You’ve probably heard the phrase “truth is stranger than fiction.” Well, nowhere does that ring more true than in the quantum realm. The microscopic world operates under rules that defy everything you learned in physics class, everything you see around you, and quite honestly, everything that seems logical. Particles vanish and reappear. Information transfers instantaneously across vast distances. Objects exist in multiple states until you dare to look at them.
These aren’t just theoretical oddities scribbled on blackboards. Scientists have observed, measured, and confirmed these behaviors in laboratories around the world. Some discoveries are so recent that the ink on the research papers is barely dry. Let’s dive into five quantum phenomena that make even the wildest science fiction look mundane by comparison.
Quantum Entanglement: The Universe’s Spookiest Connection

Quantum entanglement is the phenomenon wherein the quantum state of each particle in a group cannot be described independently of the state of the others, even when the particles are separated by a large distance. Picture two particles that share a mysterious connection, no matter how far apart they travel. Measure one, and you instantly know something about the other. It’s like having a pair of magic coins where flipping one to heads guarantees the other shows tails, even if they’re on opposite sides of the galaxy.
Einstein famously called entanglement “spooky action at a distance,” since the particles seemed to be communicating faster than the speed of light. He simply couldn’t accept it. The idea violated everything physicists believed about how the universe worked. Einstein thought there must be hidden variables, some secret information we just couldn’t access yet.
Here’s the thing, though. Einstein was wrong. Experiments have since proven that entanglement is very real and fundamental to nature. In 2025, researchers even observed entanglement to persist between unstable top quarks and their antimatter partners at distances farther than what can be covered by information transferred at the speed of light. These are the heaviest known fundamental particles, demonstrating this spooky connection under the most extreme conditions.
Entanglement underpins new technologies including quantum computing, secure communications and future quantum networks. The phenomenon that once seemed impossibly strange is now becoming the foundation for revolutionary technologies. What was once spooky is now becoming practical.
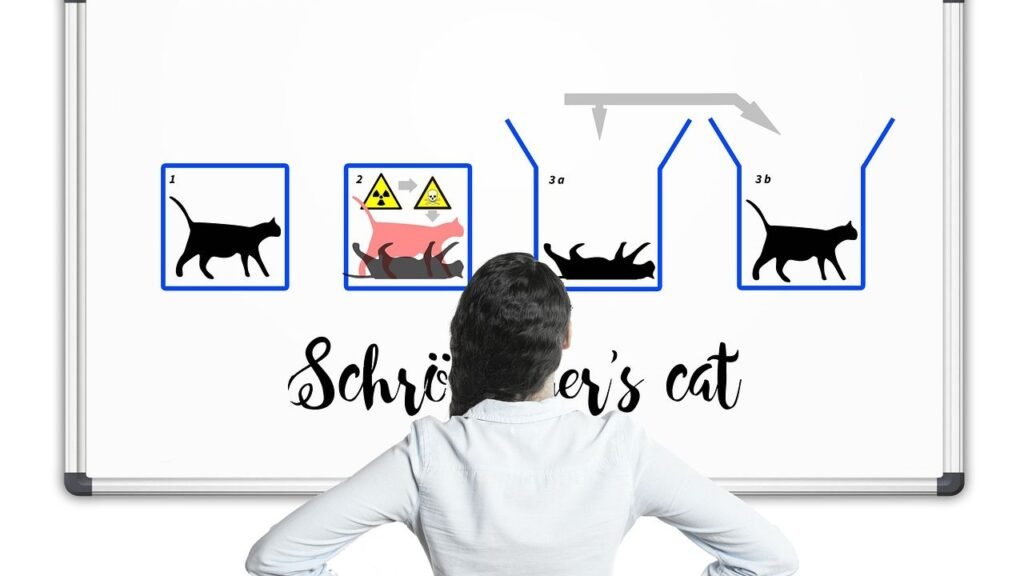
Quantum Superposition: Existing Everywhere and Nowhere

In quantum mechanics, Schrödinger’s cat is a thought experiment concerning quantum superposition. In the thought experiment, a hypothetical cat in a closed box may be considered to be simultaneously both alive and dead while it is unobserved. This famous paradox captures something genuinely bizarre about quantum mechanics: particles don’t commit to a single state until you measure them.
Think about a coin spinning in the air. It’s neither heads nor tails while it spins. Yet in the quantum world, it’s genuinely both until observation forces it to choose. States in quantum superposition are notoriously fragile, but researchers in China have reported creating such a state that lasted for a whopping 23 minutes and 20 seconds. That might not sound impressive until you realize quantum states typically collapse in fractions of a second.
Even stranger, scientists have recently pushed the boundaries of what can exist in superposition. Scientists created quantum superposition states at temperatures up to 60 times hotter than their environment. Researchers from the University of Innsbruck achieved quantum superpositions at temperatures up to 60 times warmer than their system’s surrounding environment. This challenges the long-held assumption that quantum effects require extreme cold to exist.
Let’s be real, the implications are staggering. These aren’t just abstract experiments. They’re paving the way for quantum computers that leverage superposition to perform calculations classical computers could never touch. The cat is out of the box, so to speak.
Quantum Tunneling: Walking Through Walls

