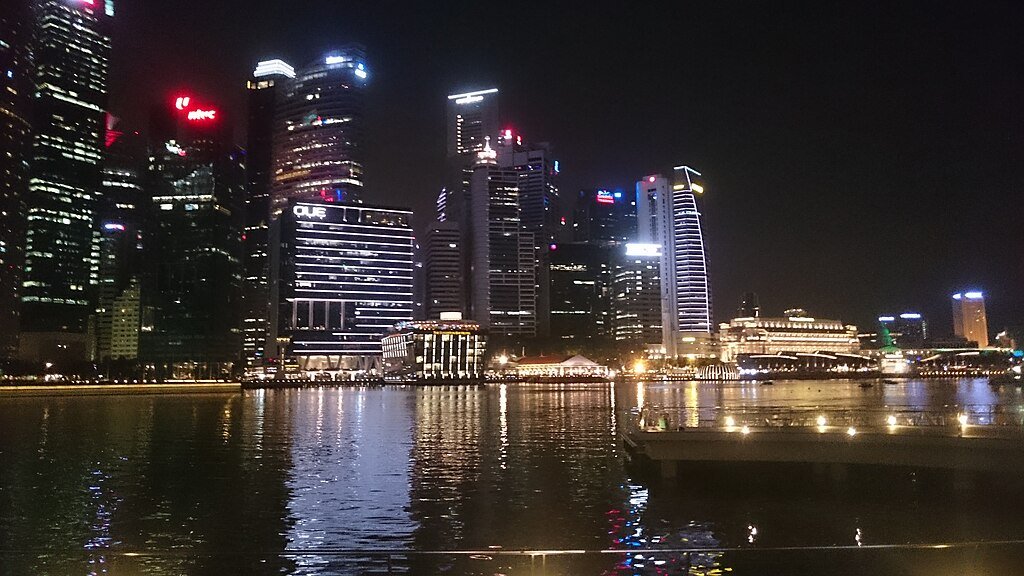
Singapore, a city-state renowned for its cleanliness and efficiency, has ascended to the pinnacle of global sustainable urban planning. Despite its limited land area and dense population, Singapore has ingeniously transformed its urban landscape into a model of ecological balance and modern living. Through a mix of innovative policies, cutting-edge technology, and community involvement, Singapore has redefined what it means to develop sustainably, offering valuable lessons to cities worldwide. This article explores the key elements that have contributed to Singapore’s success in sustainable urban planning.
Visionary Leadership

Singapore’s journey to sustainability was greatly influenced by visionary leadership. The foresight of leaders like Lee Kuan Yew set the foundation for a green and resilient city. His belief in long-term planning fostered a culture of sustainability, emphasizing greening initiatives and efficient resource management from the early days of Singapore’s independence.
