Picture this: You’re enjoying a peaceful picnic in a Georgia park when suddenly, your ankle erupts in burning pain. Within seconds, dozens of tiny warriors have swarmed your foot, each delivering a venomous sting that feels like a red-hot needle. Welcome to the world of fire ants, one of the South’s most persistent and painful invaders. These miniature terrorists have been conquering Southern landscapes for nearly a century, turning backyards into battlegrounds and forcing entire communities to rethink how they interact with their environment.
The Invasion That Changed Everything

Fire ants didn’t just sneak into the American South – they arrived like a biological tsunami that forever altered the region’s ecosystem. These aggressive insects first made landfall in Mobile, Alabama, sometime in the 1930s, likely hitching a ride on cargo ships from their native South America. What started as a few stowaways has exploded into a full-scale ecological disaster spanning over 320 million acres across 13 states.
The red imported fire ant, scientifically known as Solenopsis invicta, proved to be the perfect invasive species. They possessed an almost supernatural ability to adapt, reproduce rapidly, and dominate their new territory. Within just a few decades, these tiny conquerors had established themselves as the undisputed rulers of Southern soil, building their underground empires wherever they pleased.
Masters of Destruction: Understanding Fire Ant Biology
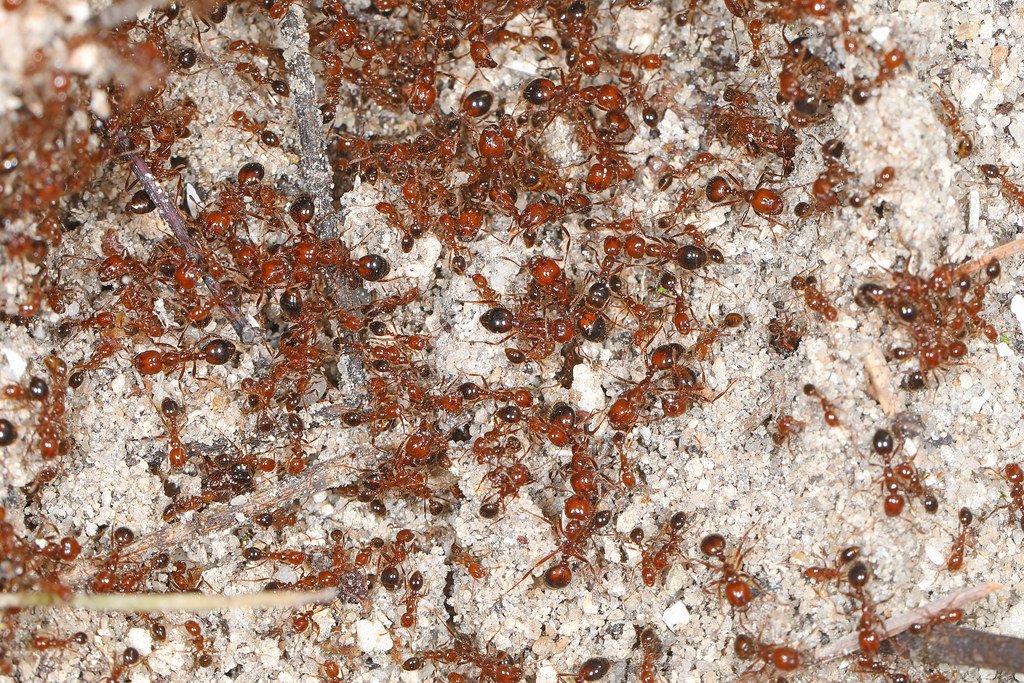

Fire ants operate like a highly efficient military organization, with each colony functioning as a superorganism capable of incredible feats of coordination and destruction. A single mature colony can house up to 500,000 individuals, all working in perfect harmony to expand their territory and eliminate threats. The queen, living up to seven years, can lay up to 1,000 eggs per day, ensuring the colony’s explosive growth.
These insects possess a unique two-part venom system that makes their stings particularly excruciating. The alkaloid venom creates that signature burning sensation, while proteins in the mixture trigger allergic reactions in many victims. What makes fire ants truly dangerous isn’t just their individual sting, but their collective response – they attack in coordinated swarms, with hundreds of workers simultaneously injecting venom into their target.
Their physical design is equally impressive and terrifying. Fire ants can lift 20 times their body weight and survive underwater for up to 24 hours by forming living rafts with their bodies. This incredible adaptability has allowed them to thrive in environments ranging from urban landscapes to pristine wilderness areas.
The Economic Warfare: Counting the Costs

