Wildfires have long been a part of California’s natural history, with the state’s climate and vegetation primed for combustion. However, in recent decades, the intensity and frequency of these fires have escalated, driven largely by climate change and human activities. This growing crisis is not only reshaping the landscape but also profoundly altering ecosystems and threatening wildlife. Let’s delve into how these blazes are leaving a lasting impact on California’s natural world.
Understanding the Scale of California’s Wildfires
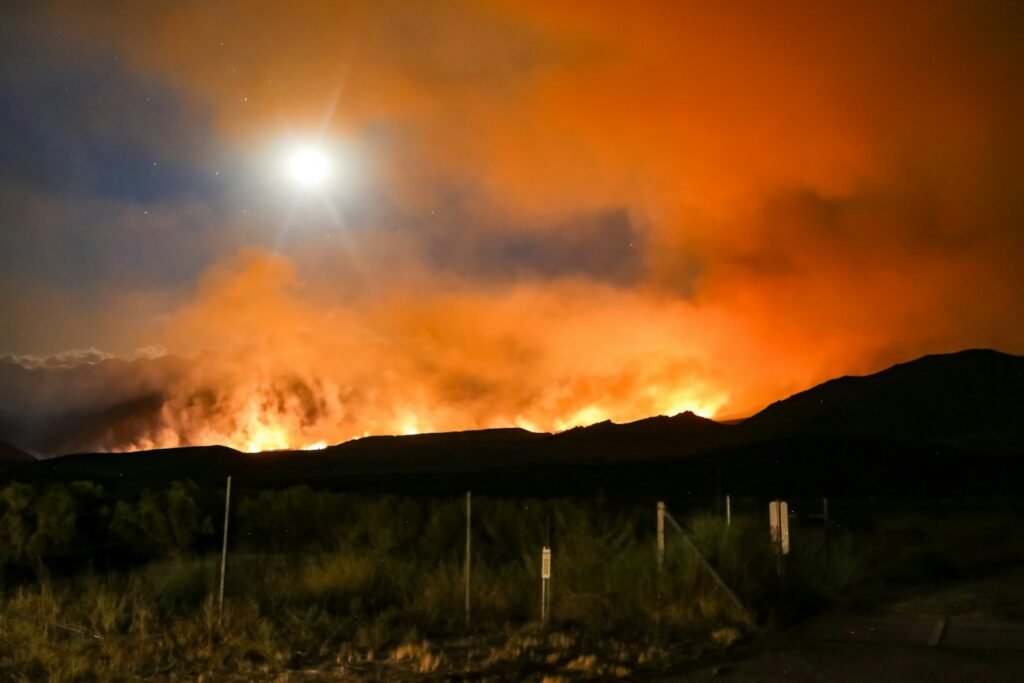

California experiences some of the largest and most destructive wildfires in the United States. The fire season, once confined to just a few months, now stretches much longer due to prolonged droughts and higher temperatures. In recent years, mega-fires have become more common, engulfing large swaths of forest and densely populated areas alike. The vast scale and frequency of these fires make them particularly devastating to the environment.
Impact on Forest Ecosystems
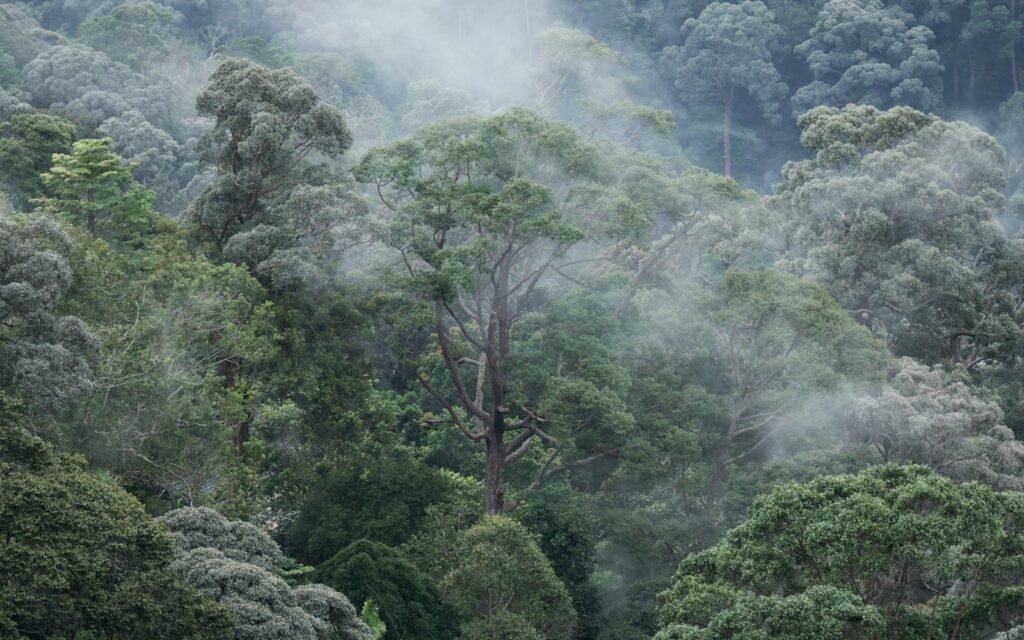