Integrated Planning Approach
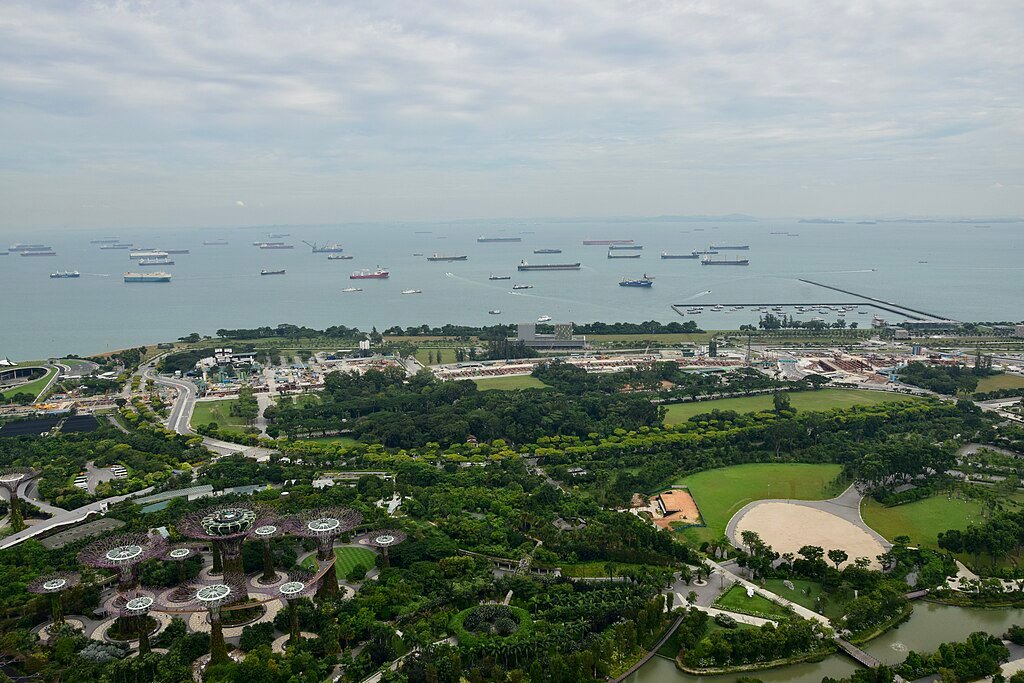

One of Singapore’s standout strategies is its commitment to a comprehensive urban planning approach. Agencies such as the Urban Redevelopment Authority (URA) and the Housing Development Board (HDB) collaborate in designing an urban environment that integrates housing, infrastructure, and green spaces strategically. This integrated planning ensures that urban growth aligns with environmental objectives.
Emphasis on Green Spaces