The financial impact of fire ant infestations reads like a economic horror story that continues to unfold across the South. Agricultural losses alone exceed $1 billion annually, as these voracious insects destroy crops, kill livestock, and damage farming equipment. Cotton farmers in Texas report losing entire fields to fire ant colonies that attack young plants and disrupt harvesting operations.
Urban areas face their own financial nightmares, with fire ants causing millions in damages to electrical equipment, air conditioning systems, and municipal infrastructure. These industrious insects have an inexplicable attraction to electrical currents, leading them to build nests inside power boxes, traffic lights, and even airport runway lighting systems. The resulting short circuits and equipment failures create cascading problems that ripple through entire communities.
Homeowners spend hundreds of millions each year on professional pest control, medical treatments, and property repairs. Insurance companies have had to create entirely new categories to address fire ant-related claims, while real estate values in heavily infested areas have suffered measurable declines.
Biological Weapons: The Science of Natural Control

Scientists have turned to nature itself to find weapons against fire ants, developing sophisticated biological control programs that read like science fiction. The most promising approach involves introducing parasitic phorid flies, tiny assassins that target fire ant colonies with surgical precision. These flies, no bigger than a pinhead, lay their eggs inside fire ant heads, where the larvae slowly consume the ant’s brain before emerging as adults.
Researchers have identified over 20 species of phorid flies native to South America that specifically target fire ants. Each species attacks different castes within the colony, from workers to reproductive individuals, creating a multi-layered assault that can significantly reduce colony effectiveness. The flies don’t eliminate fire ants entirely, but they restore some balance to the ecosystem by reducing their competitive advantage.
Other biological agents show equally promising results. Certain microsporidian pathogens can infect entire fire ant colonies, weakening their immune systems and reducing their reproductive capacity. Entomopathogenic fungi create another layer of biological warfare, with spores that can spread through colonies like a plague, slowly decimating the population from within.
Chemical Arsenals: Modern Pesticide Strategies

The chemical war against fire ants has evolved into a sophisticated science involving targeted toxins and innovative delivery systems. Modern fire ant baits represent a quantum leap from the crude pesticides of the past, using delayed-action poisons that allow worker ants to carry death back to their colonies. These baits contain slow-acting toxins that take days or weeks to kill, ensuring maximum distribution throughout the colony before the poison takes effect.
Hydramethylnon, one of the most effective active ingredients, works by disrupting cellular respiration in fire ants. Workers unknowingly share contaminated food with their nestmates, including the queen, gradually poisoning the entire colony from within. This approach proves far more effective than contact pesticides, which only kill individual workers while leaving the reproductive core intact.
Professional pest control companies have developed sophisticated application techniques that maximize bait effectiveness while minimizing environmental impact. Timing applications to coincide with peak foraging activity, typically during cooler temperatures, ensures maximum uptake by worker ants. Some companies now use GPS mapping to track treatment areas and monitor long-term effectiveness across large properties.
The Texas Two-Step: A State-Wide Battle Plan

Texas has emerged as ground zero in the fire ant wars, implementing the most comprehensive state-wide control program in the nation. The Texas Two-Step method combines broadcast baiting with targeted mound treatments, creating a systematic approach that has reduced fire ant populations by up to 90% in treated areas. This program treats entire landscapes rather than individual colonies, preventing recolonization from neighboring areas.
The first step involves broadcasting fire ant bait across entire properties using specialized equipment that ensures even distribution. Workers then follow up with direct mound treatments for any colonies that survive the initial baiting. This comprehensive approach addresses both visible colonies and hidden satellite nests that might otherwise repopulate treated areas.
Texas has invested millions in research and implementation, partnering with universities and private companies to develop new control methods. The state maintains detailed maps of fire ant populations, tracks treatment effectiveness, and shares data with other affected states. This coordinated approach has served as a model for other Southern states developing their own fire ant management programs.
Community Mobilization: Neighborhoods Fighting Back

Across the South, communities have organized grassroots movements that transform fire ant control from individual battles into coordinated campaigns. Neighborhood associations now coordinate treatment schedules, bulk-purchase baits, and share information about effective control methods. These community-wide efforts prove far more effective than individual homeowner treatments, which often leave gaps for fire ant recolonization.
Homeowner associations have developed sophisticated treatment protocols that mirror professional pest management programs. Residents contribute to community-wide baiting programs, with treatments scheduled simultaneously across entire neighborhoods. This coordinated approach prevents fire ants from simply moving from treated to untreated areas, creating genuine population suppression rather than temporary displacement.
Educational programs have become crucial components of community fire ant control efforts. Master gardener programs now include fire ant identification and control modules, while county extension offices provide regular workshops on safe and effective treatment methods. These educational initiatives ensure residents understand both the biology of fire ants and the proper application of control measures.
Agricultural Countermeasures: Protecting Crops and Livestock

