The natural world holds secrets that have revolutionized human understanding of medicine, technology, and life itself. From the smallest insect to the largest marine mammal, countless species have become unlikely partners in scientific discovery. These remarkable creatures don’t just coexist with humans—they actively contribute to breakthroughs that save lives, advance technology, and unlock mysteries of the universe. While we often think of laboratories filled with test tubes and microscopes, some of the most groundbreaking research happens when scientists step outside and observe the incredible adaptations nature has perfected over millions of years.
The Buzzing Architects of Medical Innovation
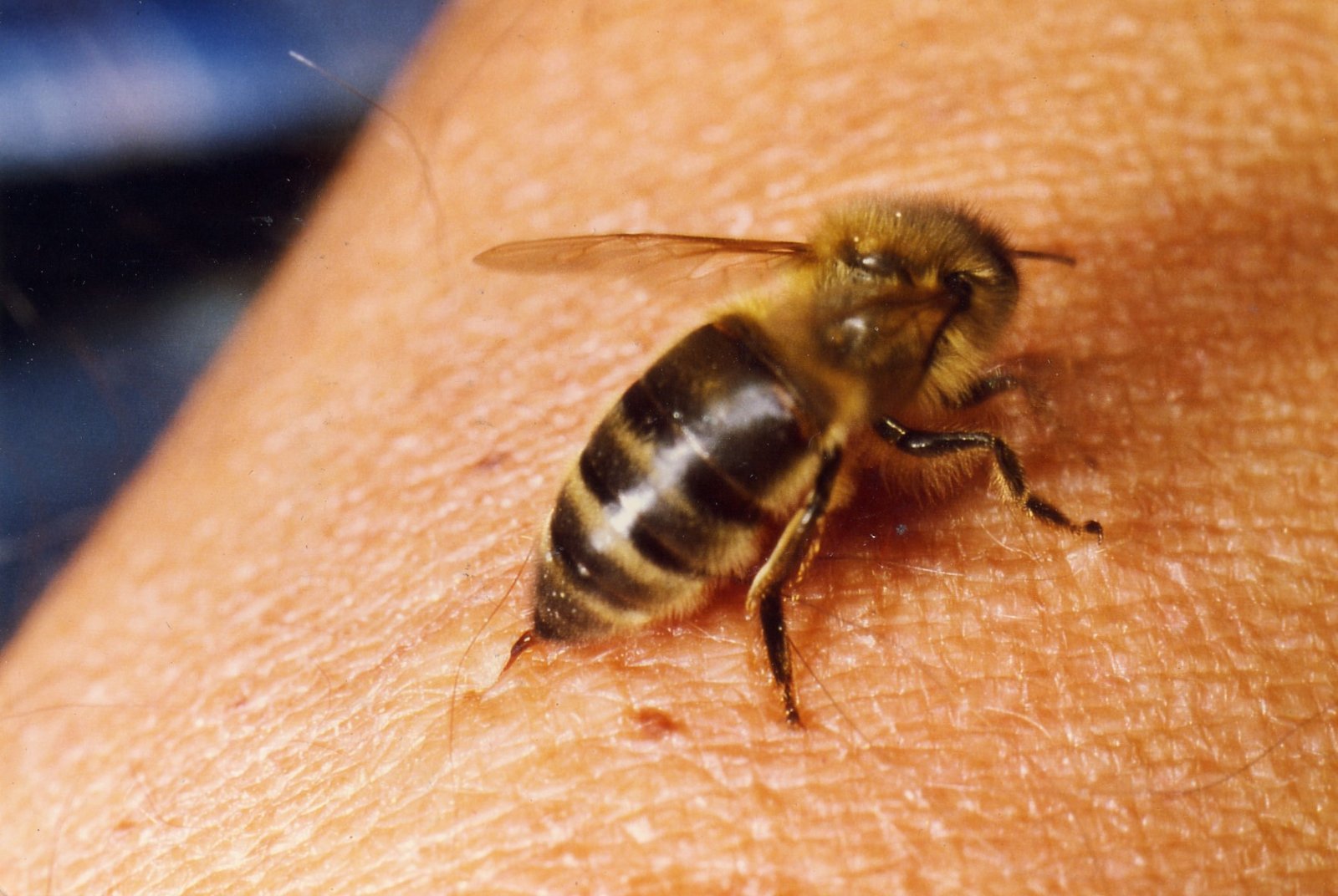