Forests play a crucial role in California’s ecosystems, providing habitat, carbon storage, and water regulation. However, intense fires can decimate large areas of forest, leading to loss of vegetation and soil degradation. This destruction disrupts natural processes and reduces biodiversity as plant and animal species struggle to recover or survive in such altered conditions.
Threats to Wildlife

California’s diverse wildlife is significantly affected by wildfires. Species such as deer, mountain lions, and smaller creatures like rodents and insects face immense pressure. Many animals can perish in the fires, while others lose their habitats and essential resources like food and water. Even species that survive can face long-term threats from changes to their ecosystems, such as altered food webs and increased competition for survival.
Alteration of Water Systems
Wildfires can profoundly impact water systems. They increase the risk of soil erosion, which can lead to sedimentation in rivers and streams, adversely affecting water quality and aquatic life. Additionally, the loss of vegetation reduces the landscape’s ability to retain water, exacerbating drought conditions and impacting animals that rely on these water sources.
Changes in Plant Life and Biodiversity

Plants and trees are at the forefront of the damage caused by wildfires. Some species, however, have evolved to endure and even thrive after fires, such as certain types of pine trees whose seeds are released by the heat. Yet, the prolonged periods between recovery and subsequent fires can hinder their regrowth, leading to potential shifts in the types of species that dominate certain areas, reducing overall biodiversity.
Effects on Soil Health

The intense heat from wildfires can strip the soil of essential nutrients and organic matter, critical for plant regrowth. It can also create a water-repellent layer in the soil, preventing water absorption and increasing runoff, which contributes to erosion. This degraded soil can take years to recover, adversely affecting ecosystem restoration.
Consequences for Human Communities and Wildlife

Human activities, such as encroaching urban developments and agricultural expansion, further complicate the recovery of ecosystems. Wildlife corridors are interrupted, leading to increased human-animal conflicts as animals wander urban areas in search of food or refuge. This not only endangers wildlife but also poses risks to human communities.
Adaptations and Future Survival

Despite the formidable challenges, some species exhibit remarkable resilience. Certain animals can adapt by altering their behavior or migration patterns, and some plants regrow with vigor thanks to adaptive traits. Understanding and supporting these natural adaptations through conservation efforts can bolster the resilience of ecosystems facing future wildfires.
Role of Climate Change

Climate change is a key driver in the increased intensity and frequency of wildfires. Warmer temperatures cause drier conditions, facilitating more frequent and intense fires. Addressing climate change through policy, innovation, and sustainable practices is crucial in mitigating wildfire risks and their lasting impact on California’s ecosystems and wildlife.
Conservation Efforts and New Strategies

Efforts are underway to preserve and restore California’s ecosystems in the aftermath of wildfires. These include reforestation projects, controlled burns to reduce fuel loads, and habitat restoration programs. Additionally, wildlife rehabilitation and relocation initiatives aim to protect vulnerable species from the immediate and long-term effects of these fires.
Conclusion: A Path Forward

California’s wildfires herald a transformative era for its ecosystems and wildlife. Understanding how fires alter these landscapes allows us to take informed action to protect and preserve them. By addressing the root causes and fostering resilience through conservation and sustainable practices, we can hope to safeguard the diverse natural heritage that defines California for generations to come.