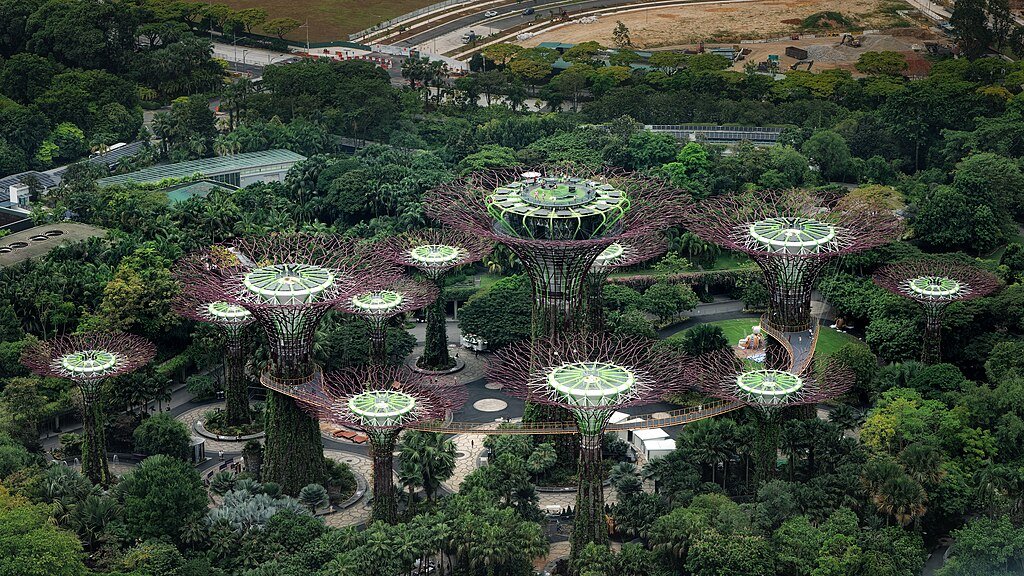

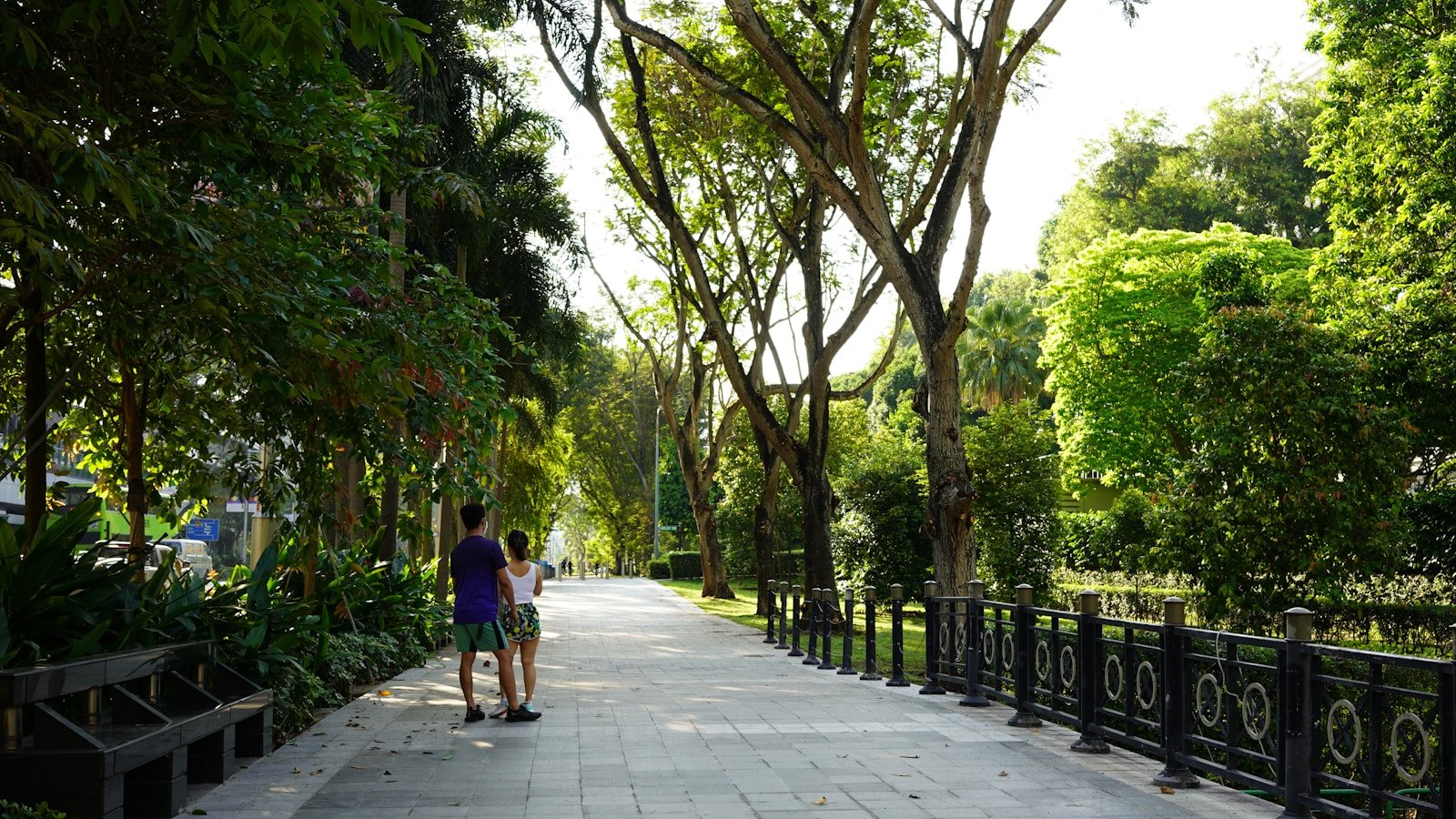
Greenery is a hallmark of Singapore’s urban landscape. The city’s ambition to be a “City in a Garden” has led to the pervasive integration of parks, gardens, and green corridors. Landmark projects like Gardens by the Bay and the Singapore Botanic Gardens, a UNESCO World Heritage site, reflect this commitment. Green roofs and vertical gardens on skyscrapers further enhance urban biodiversity and cooling.
