Imagine a world buried under miles of ancient ice, where sunlight never reaches and temperatures plunge far below freezing. Now picture vast lakes, teeming with secrets, silently lying beneath that frozen surface. It’s not science fiction—it’s happening right now in Antarctica, where a landscape of hidden lakes is coming to light as the ice shelf melts. These subglacial lakes, some larger than entire cities, are among the most mysterious environments on Earth. What could possibly survive in such harsh darkness? What ancient stories are locked away under the blue-white wilderness? The answers may surprise and even shake the foundations of what we know about life on our planet.
The Astonishing Discovery of Subglacial Lakes
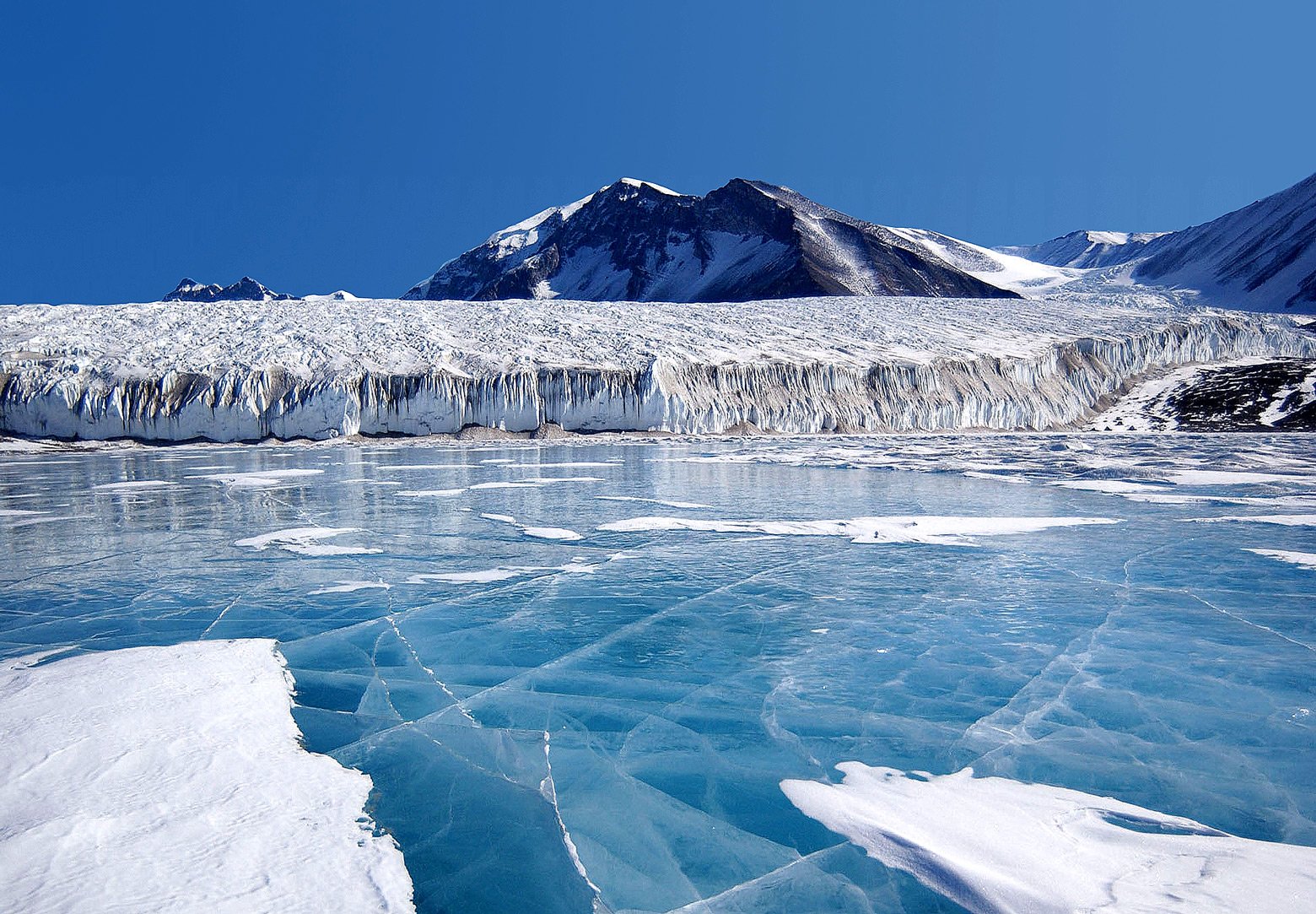

It was only a few decades ago that scientists first realized something extraordinary was lurking beneath Antarctica’s thick ice. In the late 20th century, researchers detected strange radar echoes while surveying the continent. Instead of solid rock, they found pockets of liquid water—massive lakes hidden from view for millions of years. Today, more than 400 subglacial lakes have been identified, the most famous being Lake Vostok, which stretches over 150 miles long. These discoveries were so surprising that some scientists compared it to finding a lost world, a place untouched by sunlight and time.
