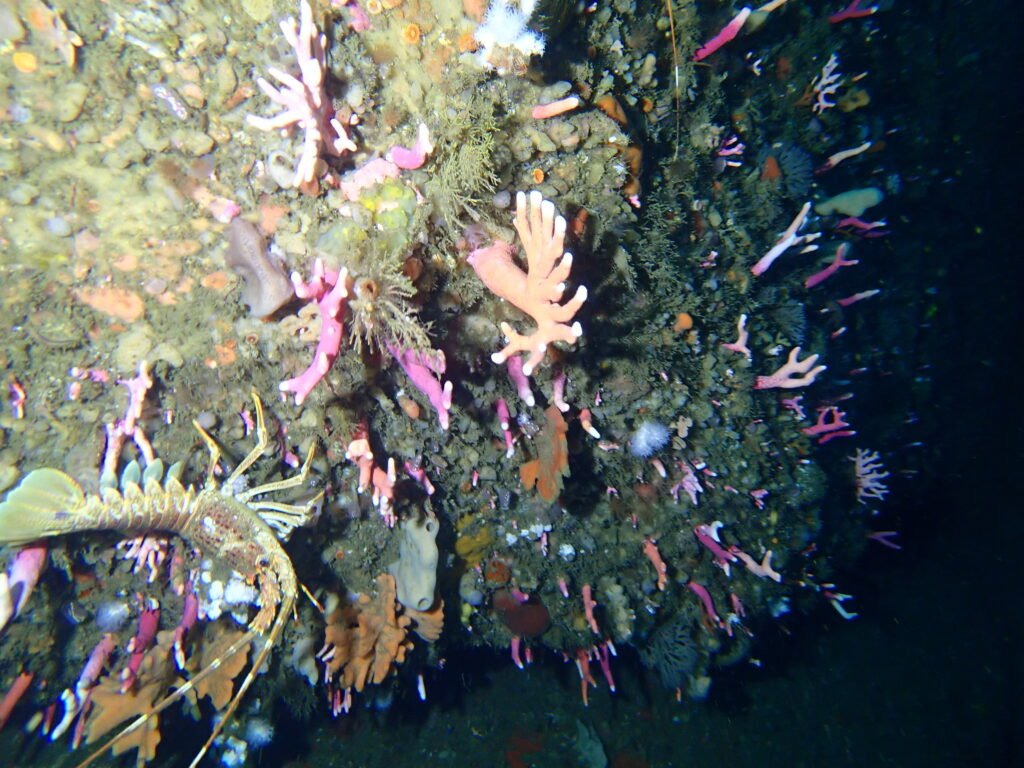
The ocean, vast and mysterious, holds secrets that most of us can only dream about. Beneath the tranquil surface lies a world teeming with life, some of which thrive in conditions that would be unthinkable for most organisms. From the icy waters of the Arctic to the crushing depths of the Mariana Trench, marine creatures have adapted to survive in the harshest environments on Earth. These adaptations are not just survival tactics; they are fascinating demonstrations of evolution in action. Let’s dive into the astonishing ways marine life has evolved to conquer the most inhospitable corners of our planet.
The Crushing Depths of the Deep Sea
Imagine living under the weight of thousands of meters of water. This is the reality for creatures inhabiting the deep sea, where pressures are so immense that they would crush a human like a tin can. Yet, animals like the anglerfish and the giant squid thrive here. These organisms have developed flexible, gelatinous bodies that can withstand pressure. Their bodies lack air-filled spaces that would collapse under such conditions. Instead, they rely on special proteins and cellular structures that maintain their shape and function. This adaptation allows them to navigate the pitch-black waters, where sunlight never penetrates.
