Imagine walking through ancient ruins where every stone bears mysterious symbols that mock centuries of scholarly effort. The Indus Script represents one of archaeology’s most tantalizing puzzles, etched into seals, tablets, and pottery by a civilization that vanished without leaving us the key to their thoughts. These enigmatic markings have frustrated linguists, archaeologists, and codebreakers for nearly a century, yet they continue to whisper secrets from a time when cities flourished along the banks of the Indus River.
The Enigmatic Harappan Civilization

The Indus Valley Civilization, also known as the Harappan Civilization, thrived between 3300 and 1300 BCE across what is now Pakistan and northwest India. This Bronze Age society built sophisticated cities like Harappa and Mohenjo-daro, complete with advanced drainage systems, standardized weights and measures, and impressive urban planning that would make modern city planners envious.
What makes this civilization truly extraordinary is its apparent peaceful nature and remarkable uniformity across vast distances. Unlike their contemporary civilizations in Mesopotamia and Egypt, the Harappans left no evidence of warfare, royal tombs, or monumental architecture dedicated to rulers. Instead, they created a society that seems to have valued trade, craftsmanship, and urban organization above all else.
Discovery of the Mysterious Script
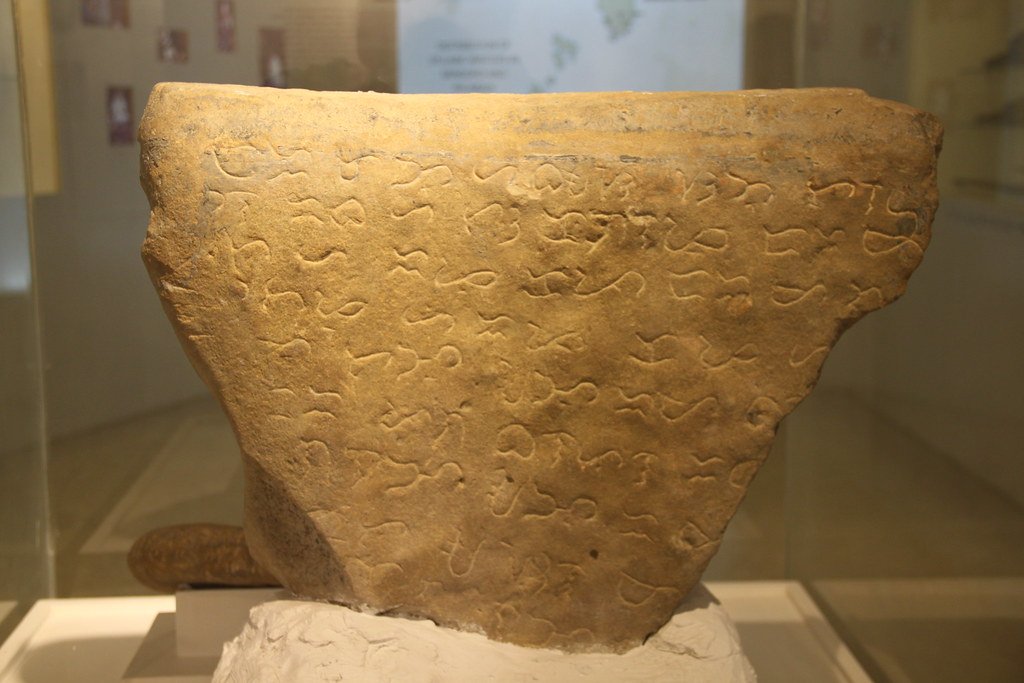