How Do Lakes Exist Beneath So Much Ice?

It might seem impossible for liquid water to exist beneath ice sheets that are sometimes more than two miles thick. But Antarctica defies expectations. The weight of the ice above creates enormous pressure, which actually lowers the freezing point of water. Add in a little geothermal heat from the Earth’s core, and the result is pockets of liquid water trapped between the ice and the bedrock. It’s a bit like the pressure cooker in your kitchen—except this one operates on a mind-boggling scale, with enough ice and water to reshape entire landscapes.
The Role of Melting Ice Shelves
As global temperatures rise, Antarctica’s ice shelves—those floating extensions of the ice sheet—are melting faster than ever. This melting isn’t just making sea levels rise; it’s also changing what happens beneath the ice. When ice shelves thin or collapse, the pressure balance shifts, allowing more water to flow into subglacial lakes and even connecting lakes through hidden channels. The melting ice acts like a secret key, unlocking pathways no one knew existed. It’s a dramatic, sometimes chaotic process, and the consequences are still unfolding.
Unraveling the Secrets of Lake Vostok
Lake Vostok is the crown jewel of Antarctica’s subglacial lakes. Isolated for at least 15 million years, it holds more water than Lake Ontario. Scientists have drilled through more than two miles of ice to reach its surface, using special clean technology to avoid contamination. The samples brought back have stunned the scientific community. They hint at unique ecosystems, with microbes that might survive entirely without sunlight—feeding instead on minerals, chemicals, or even ancient gases. Some researchers have called it a “time capsule” from a forgotten era.
Microbial Life Without Sunlight
What kind of life could possibly survive in a pitch-black, freezing, and high-pressure environment? The answer, as it turns out, is both humbling and inspiring. Microbes—tiny, hardy life forms—have been found in subglacial lakes, eking out an existence by using chemical energy instead of sunlight. Some feed on iron and sulfur, while others may even “breathe” hydrogen or methane. These survivors are like Earth’s own aliens, proving that life can thrive in the most unlikely places. Their existence opens up thrilling possibilities for life beyond our planet.
The Role of Satellites and Ice-Penetrating Radar
Exploring Antarctica’s hidden lakes isn’t easy. The thick ice makes direct observation nearly impossible. That’s where cutting-edge technology comes in. Satellites equipped with radar and gravity sensors can “see” through the ice, mapping the shape and movement of subglacial lakes. Airplanes and ground vehicles use ice-penetrating radar to send signals deep below the surface, revealing the shifting waters and boundaries of these secret lakes. Thanks to these innovations, scientists can now track the pulse of Antarctica’s hidden waterways.
Unexpected Water Highways Beneath the Ice

One of the most mind-bending discoveries is that many subglacial lakes aren’t isolated at all. Instead, they’re connected by vast networks of rivers and channels, all flowing in darkness beneath the ice. Sometimes, lakes fill up and suddenly drain, sending floods of water racing dozens of miles beneath the surface. These hidden water highways can move more water than some major rivers on the surface. The shifting, unpredictable flow can even cause the ice above to rise or fall by several feet in a matter of days.
