One of the biggest dangers to contemporary medicine is antibiotic resistance; superbugs are changing faster than we can create new medications. However, if we could monitor these bacterial changes in real time and forecast their next direction before they outmaneuver our treatments? Investigating the genetic battlefield between bacteria and antibiotics as it develops inside human patients is a novel approach that has The results imply that real-time genomic surveillance could transform the way we treat recalcitrant infections, so reversing the tide in our favor against some of medicine’s worst enemies.
The Superbug Arms Race: How Bacteria Evolve Under Fire
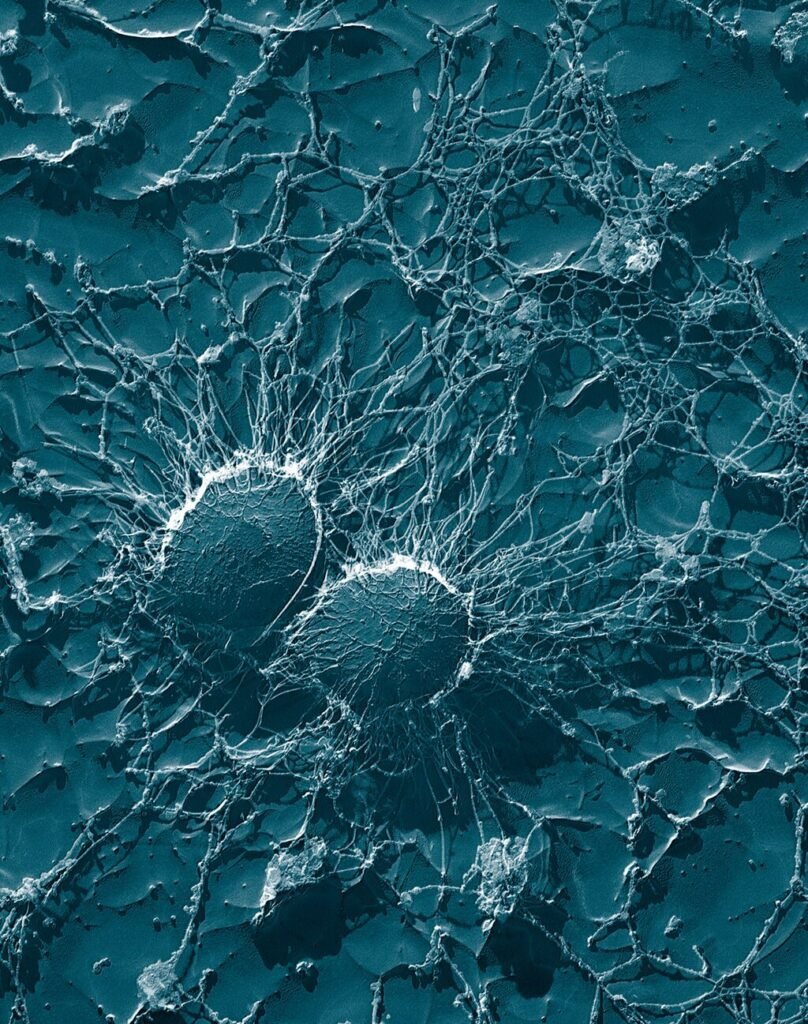
Masters of adaptation are bacterial species. To survive under antibiotic pressure, they mutate, swap genes, and even go dormant. Common but dangerous pathogen Staphylococcus aureus best illustrates this evolutionary arms struggle. About thirty percent of individuals carry it benignly, but when it becomes pathogenic it can quickly develop resistance and become a “superbug” impervious to several drugs.
Tracking these genetic changes in real time could provide doctors with a vital edge, according to a recent study in Nature Communications. Sequencing sixty strains to find adaptive mutations, researchers examined S. aureus from eleven patients with failing treatments. Remarkably, one-third displayed genetic modifications linked to resistance changes that, if discovered early on, could cause a shift to more potent antibiotics.