Honeybees have transformed from simple pollinators into sophisticated research partners, revolutionizing our understanding of neural networks and cognitive processing. These tiny insects possess brains containing only 960,000 neurons compared to humans’ 86 billion, yet they perform complex tasks that baffle scientists. Research teams worldwide study how bees navigate vast distances, communicate through intricate dances, and make collective decisions that benefit entire colonies.
The pharmaceutical industry has discovered that bee venom contains compounds with remarkable therapeutic properties. Melittin, the primary component of bee venom, shows promise in treating arthritis, multiple sclerosis, and even certain cancers. Scientists have developed synthetic versions of these compounds, creating new treatment pathways that were previously unimaginable.
Computational Marvels in the Hive

Computer scientists have borrowed heavily from bee behavior to create algorithms that solve complex optimization problems. The “bee colony optimization” algorithm mimics how bees scout for food sources and communicate their findings to the hive. Major tech companies now use these bio-inspired algorithms to improve everything from internet routing to supply chain management.
The hexagonal structure of honeycomb has inspired architectural innovations and materials science breakthroughs. Engineers study how bees create these perfect geometric patterns using minimal wax, leading to lightweight yet incredibly strong building materials. Aerospace companies have incorporated honeycomb structures into aircraft design, reducing weight while maintaining structural integrity.
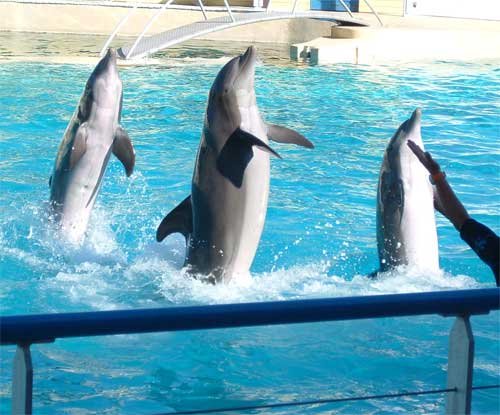
Dolphins: The Ocean’s Genius Researchers
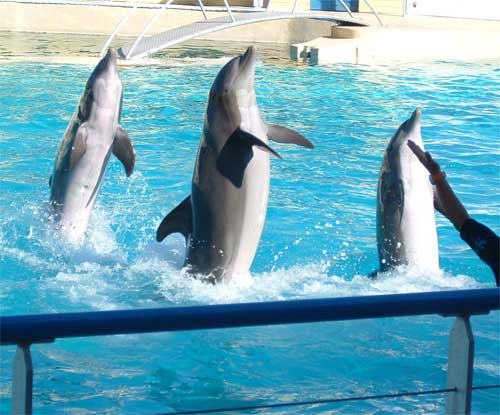

Dolphins possess cognitive abilities that rival those of great apes, making them invaluable research subjects for understanding consciousness, self-awareness, and social intelligence. These marine mammals demonstrate complex problem-solving skills, tool use, and even cultural transmission of behaviors across generations. Marine biologists have documented dolphins teaching their offspring unique hunting techniques that vary by geographic location.
The echolocation abilities of dolphins have inspired countless technological innovations. Military sonar systems, medical ultrasound equipment, and underwater navigation tools all trace their origins to dolphin research. Scientists continue studying how dolphins process acoustic information with such precision that they can detect objects smaller than a ping-pong ball from hundreds of meters away.
Medical Miracles from Marine Mammals