Ancient Sediments: A Window Into the Past
The bottom of Antarctica’s hidden lakes is layered with sediments that have built up over millions of years. These sediments are like pages in a history book, recording ancient climates, volcanic eruptions, and even the comings and goings of life. By drilling down and analyzing these layers, scientists can reconstruct what Antarctica was like when dinosaurs roamed or when the continent was covered in lush forests. It’s a bit like being able to read a diary from the dawn of time, written in mud and minerals.
Impact on Global Sea Levels
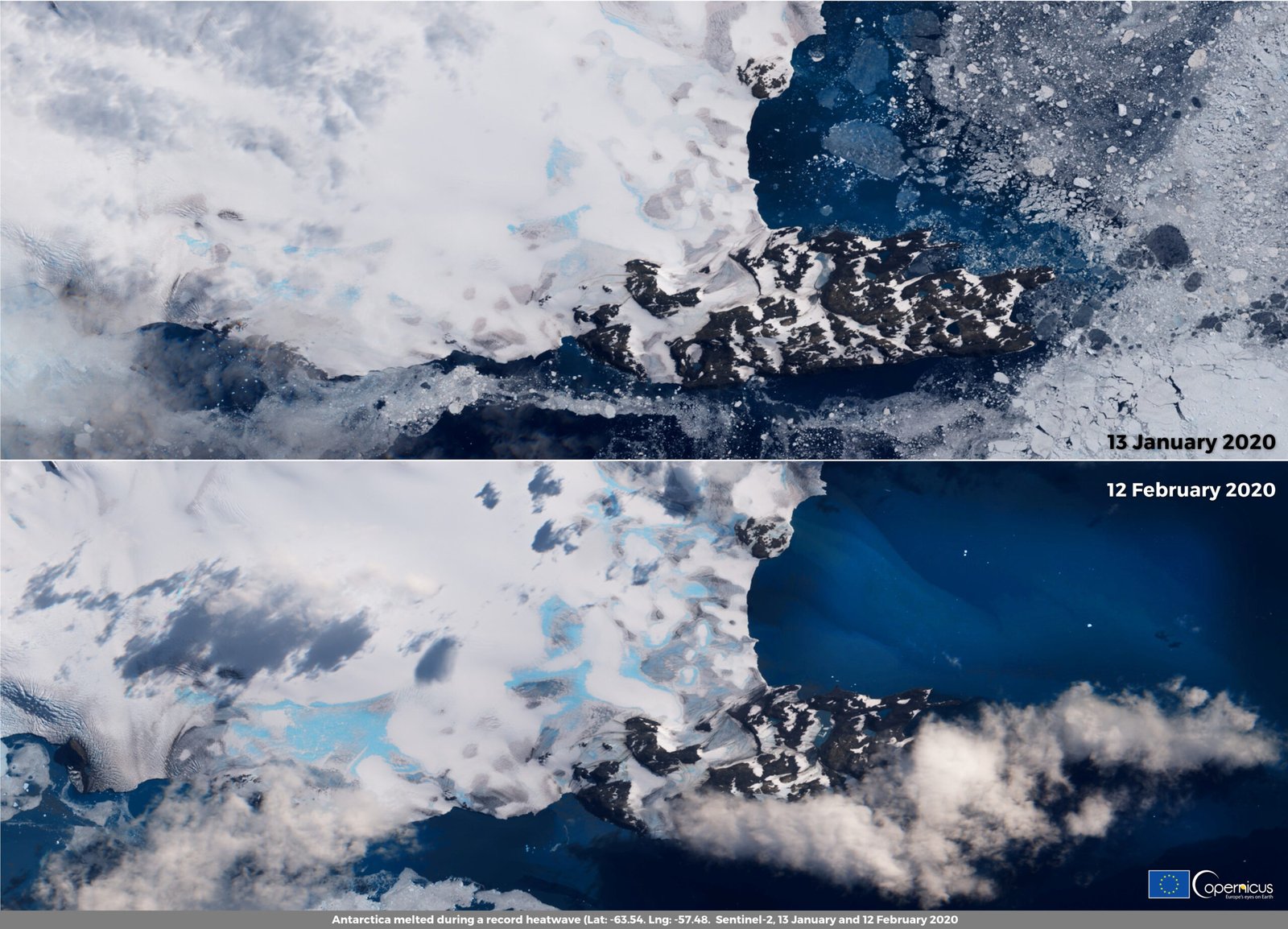

Why should we care about what happens beneath Antarctica’s ice? One huge reason: sea levels. The subglacial lakes act as lubricants, making it easier for glaciers to slide toward the ocean. When lakes suddenly drain, they can “grease the skids” and send massive amounts of ice racing into the sea. This process can speed up the loss of Antarctic ice, contributing to rising sea levels around the world. For millions living in coastal cities, what happens in Antarctica’s hidden lakes could have very real consequences.