Persistent vs. Recurrent: Why Timing Matters in Infection Battles
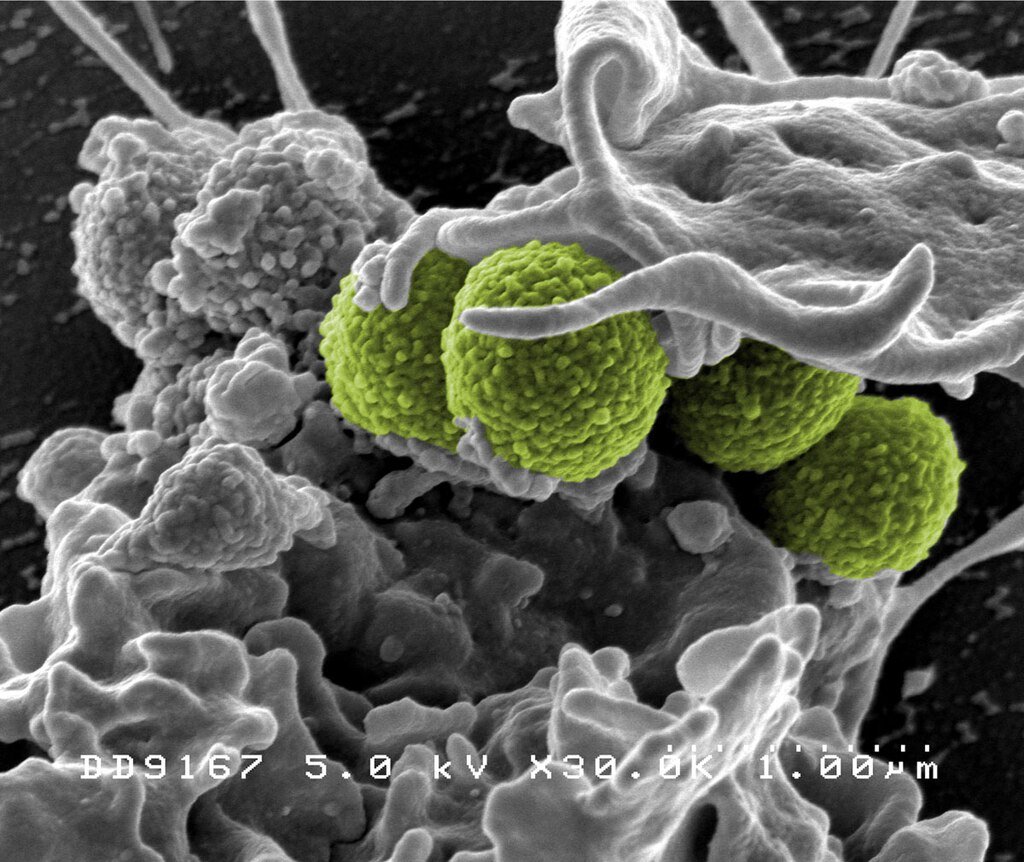
Not every superbug infection is exactly like another. While some are recurrent, appearing to go away only to resurge later, others are persistent lingering despite days of treatment. Treatment depends on knowing how different the two are.
Today, genomic sequencing can tell whether a relapse results from a new strain (indicating reinfection) or from the original strain, suggesting treatment failure. This realization in the study caused doctors to change their course of treatment 34% of the time, substituting ineffective medications for ones the bacteria hadn’t yet outwitted.
The Hidden Tricks of Bacterial Survival
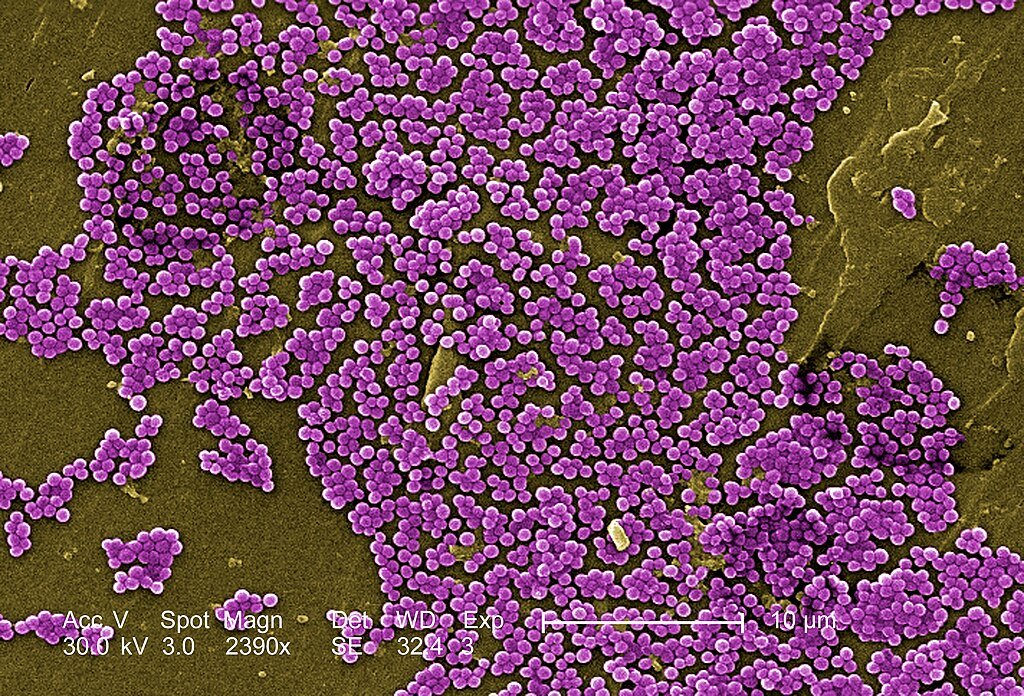
Not only do bacteria randomly mutate; they also adapt deliberately. The research revealed changes in genes regulating resistance linked to:
- Synthesizing cell walls reduces the potency of antibiotics.
- Efflux pumps, that is, drugs expelled before they can act.
- Metabolic changes slowing down to avoid detection.
These results confirm earlier studies on E. coli, in which a feature of chronic infections wrinkly mutations developed by biofilms sticky bacterial colonies allows them to cling to surfaces and resist drugs.