Surviving in the Cold Embrace of Polar Waters
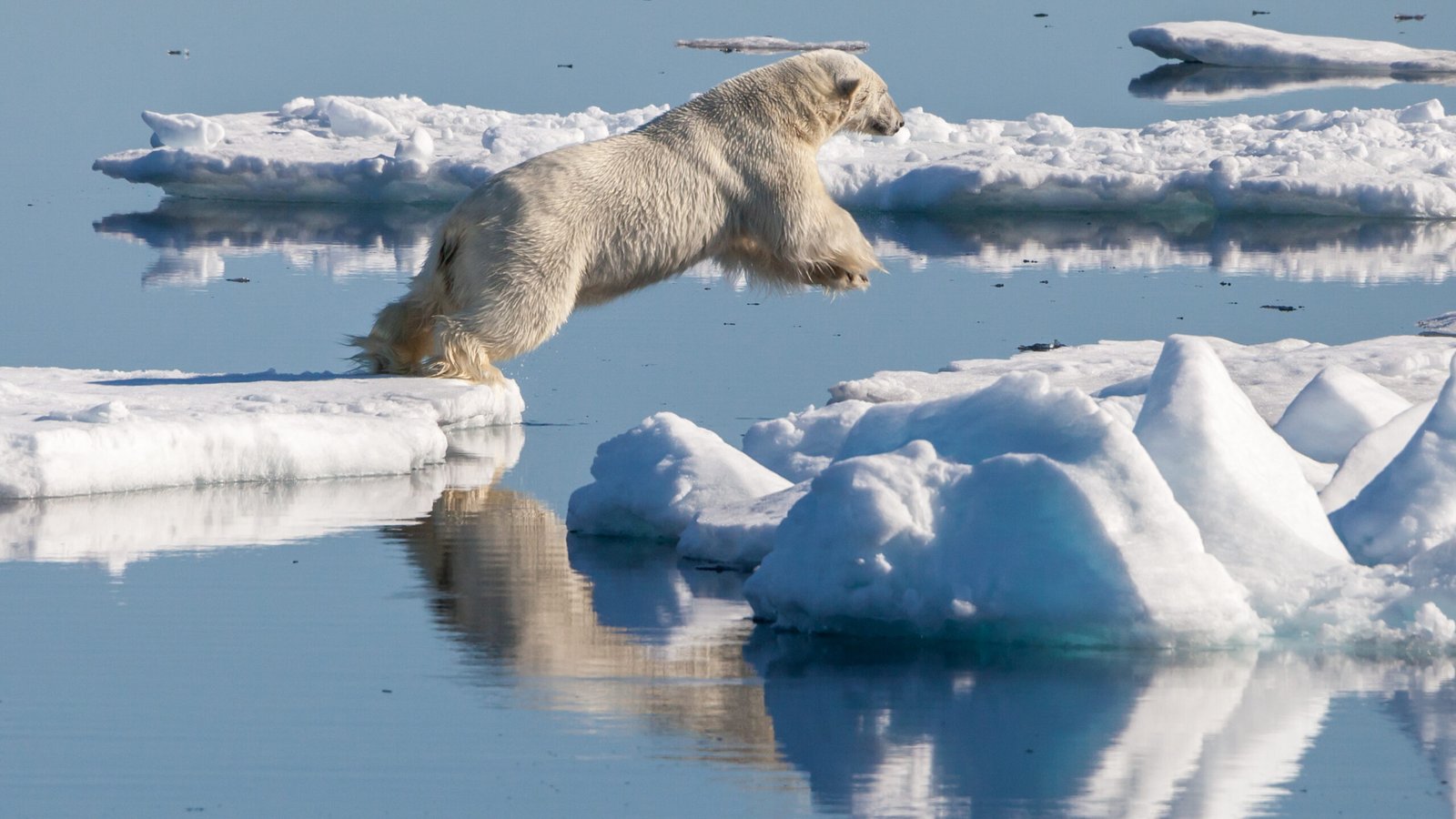

The polar regions are some of the coldest places on Earth, with temperatures that can plunge well below freezing. Yet, marine life flourishes here, employing unique adaptations to combat the cold. Take, for example, the Arctic cod, which produces antifreeze proteins that prevent their blood from freezing. Similarly, seals and penguins boast thick layers of blubber that insulate against the cold. Their bodies are streamlined for efficient swimming, allowing them to conserve energy in frigid waters. These adaptations ensure that life continues, even in the icy embrace of the poles.