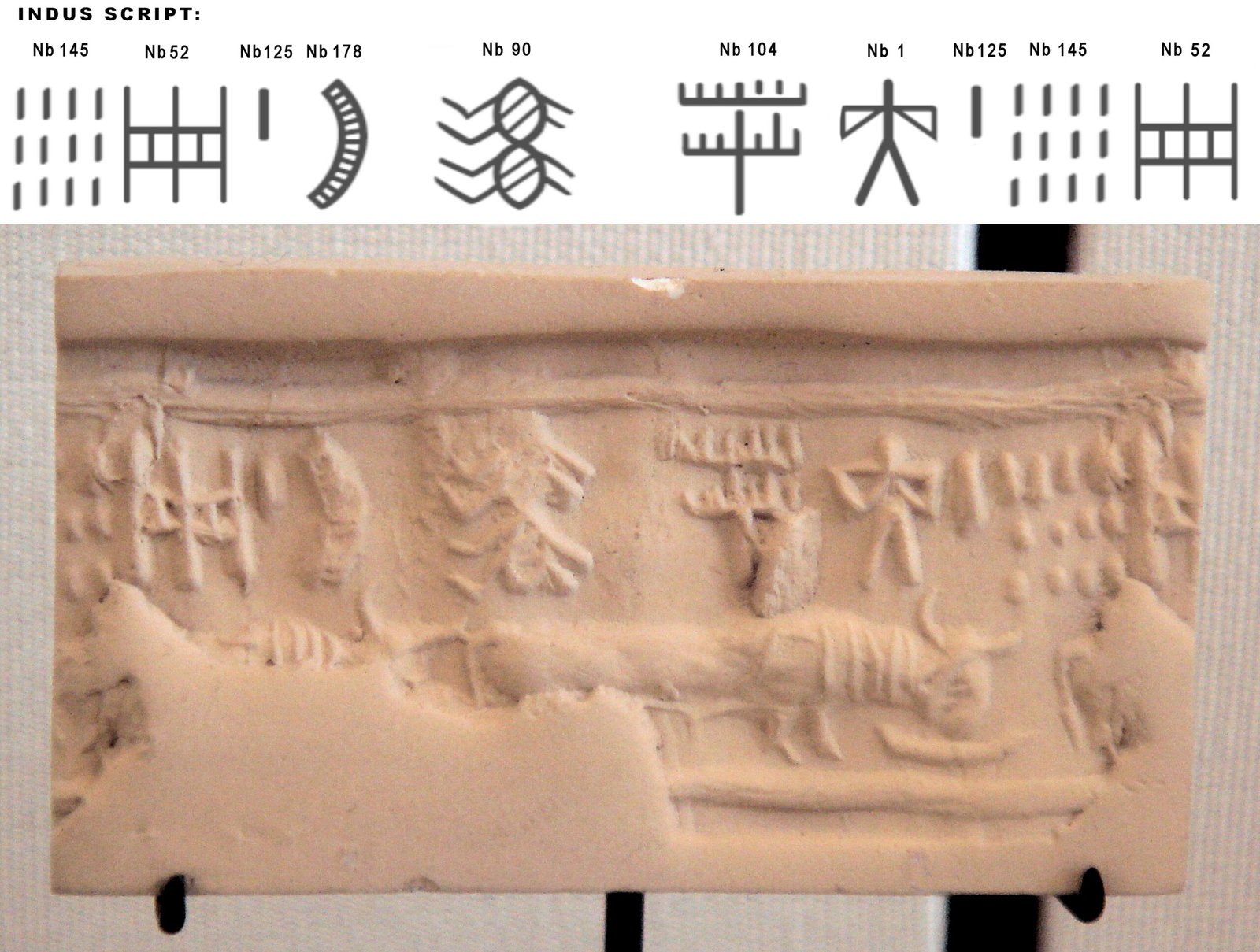
The first Indus script symbols were discovered in the 1920s when British archaeologist Sir John Marshall began excavating Harappa and Mohenjo-daro. These tiny symbols, found primarily on square steatite seals, immediately captured the attention of scholars who recognized them as a form of writing unlike anything seen before. The symbols appeared to be more than mere decorations – they seemed to carry meaning, purpose, and structure.
Since then, archaeologists have uncovered over 4,000 inscribed objects bearing these mysterious symbols. The script appears on seals, pottery, copper tablets, and even miniature signs that might have been used for identification or trade purposes. Each discovery adds another piece to the puzzle, yet the complete picture remains frustratingly out of reach.
The Peculiar Nature of Indus Symbols