Farmers across the South have developed innovative strategies that protect their crops and livestock from fire ant damage while maintaining sustainable agricultural practices. Integrated pest management approaches combine biological controls, targeted chemical applications, and habitat modifications to create hostile environments for fire ant colonies. These methods prove more effective and environmentally sound than relying solely on pesticides.
Cattle ranchers have implemented pasture management techniques that reduce fire ant populations while improving grass quality. Rotational grazing systems prevent overgrazing that creates ideal fire ant habitat, while strategic burning programs eliminate accumulated organic matter that supports colony development. Some ranchers have introduced beneficial insects that compete with fire ants for resources, creating natural population controls.
Row crop farmers have developed precision application techniques that target fire ant colonies while minimizing impacts on beneficial insects. GPS-guided equipment allows farmers to treat specific areas rather than broadcasting pesticides across entire fields. This targeted approach reduces costs while maintaining effectiveness, creating sustainable long-term fire ant management programs.
Urban Warfare: City-Wide Fire Ant Programs

Major Southern cities have implemented comprehensive fire ant management programs that treat public spaces, municipal facilities, and residential areas as interconnected battlegrounds. These programs coordinate treatments across parks, schools, airports, and government buildings, creating city-wide suppression efforts that prevent fire ant populations from rebounding in untreated areas.
Parks and recreation departments have developed specialized protocols for maintaining fire ant-free public spaces. Regular monitoring programs identify new colonies before they become established, while preventive treatments protect high-traffic areas where fire ant stings pose the greatest risk to public safety. These programs often involve partnerships with professional pest control companies that provide ongoing monitoring and treatment services.
Municipal utilities have implemented fire ant control measures that protect critical infrastructure from damage. Electrical cooperatives now treat substations and power lines proactively, preventing the short circuits and equipment failures that fire ants commonly cause. Water treatment facilities, airports, and other essential services maintain comprehensive fire ant management programs that ensure operational continuity.
Medical Frontlines: Treating Fire Ant Casualties
Emergency rooms across the South have developed specialized protocols for treating fire ant envenomation, recognizing that these tiny insects can cause serious medical emergencies. Physicians now routinely assess patients for signs of systemic allergic reactions, which can progress rapidly from localized swelling to life-threatening anaphylaxis. Emergency departments maintain epinephrine auto-injectors and antihistamines specifically for fire ant sting victims.
Dermatologists have documented the long-term effects of repeated fire ant exposure, including permanent scarring and increased sensitivity to future stings. Some patients develop chronic inflammatory conditions that require ongoing medical management, while others experience psychological trauma that affects their willingness to engage in outdoor activities. The medical community has recognized fire ant stings as a legitimate public health concern requiring specialized treatment protocols.
Research into fire ant venom has led to improved treatment methods and better understanding of allergic responses. Scientists have identified specific proteins in fire ant venom that trigger severe reactions, leading to development of more effective antihistamines and anti-inflammatory medications. This research has also contributed to development of potential immunotherapy treatments for individuals with severe fire ant allergies.
Educational Campaigns: Knowledge as Ammunition

Schools across the South have integrated fire ant education into their curricula, teaching children to identify colonies, avoid dangerous areas, and respond appropriately to stings. These educational programs create informed citizens who can contribute to community-wide fire ant management efforts while protecting themselves and their families from injury. Children learn to recognize fire ant mounds, understand the insects’ behavior patterns, and implement basic first aid for stings.
Extension services have developed comprehensive educational materials that help residents understand fire ant biology, identify effective control methods, and implement safe treatment protocols. These programs dispel myths about fire ant control while providing science-based information that improves treatment effectiveness. Educational workshops attract hundreds of participants who learn practical skills for protecting their properties and communities.
Public awareness campaigns have utilized social media, television, and print media to spread information about fire ant control methods and prevention strategies. These campaigns reach broad audiences with consistent messaging about the importance of coordinated control efforts and proper treatment techniques. The educational approach recognizes that informed citizens are the most effective weapon against fire ant infestations.
Environmental Considerations: Balancing Control and Conservation

Environmental scientists have raised important questions about the ecological impacts of fire ant control programs, particularly the effects on beneficial insect populations and soil ecosystems. Research indicates that some fire ant control methods can inadvertently harm native ant species, pollinators, and other beneficial insects that play crucial roles in ecosystem functioning. This has led to development of more selective control methods that target fire ants while preserving native species.
Integrated pest management approaches emphasize environmental stewardship while achieving effective fire ant control. These methods combine biological controls, habitat modification, and targeted chemical applications to create sustainable long-term management programs. The goal is to suppress fire ant populations while maintaining healthy ecosystems that support native wildlife and beneficial insects.
Regulatory agencies have developed guidelines for fire ant control that protect water quality, soil health, and non-target species. These regulations ensure that control programs meet environmental standards while achieving their primary objectives. The regulatory framework continues to evolve as new research reveals more about the ecological impacts of different control methods.
Technology and Innovation: Next-Generation Solutions