Imagine throwing a tennis ball at a brick wall. It bounces back, right? In quantum mechanics, a particle can, with a small probability, tunnel to the other side, thus crossing the barrier. The reason for this difference comes from treating matter as having properties of waves and particles. Particles can simply appear on the other side of barriers they shouldn’t be able to cross.
This isn’t some theoretical curiosity gathering dust. For the first time ever, scientists have watched electrons perform a bizarre quantum feat: tunneling through atomic barriers by not just slipping through, but doubling back and slamming into the nucleus mid-tunnel. Recently, Professor Dong Eon Kim and his research team have succeeded in unraveling for the first time the mystery of the electron tunneling process. A hundred years after the phenomenon was discovered, we’re finally seeing what happens during the tunnel itself.
Tunnelling plays an essential role in physical phenomena such as nuclear fusion and alpha radioactive decay of atomic nuclei. Without quantum tunneling, the sun wouldn’t shine. Stars need tunneling to fuse hydrogen atoms into helium, overcoming the enormous energy barriers between positively charged nuclei. It’s wild to think that the light warming your face relies on particles breaking classical physics rules.
Perhaps most remarkably, The Nobel Prize laureates in physics for 2025, John Clarke, Michel H. Devoret and John M. Martinis, used a series of experiments to demonstrate that the bizarre properties of the quantum world can be made concrete in a system big enough to be held in the hand. Their superconducting electrical system could tunnel from one state to another, as if it were passing straight through a wall. Macroscopic quantum tunneling is now a reality, not just a microscopic quirk.
Wave-Particle Duality: The Ultimate Identity Crisis

Is light a wave or a particle? The answer is yes. This demonstrates the wave–particle duality, which states that all matter exhibits both wave and particle properties: The particle is measured as a single pulse at a single position, while the modulus squared of the wave describes the probability of detecting the particle at a specific place on the screen giving a statistical interference pattern.
The famous double-slit experiment reveals this schizophrenic behavior perfectly. Fire light through two narrow slits, and you get an interference pattern on the screen behind them, stripes of light and dark that can only be explained if light acts like a wave. Yet when you try to detect which slit each photon passes through, the interference pattern vanishes, and light suddenly behaves like discrete particles.
Here’s where it gets truly unnerving. This demonstrated that in the double-slit interference experiment, one photon particle simultaneously passed through the two slits and interfered by itself. Even a single photon, fired alone, creates an interference pattern over time. It’s as though the photon goes through both slits simultaneously and interferes with itself.
MIT physicists performed an idealized version of the double-slit experiment, stripping it to its quantum essentials. They confirmed that light exists as both a wave and a particle but cannot be observed in both forms at the same time. The very act of observation determines which nature light will reveal. I know it sounds crazy, but this is verified reality. Einstein once said Richard Feynman believed all of quantum mechanics could be understood through careful consideration of this one experiment. He wasn’t exaggerating.
Quantum Geometry: The Hidden Shape of Reality

A hidden quantum geometry that distorts electron paths has finally been observed in real materials. This quantum metric, once thought purely theoretical, may revolutionize electronics, superconductivity, and ultrafast devices. Imagine discovering that electrons don’t simply move through materials in straight lines, but follow paths warped by an invisible geometry we never knew existed.
A team from the University of Geneva, in collaboration with the University of Salerno and the CNR-SPIN Institute, has taken a major step forward by uncovering a hidden geometry that distorts the trajectories of electrons in much the same way gravity bends the path of light. It’s like finding out that space itself, at the quantum scale, has curves and bends we couldn’t see before.
This isn’t just academic fascination. The concept of quantum metric dates back about 20 years, but for a long time it was regarded purely as a theoretical construct. Only in recent years have scientists begun to explore its tangible effects on the properties of matter. What was once mathematical abstraction is now experimentally confirmed reality.
The discovery opens doors to understanding and controlling quantum materials in ways previously unimaginable. Think of designing materials where you can manipulate electron flow by engineering this hidden quantum geometry. It’s hard to say for sure, but this could be the key to technologies we haven’t even dreamed of yet. Reality at the quantum level has more dimensions than we ever suspected.
The Quantum Future

These five phenomena represent just the tip of the iceberg in our understanding of quantum mechanics. Each discovery raises as many questions as it answers. How can particles be entangled across the universe? Why does observation change quantum behavior? What other hidden dimensions of reality are we missing?
The quantum world doesn’t care about making sense to our macroscopic brains. It operates under its own rules, rules that seem designed to perplex and astonish us. Yet these aren’t just curiosities. They’re the foundation of emerging technologies that will transform computing, communications, and materials science in the coming decades.
What makes quantum mechanics truly is this: fiction writers have to make their stories believable. Nature has no such constraint. The universe at its smallest scales is weirder, more counterintuitive, and more wonderful than any story we could invent. What do you think about these mind-bending phenomena? Does it change how you see reality?