The Indus script consists of approximately 400 to 600 distinct symbols, depending on how researchers classify variations and combinations. These symbols range from simple geometric shapes to complex pictographs depicting animals, humans, and abstract concepts. Some symbols appear frequently, while others show up only once or twice in the entire corpus of discovered texts.
What’s particularly intriguing is the brevity of most Indus inscriptions. The average text contains only four to five symbols, with the longest known inscription containing just 26 symbols. This brevity has led some scholars to question whether the Indus script represents a full writing system or something more limited, like a collection of religious or administrative symbols.
Attempts at Pattern Recognition

Modern computational analysis has revealed fascinating patterns within the Indus script that suggest it follows linguistic rules. Statistical studies show that certain symbols appear together more frequently than random chance would predict, indicating possible grammatical structures or semantic relationships. The distribution of symbols also follows patterns similar to those found in natural languages, with some symbols acting as frequent “function words” while others appear to carry more specific meanings.
Researchers have identified what they believe to be directional markers, numerical indicators, and possibly even personal names or titles. Some symbols consistently appear at the beginning or end of inscriptions, suggesting they might function as prefixes, suffixes, or determinatives that classify the content of the text.
The Great Decipherment Challenge

Deciphering the Indus script faces several monumental challenges that have stymied researchers for decades. Unlike the Rosetta Stone, which provided the key to Egyptian hieroglyphs, no bilingual text exists to help crack the Indus code. The civilization disappeared without leaving any clear descendants who might have preserved knowledge of the script or language.
The short length of most inscriptions compounds the difficulty, as there’s insufficient context to determine meaning through linguistic analysis. It’s like trying to understand a language when you only have access to business cards and name tags – you can see patterns, but the bigger picture remains elusive.
Computer-Assisted Breakthrough Attempts

The digital age has brought new hope to Indus script research through sophisticated computer analysis and machine learning algorithms. Researchers have applied techniques similar to those used in cryptography and artificial intelligence to identify patterns invisible to the human eye. These computational approaches have revealed statistical regularities that strongly suggest the symbols represent a genuine writing system rather than random decorations.
Some teams have used Markov chains and conditional entropy analysis to study symbol sequences, finding that the Indus script exhibits characteristics similar to natural languages. However, despite these technological advances, the actual meaning of the symbols remains as mysterious as ever.
The Dravidian Connection Theory

One of the most compelling theories suggests that the Indus script represents an early form of Dravidian language, related to modern Tamil, Telugu, and Malayalam. Proponents of this theory point to the geographic distribution of Dravidian languages in southern India and the possible linguistic continuity from ancient times. Some researchers claim to have identified Dravidian words in Indus inscriptions, though these claims remain highly controversial.
The Dravidian hypothesis gains some support from the fact that these languages were likely spoken in the region before the arrival of Indo-Aryan languages. However, the 4,000-year gap between the Indus civilization and the earliest known Dravidian texts makes this connection speculative at best.
Alternative Theories and Wild Speculations

The mystery of the Indus script has spawned numerous alternative theories, ranging from the plausible to the fantastical. Some researchers propose that the symbols represent a proto-writing system that never developed into full literacy, while others suggest they might be astronomical records or religious symbols rather than conventional writing.
More controversial theories have linked the script to everything from ancient Sanskrit to Easter Island’s rongorongo script. While most of these connections lack solid evidence, they demonstrate the desperation of researchers to find any clue that might unlock the mystery.
The Seal Connection Mystery