Life in the Boiling Waters of Hydrothermal Vents
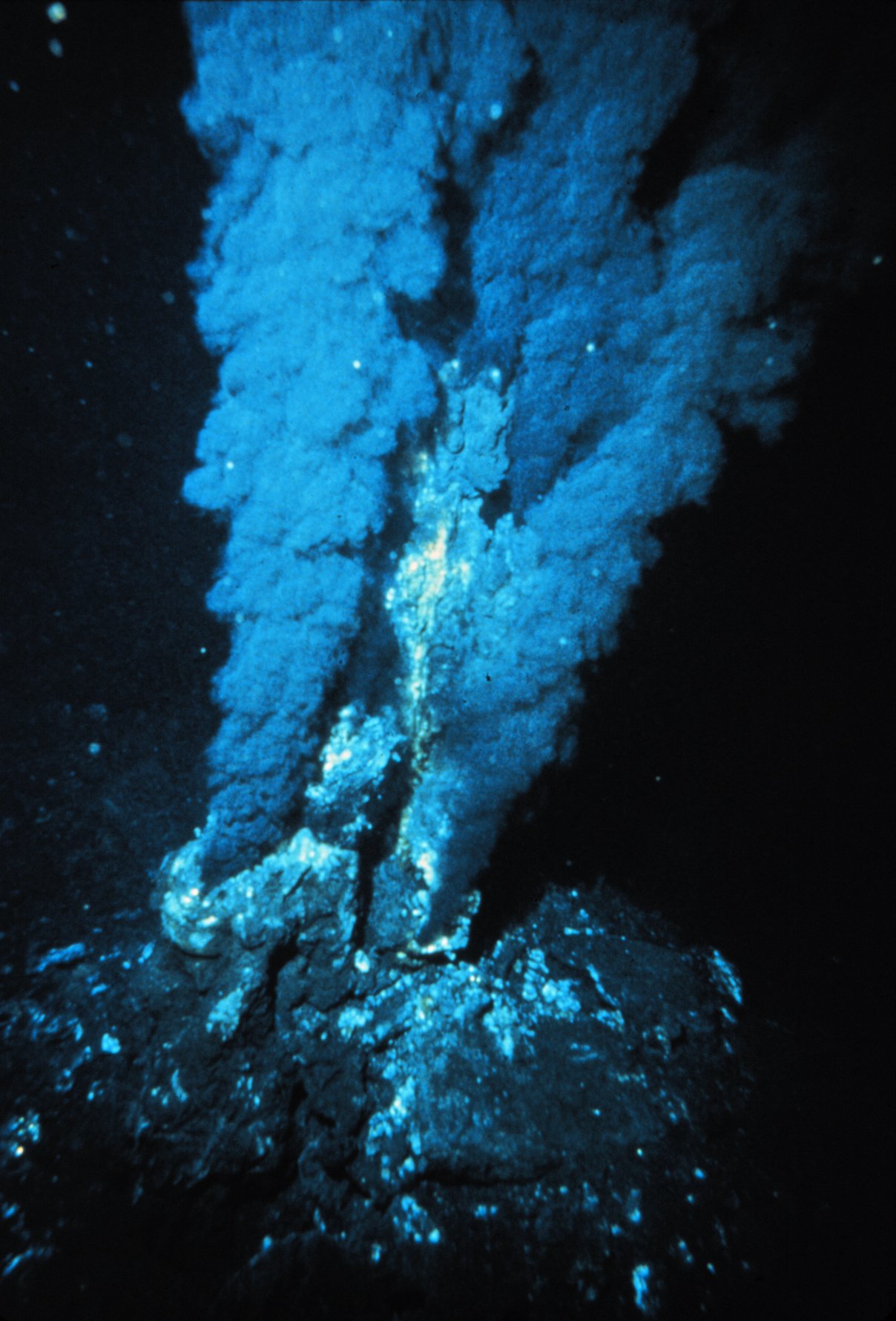
Hydrothermal vents are like underwater geysers, spewing superheated water rich with minerals. These vents can reach temperatures exceeding 700 degrees Fahrenheit. Yet, in these scalding waters, life thrives. Tube worms, crabs, and shrimp make their home here, sustained by chemosynthetic bacteria. Unlike most life forms that rely on sunlight for energy, these bacteria convert chemicals like hydrogen sulfide into food. This process, known as chemosynthesis, forms the base of the vent ecosystem, enabling life to flourish in what would seem an impossible environment.