Dolphin-assisted therapy has emerged as a controversial yet potentially beneficial treatment for various conditions including autism, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder. While scientific evidence remains mixed, some patients report significant improvements in mood, communication, and social interaction after dolphin encounters. Researchers are working to understand the mechanisms behind these reported benefits.
The cardiovascular system of dolphins has provided insights into human heart disease and diving physiology. These animals can dive to extreme depths and hold their breath for extended periods without suffering the decompression sickness that affects human divers. Medical researchers study dolphin adaptations to develop better treatments for heart conditions and improve surgical techniques.
Fruit Flies: Tiny Giants of Genetic Research
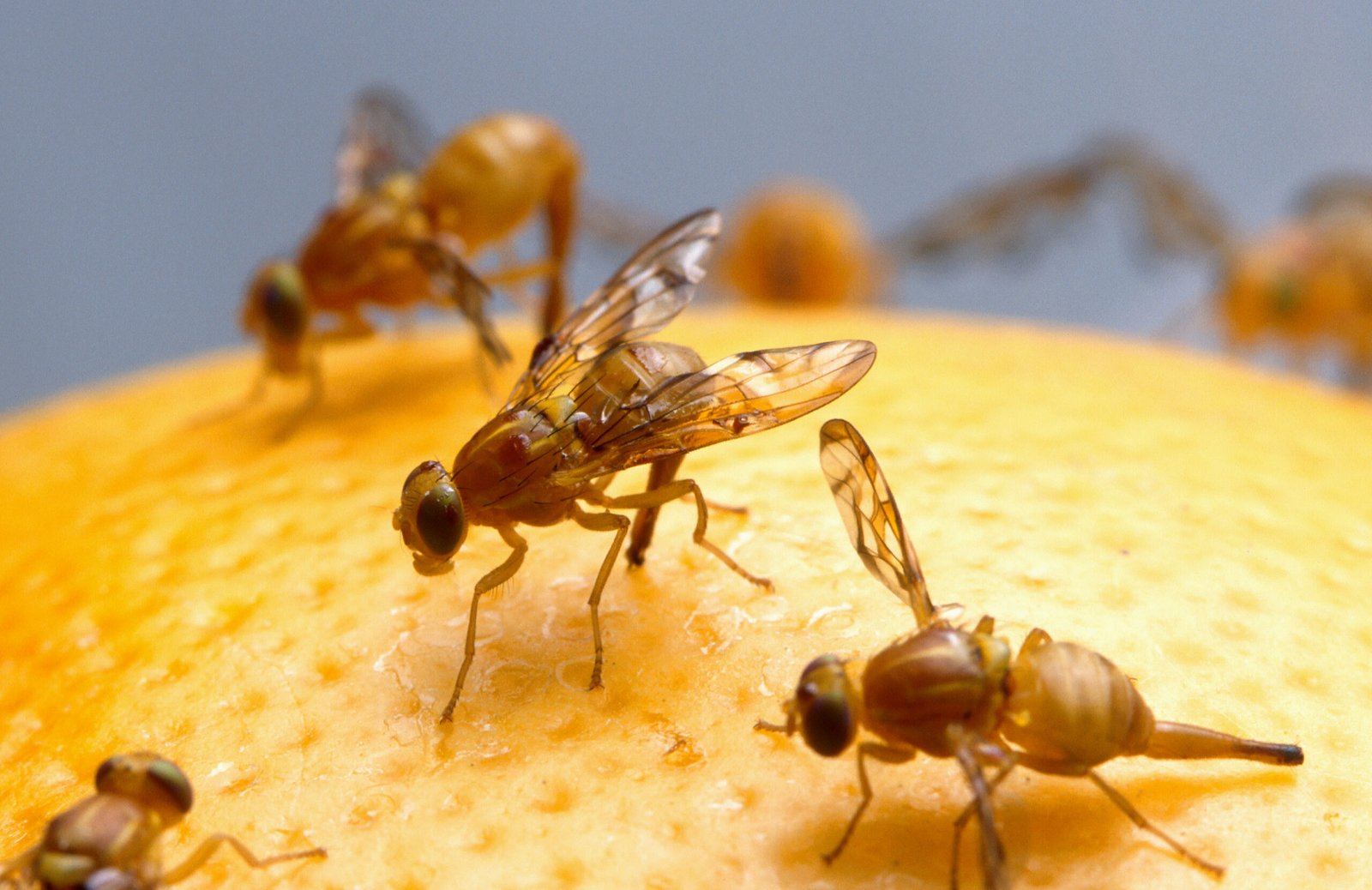