Hints of Exotic Chemistry
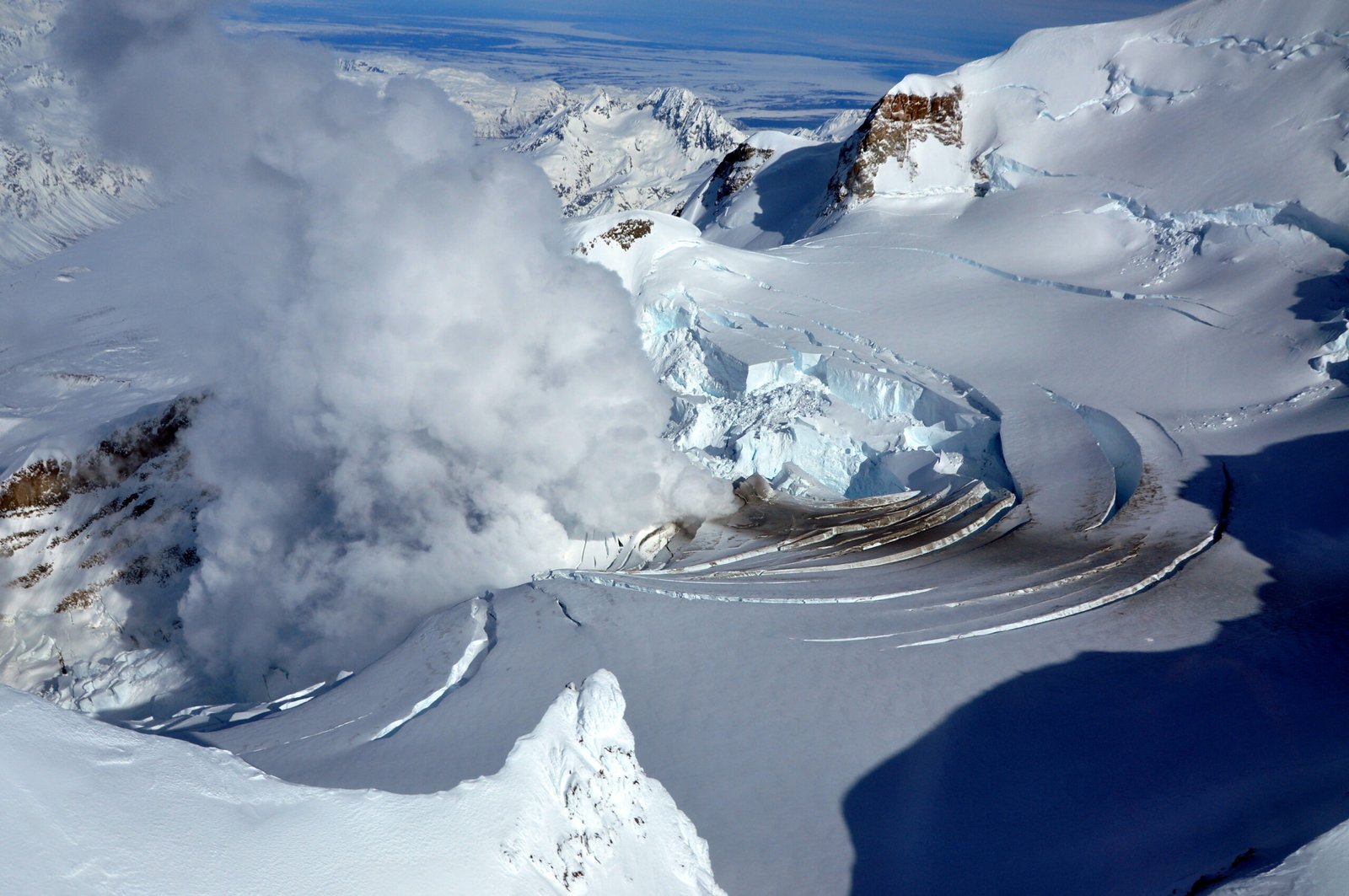

The chemistry inside these lakes is nothing like what we find on the surface. Isolated from the atmosphere and sunlight, the water is often rich in strange minerals, salts, and gases. Some lakes are packed with oxygen, while others are almost completely cut off from the air. These conditions create ideal laboratories for studying unique chemical reactions, some of which might mimic the environments on icy moons like Europa or Enceladus. The exotic chemistry is one more reason why scientists are obsessed with these hidden bodies of water.
What Lies Beneath the Ross Ice Shelf?

The Ross Ice Shelf, one of the largest floating ice platforms on Earth, hides an entire world beneath its frozen surface. In recent years, scientists have drilled through the shelf and found not