Thriving in the High-Salinity of Salt Flats
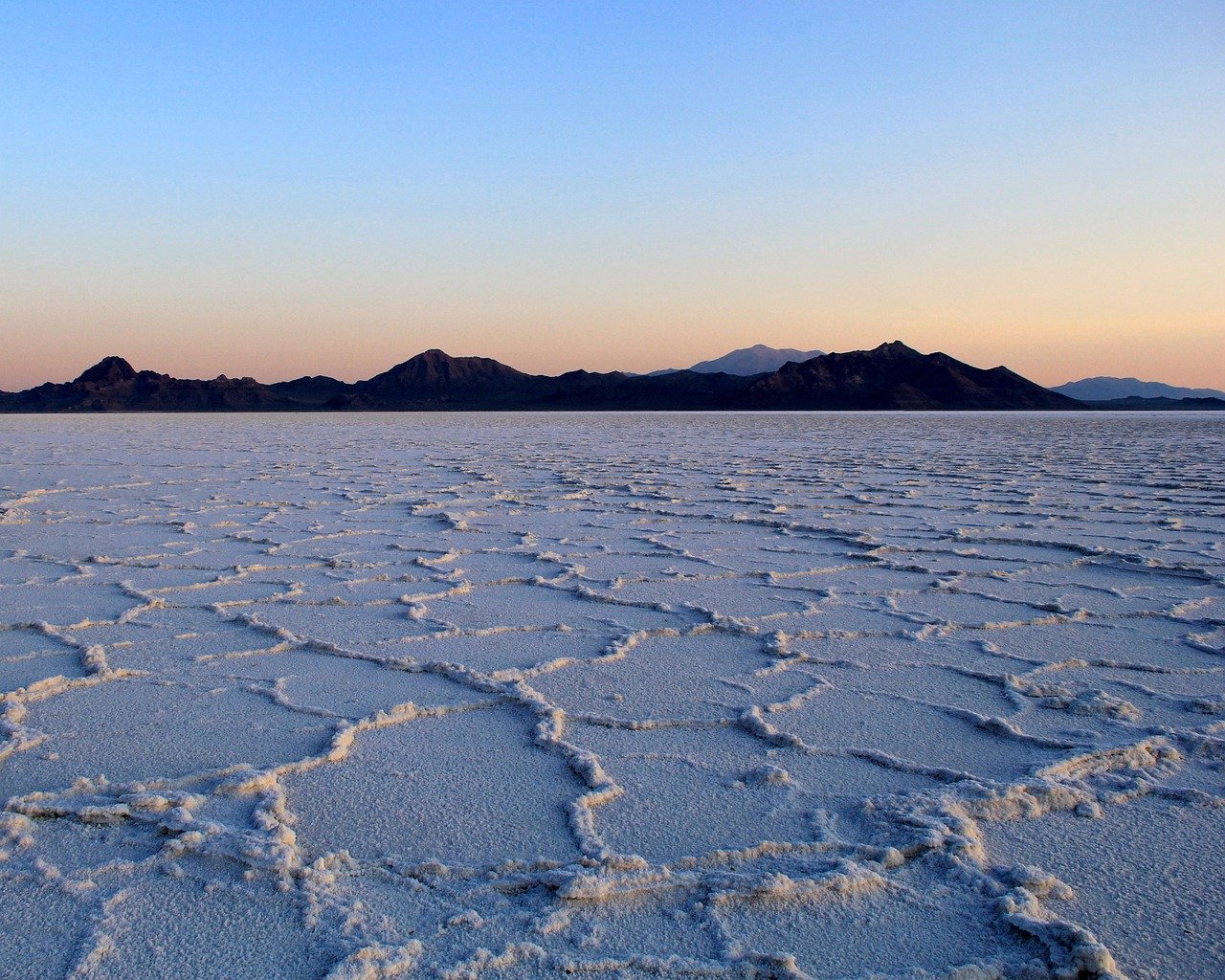

Salt flats are harsh environments where water evaporates, leaving behind layers of salt. Yet, some marine organisms have adapted to these saline conditions. Halophiles, or salt-loving microorganisms, thrive here. These tiny creatures have specialized cellular machinery that pumps excess salt out of their cells, maintaining a balance that allows them to live and reproduce. This remarkable adaptation enables them to survive where few other organisms can, showcasing the incredible resilience of life.
Adapting to the Darkness of the Abyss

The abyssal zone, located at depths of 4,000 to 6,000 meters, is shrouded in perpetual darkness. In this lightless world, marine creatures have evolved extraordinary adaptations. Many species, such as the lanternfish, have developed bioluminescence, the ability to produce light. This natural glow serves multiple purposes, from attracting prey to deterring predators. Others, like the deep-sea octopus, rely on heightened senses to navigate and hunt. These adaptations underscore the ingenuity of life in overcoming the challenges of eternal night.
Survival in the Acidic Waters of Sulfur Lakes
Sulfur lakes, with their acidic waters, create a hostile environment for most life. Yet, some fish species have adapted to these conditions. They possess specialized gills and kidneys that regulate the acidity within their bodies. This allows them to maintain homeostasis and survive in an environment that would be lethal to other organisms. This adaptation highlights the versatility of life and its ability to persist in even the most challenging circumstances.
