s, was the first U.S. space station, demonstrating the potential for long-duration human presence in orbit. Its success influenced the development of subsequent space stations, such as Russia’s Mir and the International Space Station (ISS), fostering international collaboration and technological exchange.
Space Shuttle Innovations
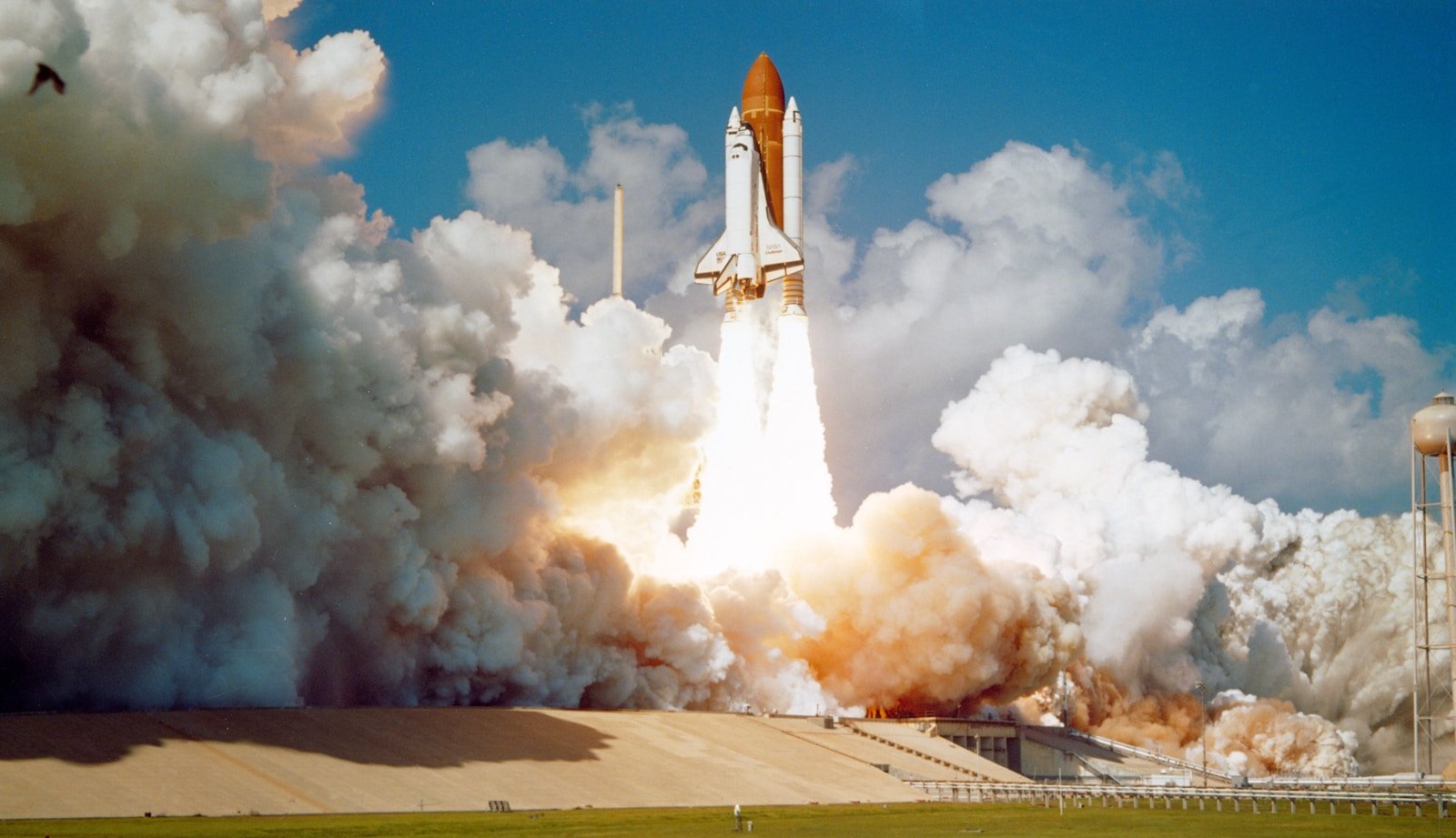

The Space Shuttle program introduced a reusable spacecraft design that significantly increased access to space and reduced costs compared to earlier expendable rockets. This innovation paved the way for today’s reusable launch vehicles, a staple in modern commercial spaceflight endeavors.
Influence on International Collaboration

The early space missions fostered international competition that eventually morphed into cooperation. The establishment of the ISS and ongoing partnerships in space agencies worldwide exemplify the spirit of shared exploration and problem-solving across nations.
Commercial Spaceflight: A New Era

Thanks to the accomplishments of early missions, private companies like SpaceX, Blue Origin, and Virgin Galactic are now pioneering commercial space travel. These companies build upon the technological foundation laid by past missions, making space travel more accessible and affordable.
Modern Challenges and Ongoing Exploration

With goals of sending humans to Mars, exploring asteroids, and returning to the Moon, modern missions tackle challenges more complex than ever. Innovations continue in propulsion, crew safety, and sustainability, building on the lessons and technologies of past missions to reach these new milestones.
Conclusion: The Enduring Legacy of Early Space Missions

The first space missions were bold and daunting undertakings that fundamentally transformed our understanding of the universe. They laid the groundwork for technological innovations and international collaboration, shaping the path of modern space exploration. As we look toward Mars and beyond, the achievements of these pioneers serve as a testament to human curiosity and our relentless pursuit of knowledge, continuing to inspire future generations to reach for the stars.