Drosophila melanogaster, the common fruit fly, has contributed more to genetic research than perhaps any other organism. These seemingly insignificant insects share approximately 75% of known human disease genes, making them ideal models for studying everything from cancer to neurological disorders. Scientists have used fruit flies to identify genes responsible for memory formation, aging, and circadian rhythms.
The rapid reproduction cycle of fruit flies allows researchers to observe multiple generations within weeks, accelerating genetic studies that would take years or decades with other organisms. Major pharmaceutical companies rely on fruit fly models to test new drugs before advancing to human trials. The 2017 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine was awarded to researchers who used fruit flies to discover the molecular mechanisms controlling circadian rhythms.
Genetic Engineering Breakthroughs

Fruit flies have become living laboratories for testing gene therapy techniques and understanding genetic mutations. Scientists can easily manipulate fruit fly genes, creating models of human diseases and testing potential treatments. This research has led to breakthroughs in understanding Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease, and various forms of cancer.
The CRISPR gene editing technology was partially developed using fruit fly models. Researchers could quickly test different editing techniques and observe the results across multiple generations. This foundational work paved the way for human gene therapy trials that are now showing promise for treating previously incurable genetic disorders.
Laboratory Mice: The Mammalian Research Standard
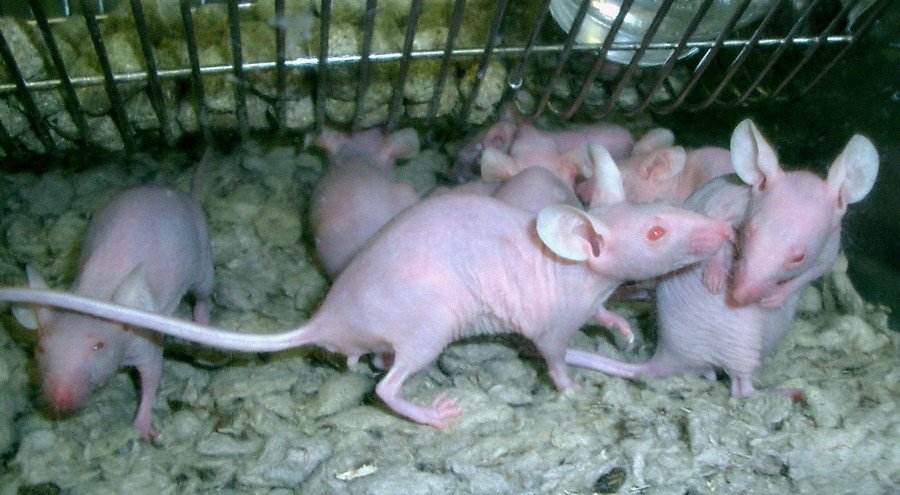