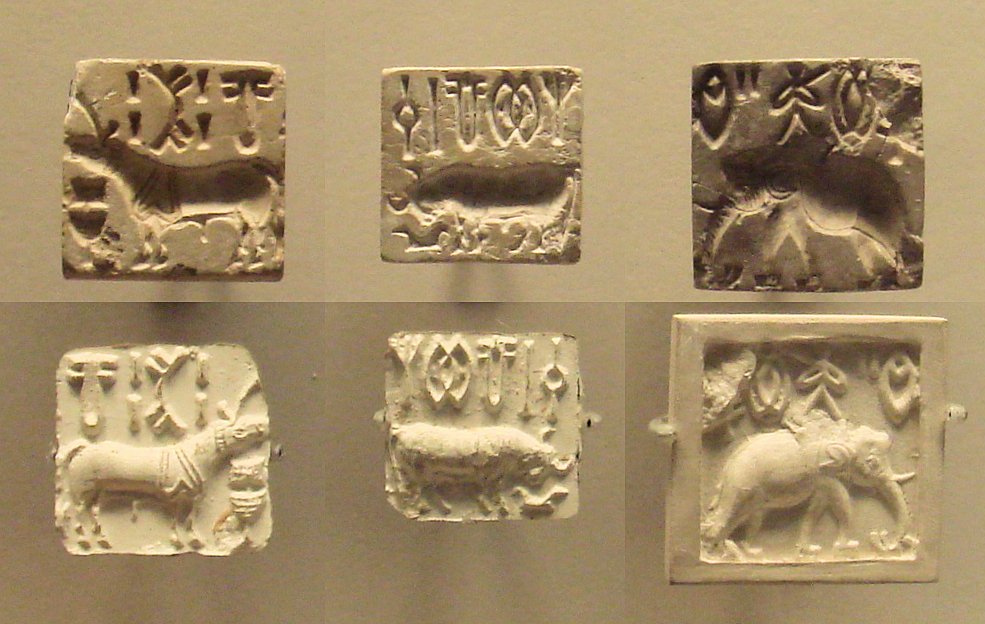
The majority of Indus script inscriptions appear on small square seals, typically measuring about 2-3 centimeters per side. These seals often feature beautifully carved animals – unicorns, bulls, elephants, and tigers – alongside the mysterious script. The seals were likely used for trade, pressed into clay to mark goods or document transactions across the vast Harappan trading network.
The relationship between the animal imagery and the script remains unclear. Some researchers believe the animals represent clan totems or gods, while others think they might be phonetic elements that help pronounce the written words. The recurring “unicorn” seal, found in hundreds of examples, might hold particular significance as it appears to represent a standardized symbol of authority or identity.
Regional Variations and Evolution

Analysis of Indus script samples from different sites reveals subtle regional variations that might provide clues about the language’s development and use. Northern sites like Harappa show slightly different symbol frequencies compared to southern sites like Dholavira, suggesting possible dialectical differences or specialized local uses.
The script also appears to have evolved over time, with earlier examples showing more pictographic elements while later inscriptions become increasingly abstract. This evolution mirrors the development of other ancient writing systems, providing hope that understanding these changes might reveal the script’s underlying logic.
The Mathematics of Ancient Writing

Recent mathematical analysis has revealed that the Indus script follows Zipf’s law, a statistical principle that governs the frequency distribution of words in natural languages. This finding strongly suggests that the symbols represent a genuine writing system rather than random decorative elements or simple pictographs.
The entropy levels of Indus inscriptions fall between those of purely random sequences and highly structured systems like DNA, positioning them squarely in the range typical of human languages. These mathematical insights provide compelling evidence that the Harappans possessed a sophisticated writing system, even if we can’t read it yet.
Archaeological Context Clues

The archaeological context of Indus script discoveries offers tantalizing hints about their purpose and meaning. Many inscribed objects were found in what appear to be administrative areas, suggesting the script served bureaucratic functions. Other inscriptions appear on pottery and personal items, indicating the writing system had broader social applications beyond official use.
The careful craftsmanship of the seals and the standardization of symbols across vast distances implies a highly organized society with established writing conventions. This level of standardization suggests the script was widely understood and used for important communications, making its complete disappearance all the more mysterious.
Modern Technology Meets Ancient Mystery