Water Management and Conservation
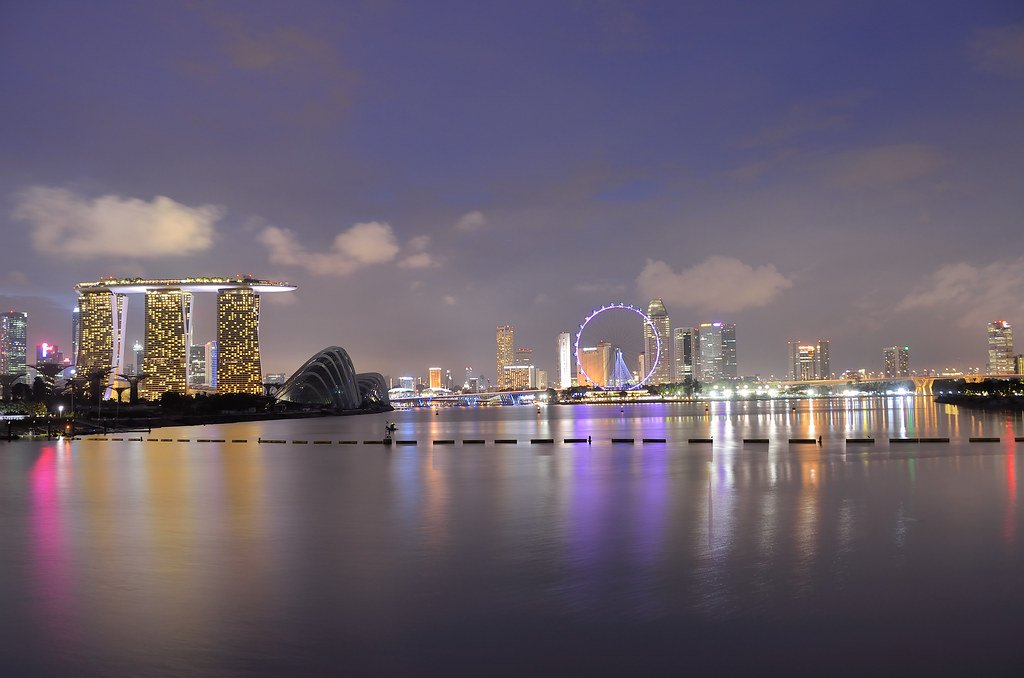

Singapore’s expertise in water management is world-renowned. Faced with limited water resources, the city-state has implemented a multifaceted approach that includes rainwater harvesting, desalination, and recycling treated sewage into potable water. The Marina Barrage captures rainwater, providing flood control and a fresh water reservoir while also creating recreational space.
Advanced Waste Management Systems

Singapore’s waste management practices are pivotal in its sustainability achievements. With a focus on the 3Rs—Reduce, Reuse, Recycle—Singapore has achieved high recycling rates. The Semakau Landfill, an engineering marvel, is an offshore facility that provides a sustainable solution to the city’s waste disposal needs without harming the environment.