Laboratory mice have served as the gold standard for biomedical research for over a century, contributing to virtually every medical breakthrough of the modern era. These rodents share 95% of human genes and develop many of the same diseases that affect humans, including cancer, diabetes, and heart disease. The controlled breeding of laboratory mice has created specialized strains that model specific human conditions with remarkable accuracy.
Mouse models have been instrumental in developing treatments for major diseases affecting millions of people worldwide. From insulin therapy for diabetes to chemotherapy protocols for cancer, most medical interventions undergo extensive testing in mouse models before human trials. The development of COVID-19 vaccines relied heavily on mouse studies to ensure safety and efficacy before human testing began.
Neurological Research and Brain Studies
The mouse brain, while much smaller than the human brain, contains similar structures and neural pathways that make it invaluable for neurological research. Scientists study mouse behavior, memory formation, and responses to various stimuli to understand how the human brain processes information. These studies have led to new treatments for depression, anxiety, and neurodegenerative diseases.
Genetically modified mice have revolutionized our understanding of human psychology and behavior. Researchers can create mice with specific genetic modifications that mimic human conditions, allowing them to test potential treatments in controlled environments. This research has contributed to the development of antidepressants, anti-anxiety medications, and treatments for attention deficit disorders.
Zebrafish: Transparent Windows into Development
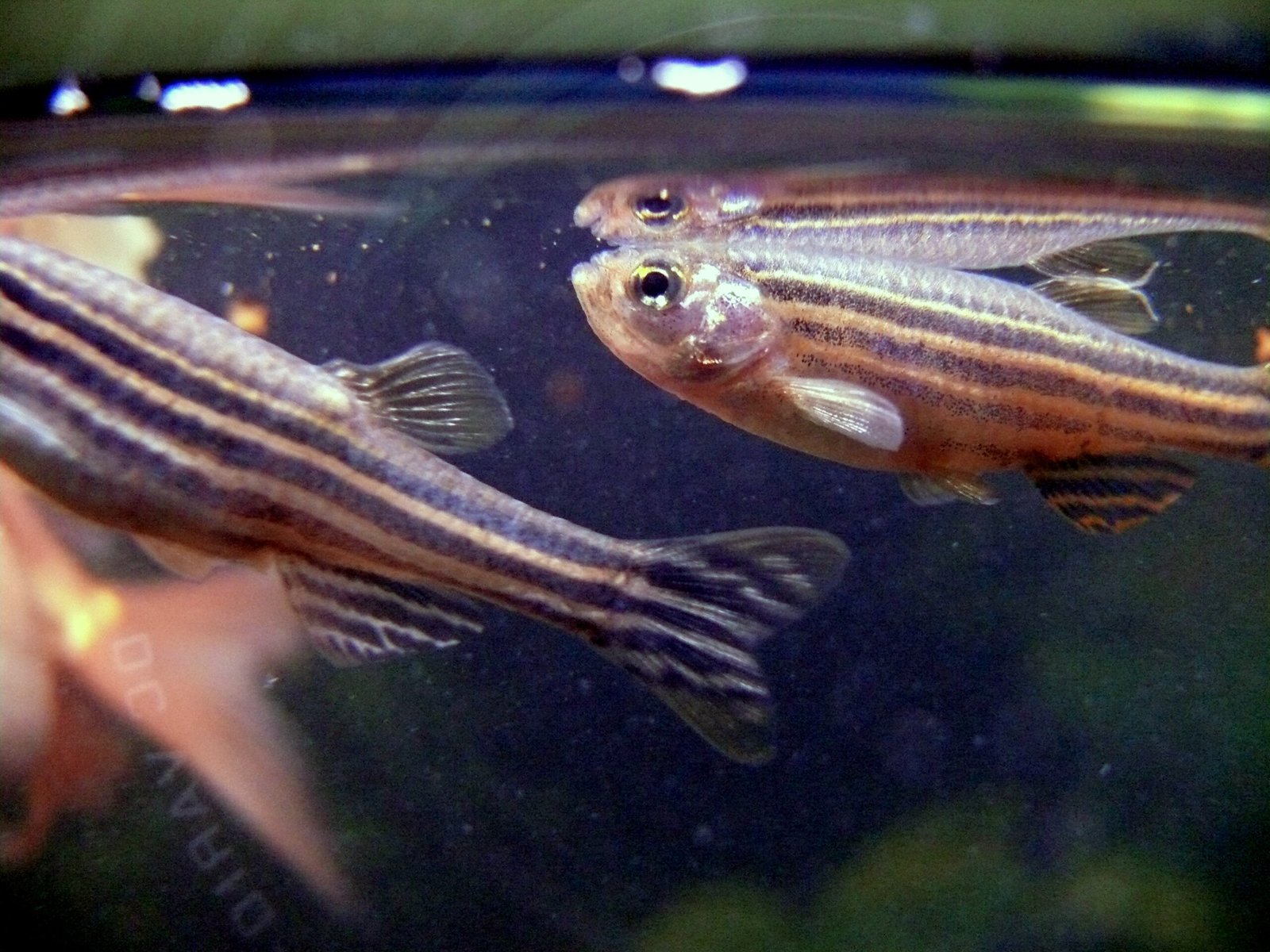