just water, but signs of living creatures—tiny fish and invertebrates swimming in total darkness. These discoveries challenge our understanding of what’s possible and suggest that even the coldest, darkest places on Earth can be full of surprises.
Challenges of Drilling and Exploration
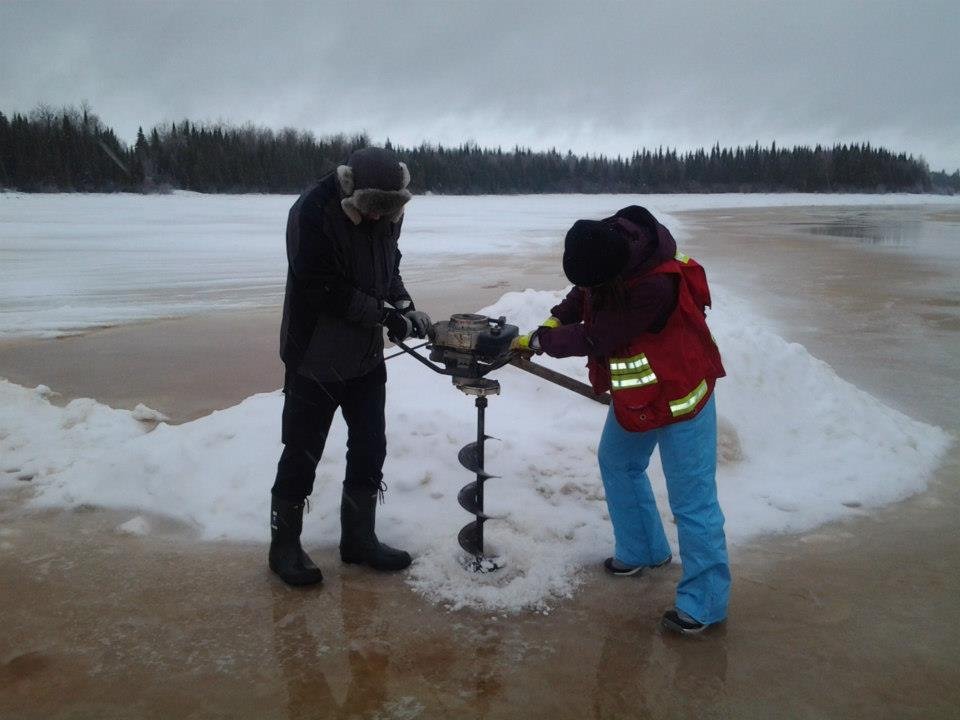

Accessing subglacial lakes isn’t just difficult—it’s one of the greatest technical challenges in modern science. Drills must pierce through miles of ice without contaminating the pristine environment below. Researchers use sterile, hot-water drilling, and every piece of equipment must be scrubbed clean. The logistics are staggering: supplies, fuel, and people must be flown in, and the work is done in some of the harshest conditions on the planet. Every new success is a triumph of ingenuity and determination.