Smart City Initiatives
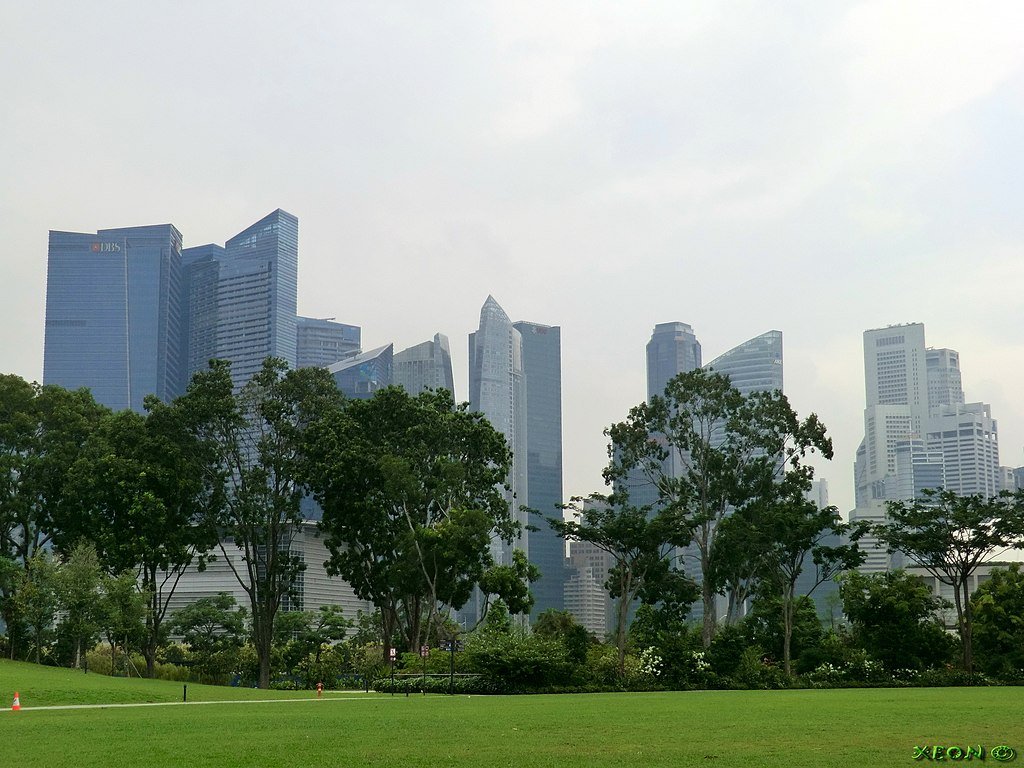

As a leader in technology and innovation, Singapore employs smart solutions to enhance urban living. The Smart Nation initiative integrates data analytics, sensors, and technology to improve city services, traffic management, and energy consumption. This allows Singapore to enhance efficiency while reducing its carbon footprint.
Public Transportation Network
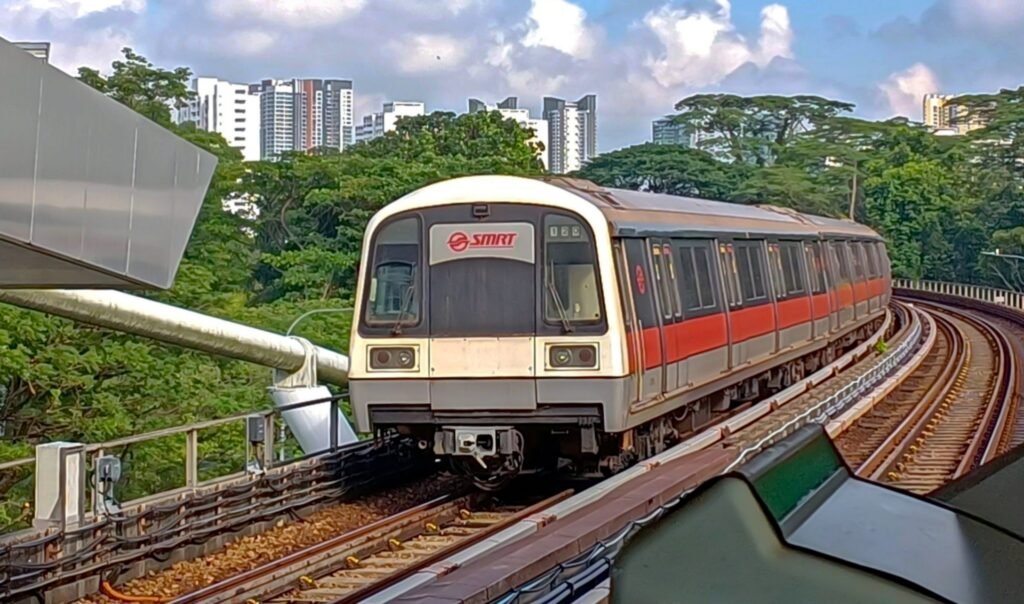

Singapore boasts one of the world’s most efficient public transportation systems, crucial for reducing urban congestion and pollution. The Mass Rapid Transit (MRT) system, complemented by a comprehensive bus network, offers residents convenient and eco-friendly commuting options. Continuous investments in expanding and upgrading these systems ensure minimal reliance on personal vehicles.