Zebrafish have become superstar research subjects due to their transparent embryos, which allow scientists to observe development in real-time. These small freshwater fish share 70% of human genes and develop organs remarkably similar to those found in humans. Researchers can watch as zebrafish hearts begin beating, blood vessels form, and nervous systems develop, providing unprecedented insights into human development.
The regenerative abilities of zebrafish have inspired groundbreaking research into human tissue repair and organ regeneration. Unlike humans, zebrafish can regrow lost fins, repair damaged hearts, and even regenerate parts of their brains and spinal cords. Scientists study the molecular mechanisms behind these abilities, hoping to unlock similar regenerative potential in humans.
Drug Discovery and Toxicology Testing
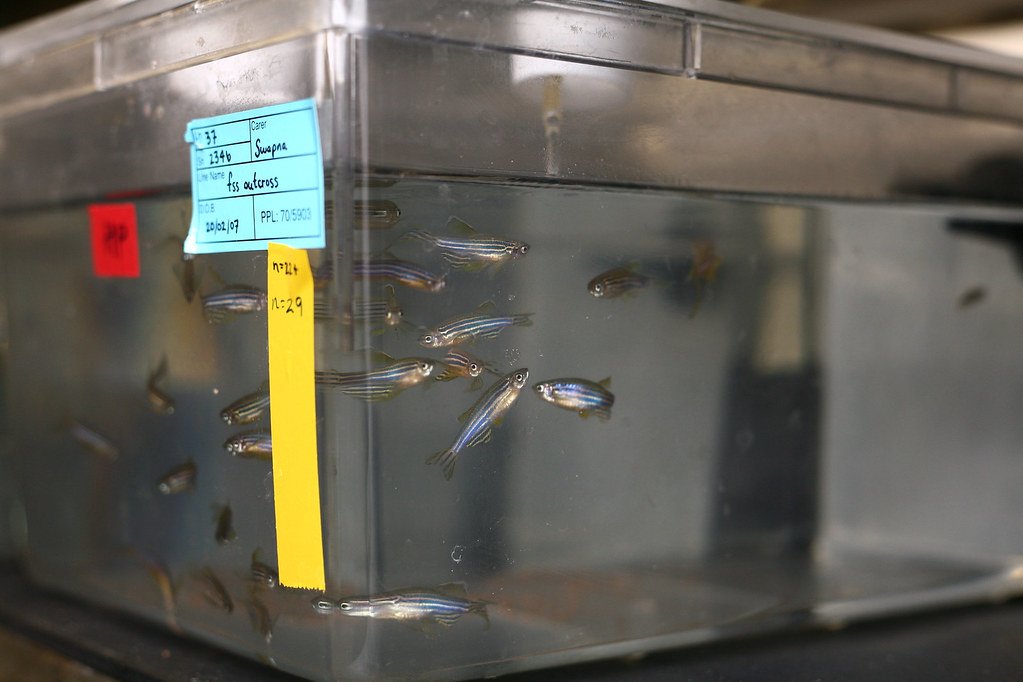

Pharmaceutical companies increasingly rely on zebrafish models for early-stage drug testing and toxicology studies. The transparent nature of zebrafish embryos allows researchers to observe how drugs affect organ development and function in real-time. This approach has accelerated drug discovery timelines and reduced the need for more expensive mammalian testing in early research phases.
Zebrafish have contributed to the development of treatments for various human diseases, including cancer, cardiovascular disease, and neurological disorders. Their rapid development and large clutch sizes make them ideal for high-throughput screening of potential therapeutic compounds. Many drugs currently in clinical trials were first tested and refined using zebrafish models.
Chimpanzees: Our Closest Genetic Relatives
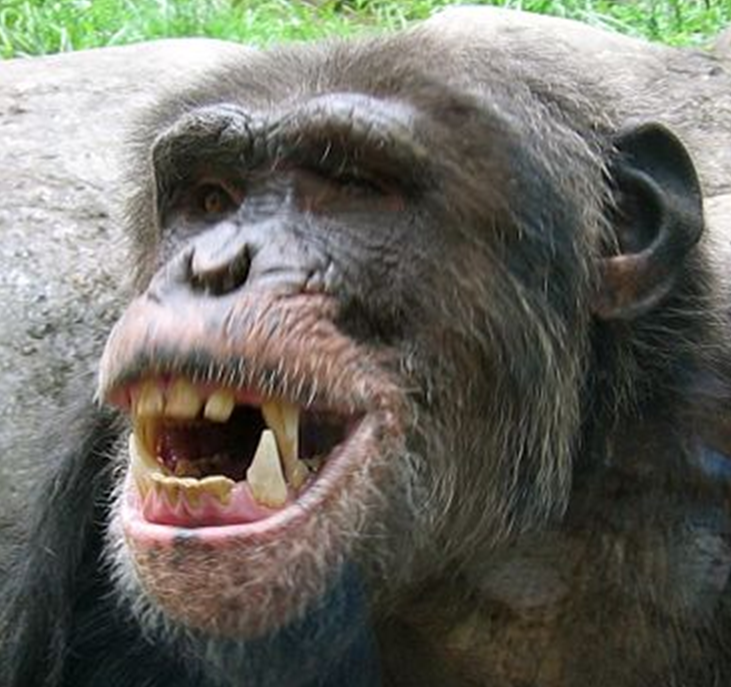