The Search for Ancient Life
If life can exist in Antarctica’s hidden lakes, could it have survived here since before the continent froze over? Some scientists believe the answer is yes. DNA fragments found in lake samples hint at ancient lineages, possibly dating back millions of years. These organisms might hold clues to how life adapts, endures, and even thrives when conditions turn brutal. The idea that we might find living “fossils” beneath the ice is as thrilling as it is mysterious.
Implications for Life Beyond Earth
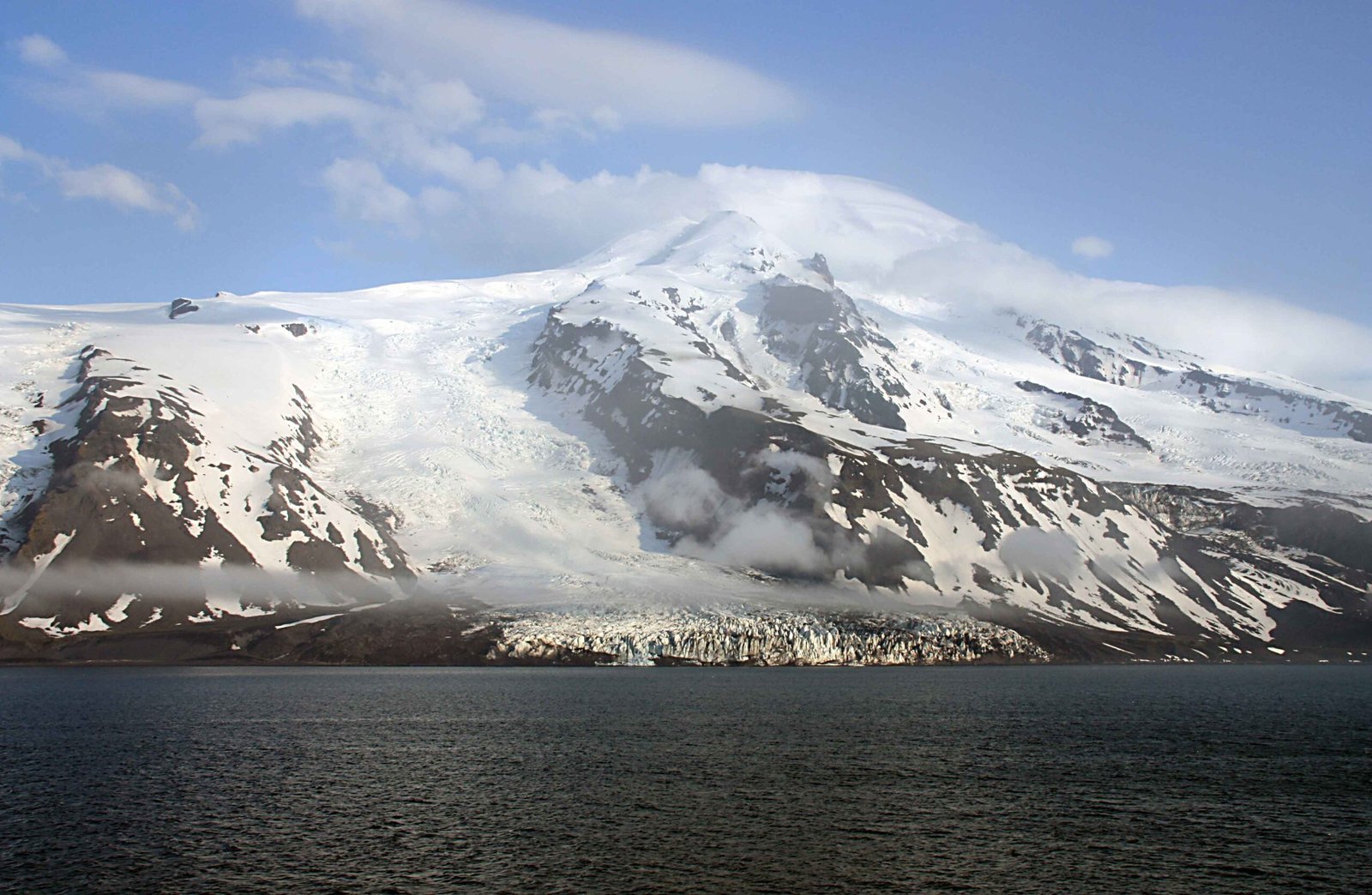

Perhaps the most tantalizing question of all: if life can survive beneath Antarctica’s ice, could it exist elsewhere in our solar system? The moons Europa and Enceladus, for example, have thick ice shells covering hidden oceans. The lessons learned from Antarctica’s subglacial lakes are guiding the search for extraterrestrial life. NASA and other space agencies are already planning missions that will use similar drilling and detection techniques to look for life on these distant, icy worlds.
The Dynamic Nature of Subglacial Systems
Far from being static, Antarctica’s hidden lakes are constantly changing. New lakes appear, old ones drain, and water flows in unpredictable ways. Recent satellite data show that the network of subglacial lakes is much more active