Cutting-edge technology has revolutionized fire ant detection and control, with researchers developing smartphone apps that help citizens identify fire ant colonies and report infestations to authorities. These crowd-sourcing applications create real-time databases of fire ant populations that help coordinate control efforts across large areas. GPS mapping allows precise tracking of treatment areas and monitoring of long-term effectiveness.
Drone technology has emerged as a powerful tool for fire ant surveillance and treatment in areas that are difficult to access by ground crews. Drones equipped with specialized cameras can identify fire ant mounds across large properties, while others carry precision application equipment that delivers treatments directly to colonies. This technology proves particularly valuable for treating sensitive areas like wetlands or protected habitats.
Advanced bait formulations utilize nanotechnology to improve delivery of active ingredients to fire ant colonies. These innovations increase bait attractiveness while reducing the amount of active ingredient required for effective control. Smart baits contain multiple active ingredients that work synergistically to overcome potential resistance development in fire ant populations.
Success Stories: Victories in the Fire Ant War

Several Southern communities have achieved remarkable success in their battles against fire ants, demonstrating that coordinated control efforts can achieve significant population reductions. The city of Austin, Texas, reduced fire ant populations by over 85% through a comprehensive program that combined professional treatments, community education, and ongoing monitoring. This success story has inspired similar programs in other cities across the region.
Agricultural success stories include cattle ranches that have eliminated fire ant problems through integrated pasture management programs. These operations demonstrate that sustainable fire ant control is possible without relying heavily on pesticides. The ranchers have reported improved cattle health, reduced veterinary costs, and increased productivity following implementation of comprehensive fire ant management programs.
Residential communities have achieved similar successes through coordinated neighborhood treatment programs. Subdivisions that implement community-wide baiting programs report dramatic reductions in fire ant populations and corresponding improvements in quality of life. These success stories demonstrate the effectiveness of coordinated approaches compared to individual treatment efforts.
Looking Forward: The Future of Fire Ant Control

Research continues to develop new weapons in the ongoing war against fire ants, with scientists exploring genetic control methods that could provide long-term solutions to fire ant infestations. Gene drive technology might eventually allow researchers to introduce genetic modifications that reduce fire ant reproductive capacity or increase their susceptibility to biological control agents. These futuristic approaches could revolutionize fire ant management in the coming decades.
Climate change models suggest that fire ant ranges will continue to expand northward, requiring new control strategies for areas that have never experienced fire ant infestations. Researchers are developing predictive models that help identify areas at risk for future fire ant invasions, allowing proactive implementation of control measures before colonies become established.
International cooperation has become increasingly important as fire ants spread to new continents and countries. The Southern United States serves as a testing ground for control methods that may eventually be needed in other parts of the world. Scientific collaboration ensures that effective control methods are shared globally, while research continues to develop new solutions for this persistent pest.
The Ongoing Battle: Why Persistence Matters

The fight against fire ants requires sustained commitment from individuals, communities, and governments across the affected regions. Short-term control efforts typically fail because fire ants quickly recolonize treated areas from neighboring populations. Successful programs maintain consistent pressure on fire ant populations through ongoing monitoring, regular treatments, and adaptive management strategies that respond to changing conditions.
Fire ant control represents a marathon rather than a sprint, requiring long-term perspectives and sustained funding commitments. Communities that achieve lasting success recognize that fire ant management is an ongoing process rather than a one-time solution. This understanding leads to development of sustainable programs that maintain effectiveness over time while adapting to new challenges and opportunities.
The economic and social benefits of effective fire ant control justify the ongoing investment required for successful programs. Reduced medical costs, increased property values, and improved quality of life create positive returns that far exceed the costs of comprehensive control programs. These benefits accumulate over time, creating lasting improvements for affected communities.
The battle against fire ants continues to evolve as new technologies, biological agents, and management strategies emerge from ongoing research efforts. The South’s experience with fire ant control has created a wealth of knowledge that benefits not only the region but also other areas facing similar invasive species challenges. Through persistence, innovation, and coordinated effort, communities across the South are proving that even the most formidable invasive species can be controlled and managed effectively. What started as a biological invasion has become a testament to human ingenuity and determination in the face of environmental challenges.