Chimpanzees share approximately 98.8% of human DNA, making them invaluable for understanding human evolution, behavior, and disease susceptibility. While ethical considerations have significantly limited chimpanzee research in recent years, historical studies with these primates have provided crucial insights into human psychology, social behavior, and cognitive development. Researchers have observed tool use, complex social hierarchies, and even rudimentary forms of culture among chimpanzee populations.
Medical research involving chimpanzees has contributed to the development of vaccines for hepatitis B and treatments for various infectious diseases. These studies helped scientists understand how human immune systems respond to pathogens and how to develop effective preventive measures. The development of modern organ transplantation techniques also benefited from early chimpanzee research.
Behavioral and Cognitive Studies

Chimpanzee studies have revolutionized our understanding of human consciousness, emotion, and social intelligence. Researchers have documented chimpanzees displaying empathy, grief, and even what appears to be moral behavior. These observations have challenged traditional views of human uniqueness and contributed to developments in psychology, anthropology, and philosophy.
The study of chimpanzee communication has influenced research into human language development and autism spectrum disorders. Scientists have observed how young chimpanzees learn to communicate through gestures and vocalizations, providing insights into the evolutionary origins of human language. This research has informed therapeutic approaches for children with communication disorders.
Octopuses: Masters of Neural Complexity
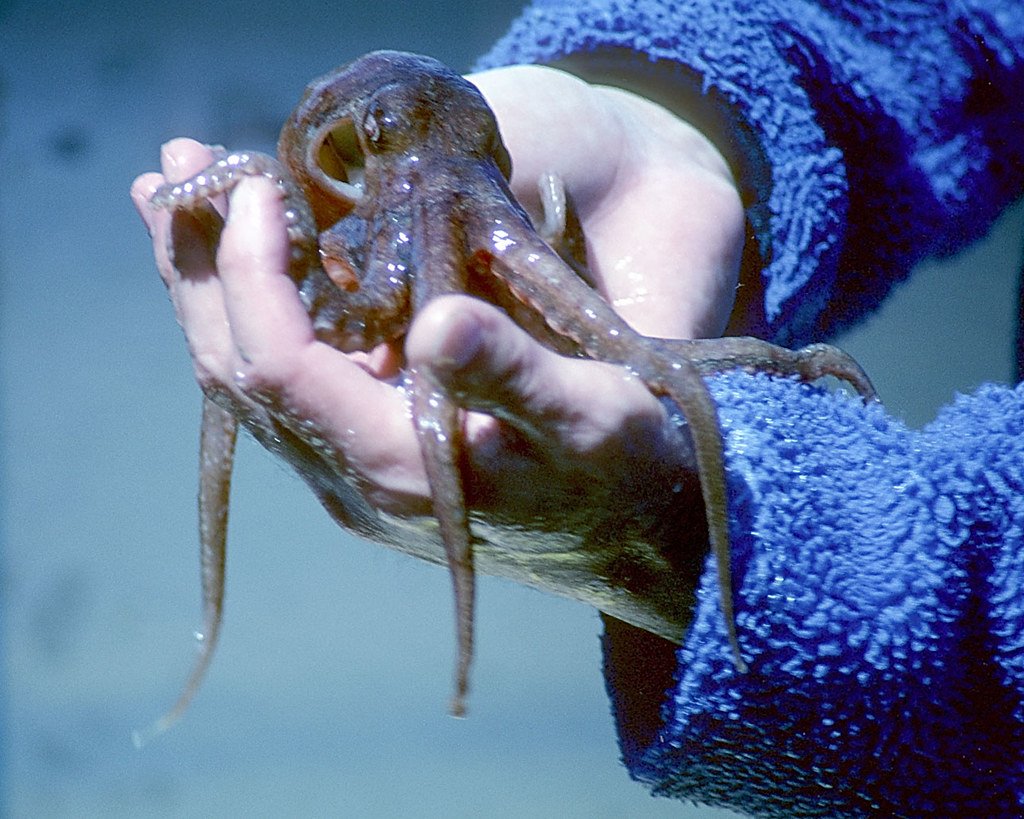