Sustainable Building Practices
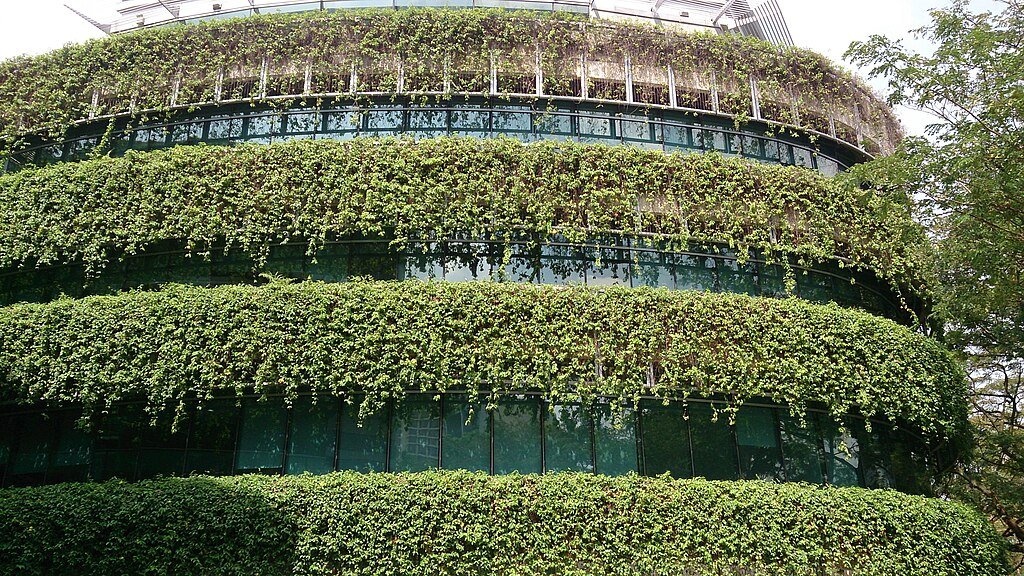

Building sustainably is a priority in Singapore’s urban development. The country has implemented stringent green building standards through the Building and Construction Authority’s Green Mark Scheme. This initiative incentivizes developers to construct environmentally friendly buildings, reducing energy consumption and environmental impact.