The Resilience of Coral Reefs in Warming Oceans
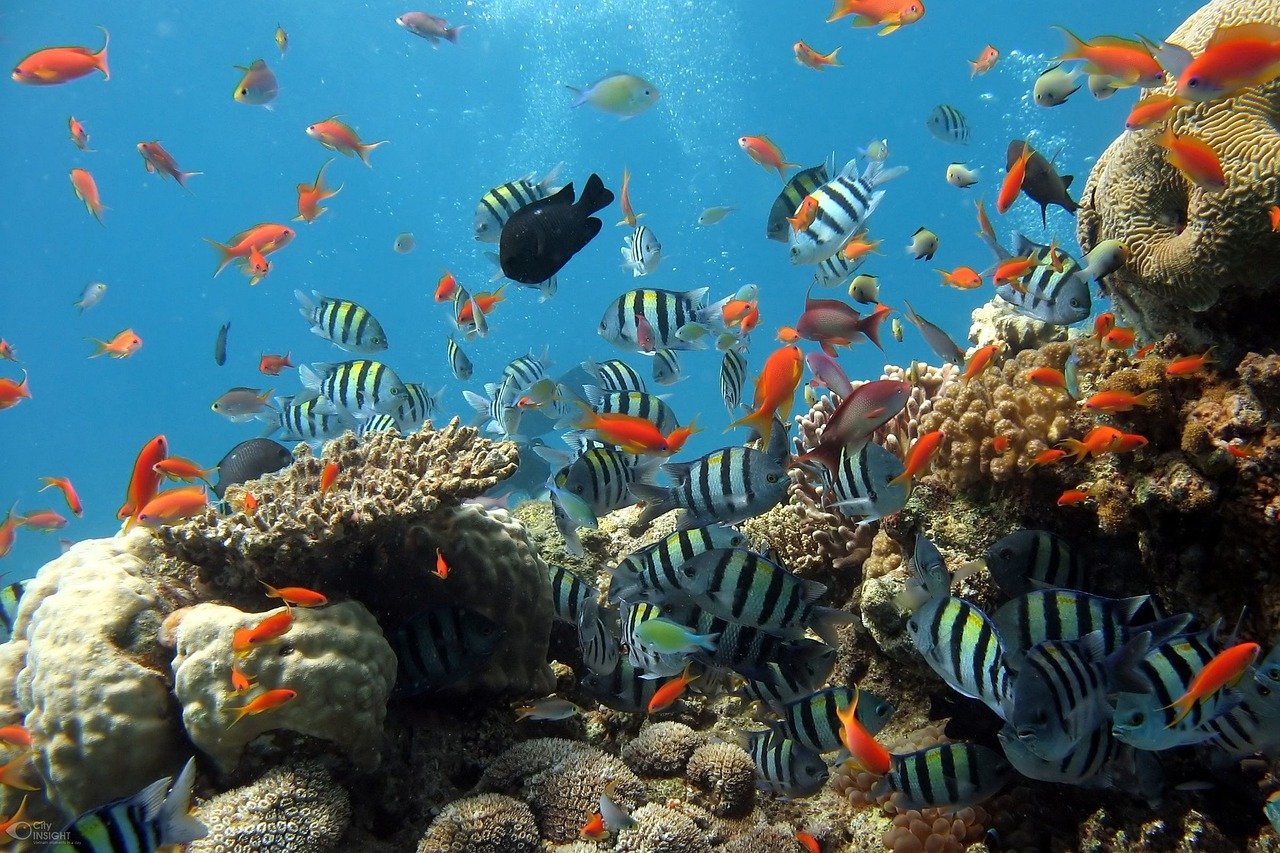

Coral reefs, often referred to as the “rainforests of the sea,” are facing unprecedented threats from warming oceans. Yet, some corals have shown remarkable resilience, adapting to higher temperatures. Through a process known as bleaching, corals expel their symbiotic algae when stressed. While this often leads to coral death, some species can reestablish these relationships with more heat-tolerant algae. This adaptation provides a glimmer of hope for the future of coral reefs in an era of climate change.
Endurance in the Oxygen-Poor Waters of Dead Zones

Dead zones are areas in the ocean with depleted oxygen levels, often a result of pollution and algal blooms. Despite these inhospitable conditions, some fish and invertebrates have adapted to survive here. They possess specialized hemoglobin that allows them to extract more oxygen from the water. Additionally, they exhibit behaviors such as reduced activity to conserve energy. These adaptations enable them to endure in environments where oxygen is scarce.
Living in the Turbulent Waters of Intertidal Zones

The intertidal zone, where the ocean meets the land, is a dynamic environment subject to constant changes in tides, temperature, and salinity. Organisms like barnacles and mussels have evolved to withstand these fluctuations. They have strong shells that protect them from desiccation during low tide and powerful attachments that anchor them against crashing waves. These adaptations allow them to thrive in a world of relentless change.
Concluding Thoughts
The adaptability of marine life is a testament to the resilience of life on Earth. From the crushing depths of the ocean to the boiling waters of hydrothermal vents, marine creatures have evolved remarkable strategies to survive. These adaptations not only highlight the wonders of evolution but also remind us of the intricate connections within our planet’s ecosystems. As we continue to explore and understand these incredible environments, we gain insights that can inspire conservation efforts and deepen our appreciation for the natural world.