Octopuses possess one of the most sophisticated nervous systems in the invertebrate world, with approximately 500 million neurons distributed throughout their bodies. These remarkable creatures demonstrate problem-solving abilities, memory formation, and even personality traits that rival those of vertebrates. Researchers study octopus intelligence to understand how complex cognition can emerge from neural networks organized differently from mammalian brains.
The unique neural architecture of octopuses has inspired advances in artificial intelligence and robotics. Unlike vertebrates, octopuses have distributed processing power, with two-thirds of their neurons located in their arms rather than their central brain. This decentralized approach to neural processing has influenced the development of more efficient AI algorithms and autonomous robotic systems.
Camouflage and Materials Science

The incredible camouflage abilities of octopuses have revolutionized materials science and military technology. These animals can change color, texture, and shape within seconds, creating nearly perfect camouflage that adapts to their surroundings. Scientists study the cellular mechanisms behind these transformations to develop adaptive camouflage systems for military applications and smart materials that respond to environmental changes.
Octopus-inspired technologies have led to the development of soft robotics and flexible electronics. The boneless bodies of octopuses can squeeze through impossibly small spaces and manipulate objects with incredible dexterity. Engineers study these capabilities to create robots that can navigate confined spaces and perform delicate tasks in environments where rigid robots would fail.
The Future of Cross-Species Research

As technology advances, the potential for learning from other species continues to expand exponentially. Emerging fields like biomimetics and synthetic biology are creating new opportunities to harness the wisdom of nature for human benefit. Scientists are now using advanced genetic sequencing, artificial intelligence, and real-time monitoring systems to study animal behavior and physiology in ways that were previously impossible.
The integration of different species’ capabilities into human technology represents the next frontier of scientific innovation. From developing new medical treatments based on animal immune systems to creating robots inspired by animal locomotion, the possibilities seem limitless. As we face global challenges like climate change, disease outbreaks, and technological limitations, the natural world continues to offer solutions that human ingenuity alone might never discover.
Ethical Considerations and Future Directions

The use of animals in research raises important ethical questions that the scientific community continues to address through improved protocols, alternative methods, and stricter oversight. Modern research increasingly emphasizes the principles of replacement, reduction, and refinement—replacing animal models where possible, reducing the number of animals used, and refining techniques to minimize stress and discomfort. These ethical frameworks ensure that the benefits of animal research are balanced against the welfare of the creatures that contribute to scientific progress.
Looking forward, technological advances are creating new opportunities to study animals without invasive procedures. Remote monitoring systems, advanced imaging techniques, and genetic analysis of environmental samples allow researchers to gather valuable data while minimizing direct impact on animal subjects. These innovations promise to expand our understanding of animal behavior and physiology while addressing ethical concerns about research practices.
Conclusion

The remarkable partnership between humans and other species in scientific research has yielded discoveries that have transformed our world and continue to shape our future. From the humble honeybee’s contribution to computer algorithms to the dolphin’s inspiration for medical technology, these unlikely research collaborators have proven that innovation often comes from the most unexpected sources. As we move forward, the lessons learned from studying these incredible creatures will undoubtedly continue to drive scientific breakthroughs that benefit both humanity and the natural world.
The seven species highlighted here represent just a fraction of the countless animals that have contributed to human knowledge and advancement. Each creature offers unique insights into the complexities of life, challenging our assumptions and expanding our understanding of what’s possible. As we face an uncertain future filled with global challenges, perhaps our greatest hope lies not in human technology alone, but in the wisdom we can gain from the remarkable creatures that share our planet.
What other species might hold the keys to solving humanity’s greatest challenges?