Community Involvement and Education
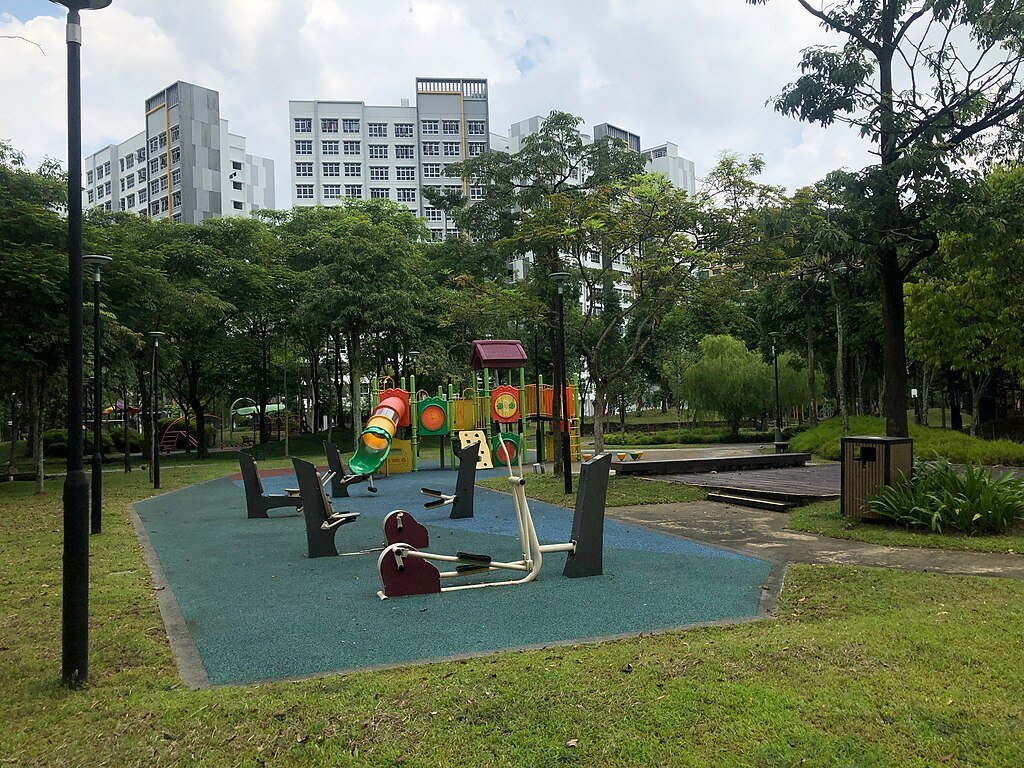

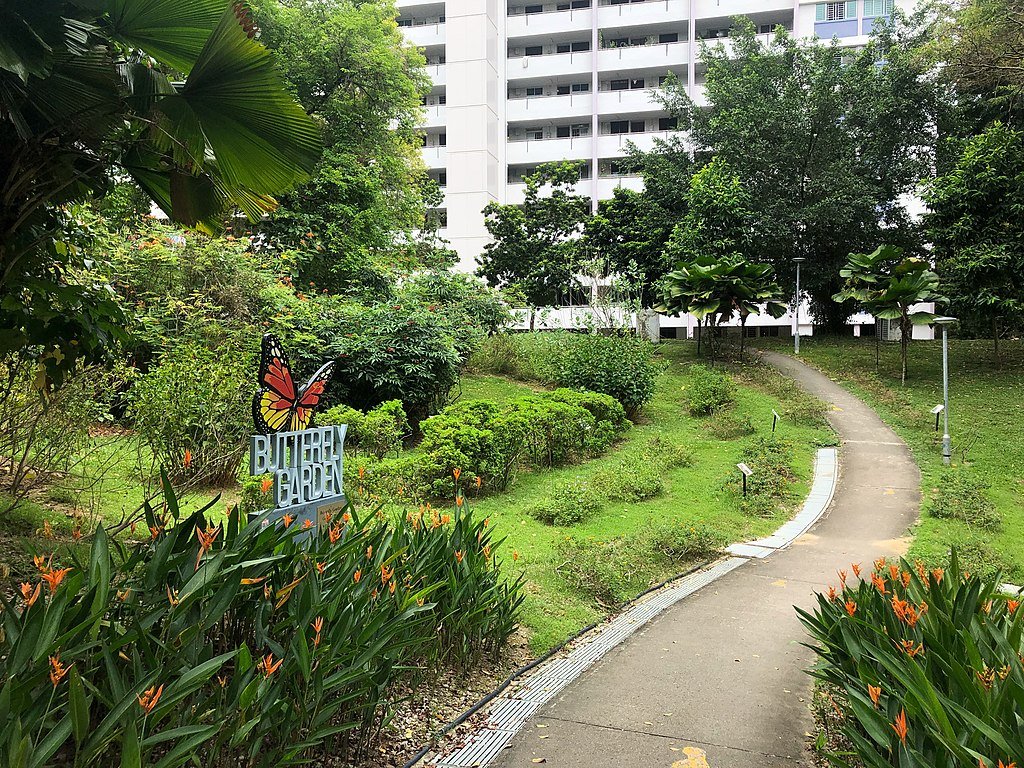
Singapore’s sustainable success has been partly due to extensive community involvement. Public awareness campaigns and educational programs encourage residents to take proactive roles in sustainability efforts. Community gardens, recycling initiatives, and citizen science projects boost public engagement in green efforts.