From Lab to Clinic: Can Doctors Use This Data in Real Time?
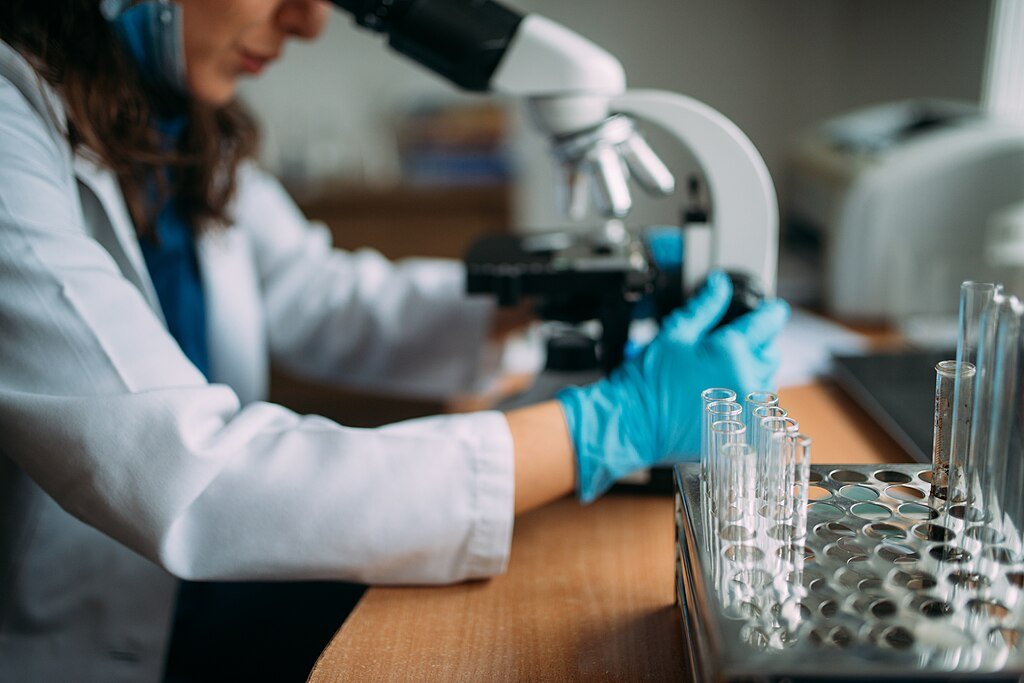

The main question is: Will this be useful in actual application? Researchers gave 25 infectious-disease experts case studies—some including evolutionary data, some without to test this. Hence, Given genetic insights, more than a third changed their treatment plans.
Still, there are obstacles. Slow and expensive current sequencing takes days when infections call for hours. Real-time resistance tracking may soon be possible, though, given prices collapsing from $1 million per genome in 2007 to under $600 today and artificial intelligence accelerating analysis.
Beyond Bacteria: Could This Work for Viruses and Fungi?
The same ideas apply to other pathogens. Genomic surveillance tracking variants like Delta and Omicron during COVID-19 exposed mutations that escaped immunity. Comparably, fungal superbugs such as Candida auris whose clonal spread was verified by whole-genome sequencing could be watched for developing resistance.
Experts advise combining genomics with conventional diagnostics to build a “dual surveillance” system for pandemics.
The Future: AI, CRISPR, and Personalized Antibiotic Plans
The frontier of next importance is Combining real-time sequencing with:
- Forecasting resistance before it arises driven by artificial intelligence.
- Faster mutation detection enabled by CRISpen-based diagnostics
- Tailored to a patient’s particular bacterial strain, personalized antibiotic regimens
“Seeing evolution happen in real time isn’t just fascinating, it’s lifesaving,” says microbiologist studying bacterial evolution Dr. Vaughn Cooper.
Conclusion: A New Era in the Fight Against Superbugs
We are stepping into a period where healthcare no longer solely responds to infections, but proactively predicts them. Understanding bacterial evolution in real time would allow physicians to outsmart them and alter the course of a battle we have been losing for years. What matters now is how quickly, inexpensively, and easily available the tools are before the next superbug surfaces.
“As Dr. Quyen Nguyen from Pittsburgh University put it, “this is not only science, but is a radical shift on how we approach medicine.”
Sources:

Suhail Ahmed is a passionate digital professional and nature enthusiast with over 8 years of experience in content strategy, SEO, web development, and digital operations. Alongside his freelance journey, Suhail actively contributes to nature and wildlife platforms like Discover Wildlife, where he channels his curiosity for the planet into engaging, educational storytelling.
With a strong background in managing digital ecosystems — from ecommerce stores and WordPress websites to social media and automation — Suhail merges technical precision with creative insight. His content reflects a rare balance: SEO-friendly yet deeply human, data-informed yet emotionally resonant.
Driven by a love for discovery and storytelling, Suhail believes in using digital platforms to amplify causes that matter — especially those protecting Earth’s biodiversity and inspiring sustainable living. Whether he’s managing online projects or crafting wildlife content, his goal remains the same: to inform, inspire, and leave a positive digital footprint.