than anyone thought, with water moving hundreds of miles under the ice in just a few years. This dynamism is a reminder that Antarctica is alive with motion, even if we can’t see it with the naked eye.
The Threat of Climate Change
Climate change is reshaping Antarctica faster than ever before. Warming temperatures are increasing the rate of melting, threatening to destabilize the delicate balance of subglacial lakes and rivers. As the ice thins, new pathways open up, potentially accelerating the flow of ice into the ocean. The fate of these hidden lakes is closely tied to the future of our planet, and their study is becoming an urgent scientific mission.
Cutting-Edge Robotics and Future Missions
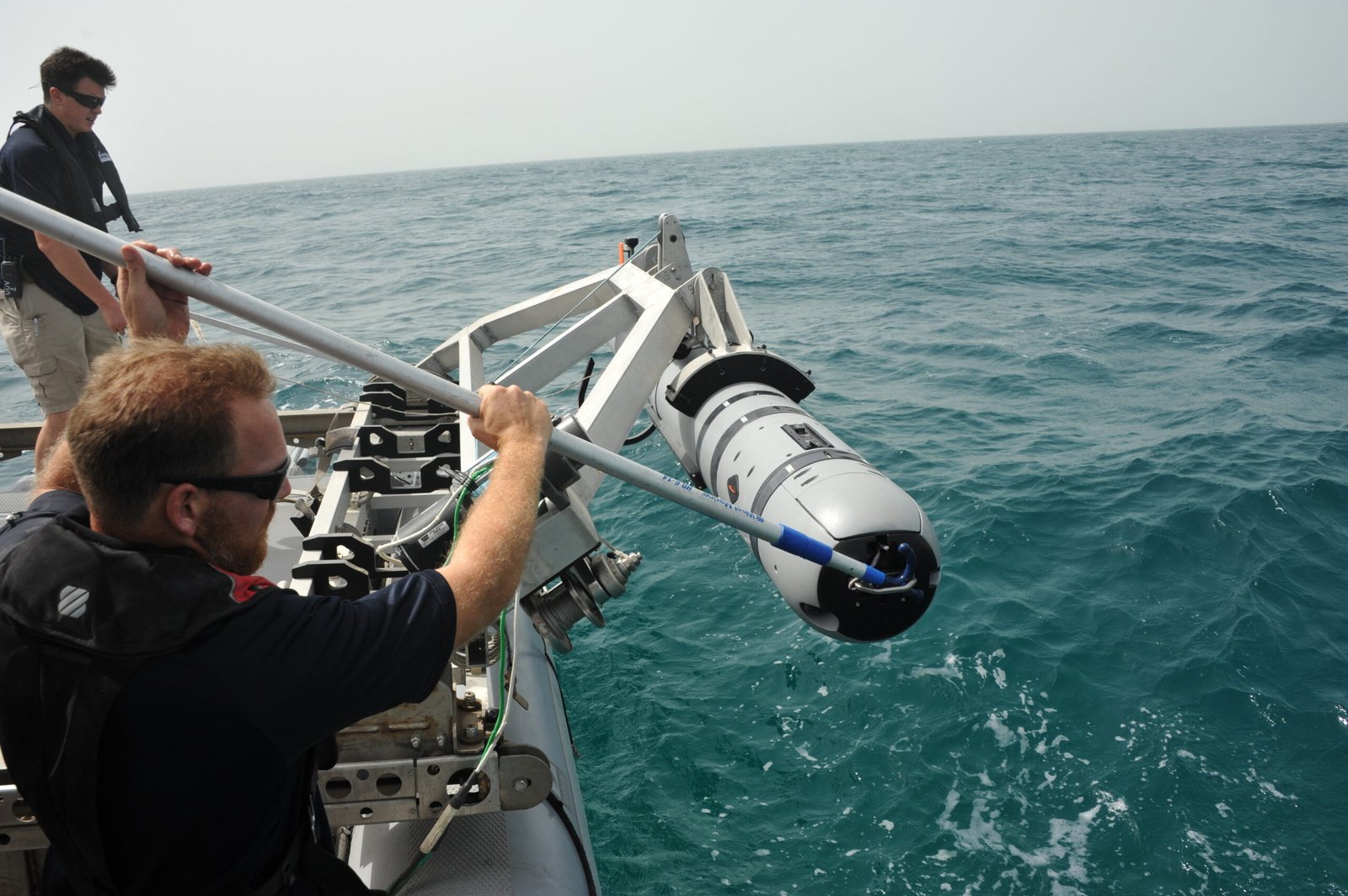

To keep up with the mysteries beneath the ice, scientists are turning to advanced robotics. Drones, autonomous underwater vehicles, and even tiny robots are being developed to slip through narrow boreholes and explore the lakes firsthand. These machines can collect water, sediment, and even biological samples, sending back data in real time. Every mission brings us closer to understanding what’s really happening in these dark, silent worlds.
The Human Element: Tales from the Ice
Behind every discovery in Antarctica are stories of grit, teamwork, and wonder. Scientists endure months of darkness, bone-chilling cold, and isolation to unlock the secrets beneath the ice. Many describe their work as a calling, driven by the thrill of exploring the unknown. “Every sample we bring up is a step into another world,” one researcher said, “and you never know what you’ll find.” Their passion is contagious, reminding us of the boundless curiosity that drives human progress.
Unanswered Questions and Future Prospects
Despite all we’ve learned, Antarctica’s hidden lakes are still full of mysteries. What undiscovered creatures swim in their depths? How quickly will melting ice change the landscape below? And what can these lakes teach us about the resilience of life itself? The next decade promises even more breakthroughs, as technology improves and international teams work together to solve these puzzles. With each new discovery, we’re reminded just how little we truly know about our own planet.
Antarctica’s hidden lakes are more than just scientific curiosities—they are windows into Earth’s past, present, and perhaps even its future. As the ice continues to melt, new secrets will inevitably come to light, challenging our understanding of life, climate, and the very nature of our world. What lies beneath may inspire the next generation of explorers, scientists, and dreamers. What do you hope we’ll find next?