Today’s researchers employ cutting-edge technology to analyze the Indus script in ways previous generations couldn’t imagine. High-resolution 3D scanning reveals subtle details invisible to the naked eye, while artificial intelligence algorithms search for patterns in massive databases of inscriptions. Genetic algorithms attempt to evolve possible translations, while neural networks trained on known ancient languages look for structural similarities.
Despite these technological marvels, the fundamental challenge remains: without a bilingual text or a clear understanding of the underlying language, even the most sophisticated computer analysis can only reveal patterns, not meanings. The human element – intuition, cultural understanding, and linguistic creativity – remains essential to any breakthrough.
The Skeptics’ Perspective

Not all scholars agree that the Indus script represents true writing. Some archaeologists argue that the symbols might be religious or ritual markers, similar to the complex iconography found in pre-Columbian American cultures. They point to the brevity of inscriptions and the lack of clear grammatical structure as evidence against a full writing system.
These skeptics suggest that the Harappans might have been a largely oral culture that used symbols for specific, limited purposes like trade identification or religious ceremonies. This perspective challenges the assumption that all complex civilizations must have developed writing systems, forcing researchers to reconsider their fundamental assumptions about literacy and communication in ancient societies.
International Collaborative Efforts

The challenge of deciphering the Indus script has brought together researchers from around the world, creating unprecedented international collaboration. Teams from India, Pakistan, the United States, Europe, and Japan share data, methodologies, and insights in the common quest to unlock this ancient mystery.
These collaborative efforts have standardized the classification of symbols and created comprehensive databases accessible to researchers worldwide. The shared resources and diverse perspectives have accelerated research progress, though the ultimate breakthrough remains elusive. The international nature of this effort reflects the universal human fascination with lost languages and forgotten civilizations.
What Success Would Mean

Successfully deciphering the Indus script would represent one of archaeology’s greatest triumphs, comparable to the decipherment of Egyptian hieroglyphs or Mesopotamian cuneiform. It would open a window into the thoughts, beliefs, and daily lives of one of humanity’s earliest urban civilizations, revealing their literature, religion, governance, and social structures.
The breakthrough would also provide crucial insights into the development of human writing systems and the evolution of language itself. Understanding how the Harappans organized their society, managed their extensive trade networks, and conceptualized their world would reshape our understanding of Bronze Age civilizations and human cultural development.
The Enduring Mystery
Despite nearly a century of intensive research, the Indus script remains as mysterious as ever. Each new discovery adds complexity rather than clarity, revealing the sophisticated nature of this ancient writing system while keeping its secrets locked away. The symbols continue to mock our modern analytical capabilities, reminding us that human ingenuity can create puzzles that transcend time.
Perhaps the script’s greatest gift lies not in its eventual decipherment, but in the questions it forces us to ask about communication, civilization, and the nature of human expression. It challenges our assumptions about how complex societies function and reminds us that the past holds mysteries that may never be fully solved.
Hope for the Future

While complete decipherment may remain elusive, ongoing research continues to reveal new aspects of Harappan civilization and their remarkable script. Advanced imaging techniques might uncover previously invisible inscriptions, while new archaeological discoveries could provide the bilingual text that researchers desperately need. The next generation of artificial intelligence might finally crack the code that has resisted human analysis for so long.
The mystery of the Indus script serves as a humbling reminder that our ancestors were capable of creating systems of thought and communication that still challenge our understanding today. Whether we eventually decode these ancient symbols or they remain forever mysterious, they continue to inspire wonder and curiosity about the remarkable achievements of human civilization. Will the next archaeological season finally bring the key to unlock this 4,000-year-old puzzle, or will these enigmatic symbols keep their secrets for another century?