International Collaborations and Research

Singapore actively participates in global sustainability discussions and collaborates with international institutions for research. Joint projects, such as those with the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), contribute to pioneering sustainable urban solutions and position Singapore as a leader in urban research and innovation.
Adaptive Policies for Climate Resilience

The city-state’s approach to climate change is proactive. Singapore has committed to the Paris Agreement and established its own Climate Action Plan. Adaptive policies focus on flood prevention, coastal protection, and enhancing the city’s resilience to climate-related impacts through continuous monitoring and upgrades.
Conclusion
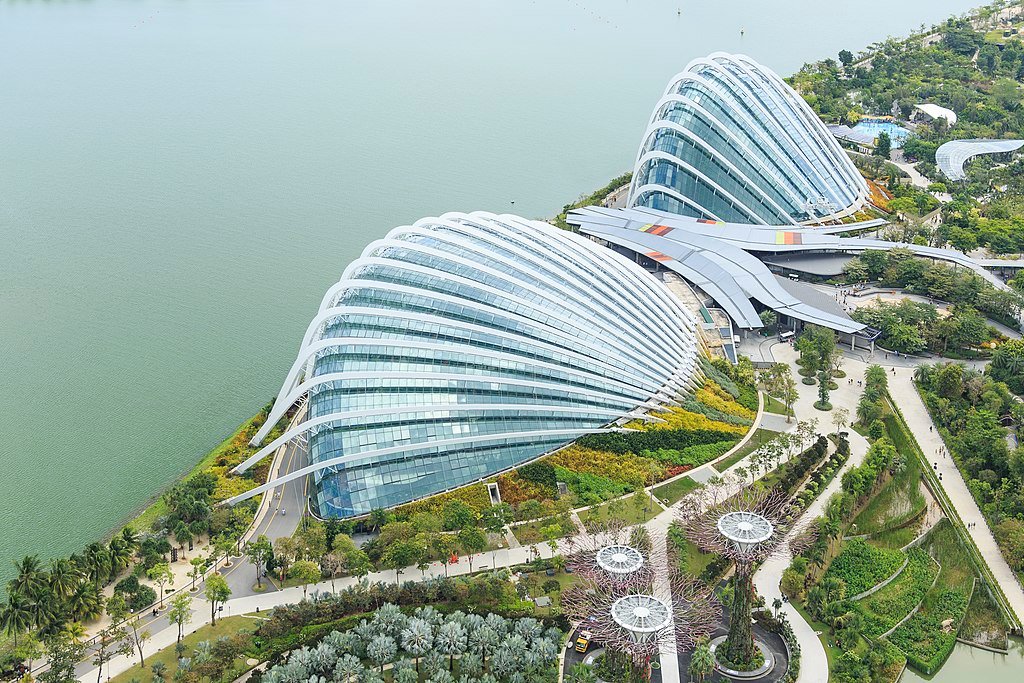

Singapore’s remarkable transformation into a global leader in sustainable urban planning demonstrates the power of strategic vision and collective effort. By integrating innovative technology, community initiatives, and robust policy frameworks, Singapore has created a thriving urban environment that balances progress with environmental stewardship. As cities worldwide face the challenges of rapid urbanization and climate change, Singapore stands as a beacon of sustainable possibilities, paving the way for a greener, smarter future.