Imagine plunging into the ocean, deeper and deeper, until sunlight fades and the world turns a mysterious blue-black. Here, in the vast, shadowy realm known as the twilight zone, life thrives against all odds. It’s an alien world just beneath our feet, a place where bizarre creatures glow in the dark, and the rules of survival are rewritten every day. The twilight zone, or mesopelagic, is a realm so hidden that more people have walked on the moon than have explored its depths. Yet, it’s a place that holds secrets about our planet’s past, present, and possibly its future. Let’s journey into this enigmatic layer and discover the breathtaking wonders that await.
What Is the Twilight Zone?

The twilight zone, scientifically called the mesopelagic zone, lies between 200 and 1,000 meters (about 650 to 3,300 feet) below the ocean’s surface. Sunlight barely reaches this depth, creating a dim, blue world that is neither pitch dark nor fully lit. Temperatures drop rapidly, and the pressure increases dramatically with each descending meter. This zone acts as a buffer between the sunlit surface and the completely dark abyss below. It’s a region of transition, where the surface world’s energy dwindles, and only the hardiest organisms survive. The twilight zone covers a massive area, making up about 20% of the world’s ocean volume, yet it remains one of the least explored places on Earth.
Why Is It Called the Twilight Zone?
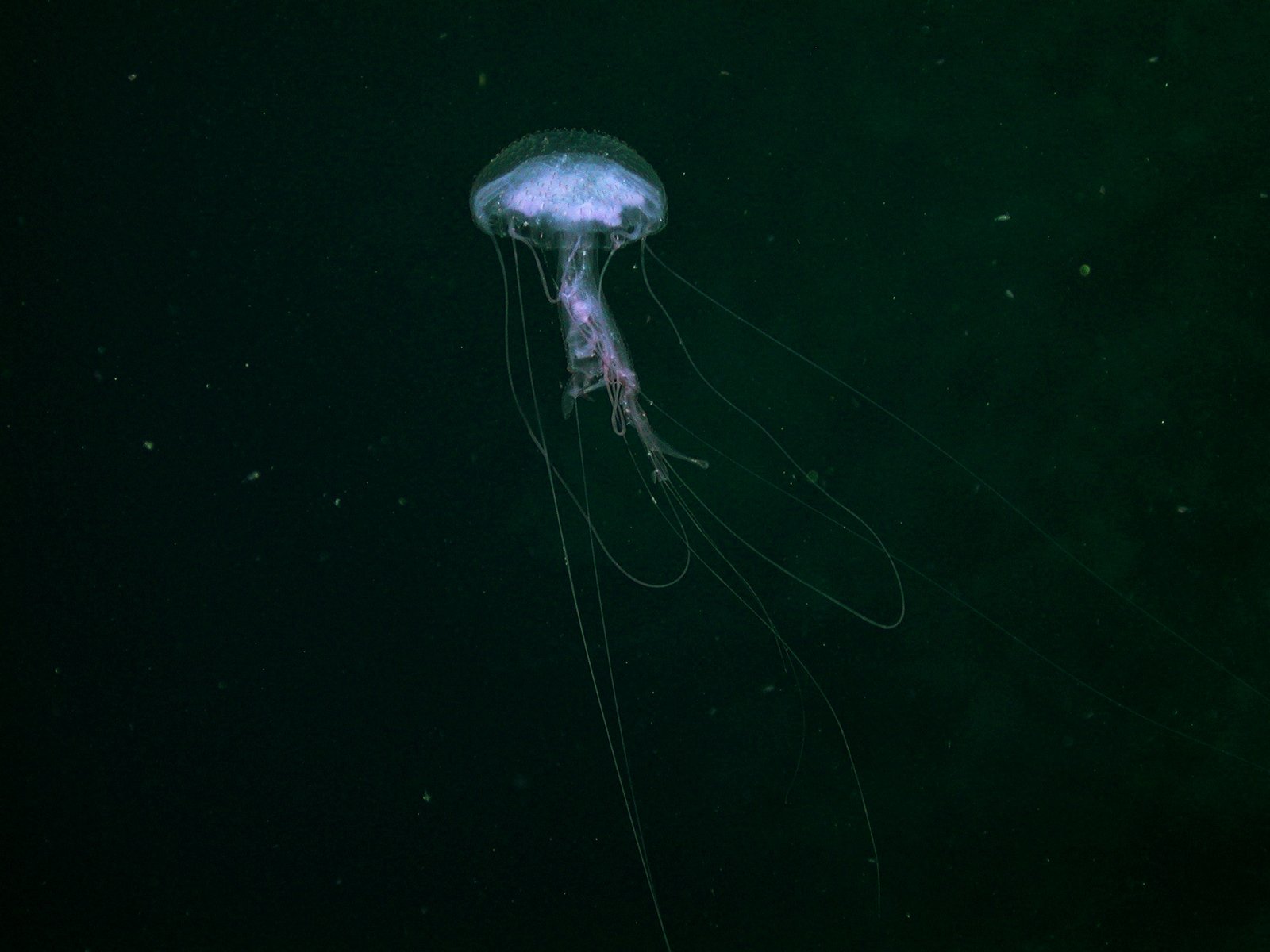

The name “twilight zone” captures the essence of this mysterious region. Just like dusk on land, the light here is faint and ghostly, never quite illuminating but never fully dark either. Scientists use the term to highlight the zone’s unique lighting conditions—it’s not bright enough for photosynthesis, but not so dark that life disappears entirely. The twilight creates surreal scenes, with flashes of bioluminescence and the silhouettes of strange creatures drifting by. This ambiguous lighting has shaped the lives and adaptations of its inhabitants, turning the zone into a living laboratory of evolution and survival.
The Mesopelagic: An Oceanic Borderland
The mesopelagic zone is more than a simple layer; it’s a borderland between two worlds. Above, the sunlit epipelagic teems with familiar fish and plankton. Below, the midnight zone plunges into total darkness and crushing pressure. The twilight zone sits between these extremes, absorbing nutrients and organic material drifting down from above. It acts like a cosmic crossroads, where creatures from the surface may mingle with those rising from the depths. This crossroads is crucial for nutrient cycling, supporting a complex web of life that connects the entire ocean.
Temperature and Pressure: Life Under Extreme Conditions
Conditions in the twilight zone are not for the faint of heart. Temperatures can plummet to near-freezing, often hovering between 4°C and 13°C (39°F to 55°F). Meanwhile, pressure climbs to over 100 times what we experience at sea level. Imagine the weight of a car pressing on every square inch of your body—this is daily life for twilight zone residents. To survive, animals here have evolved flexible bodies, special proteins, and slow metabolisms. Some creatures, like the jelly-like salps, seem almost otherworldly, with forms that bend and flow to withstand the crushing depths.
Bioluminescence: Nature’s Living Light Show
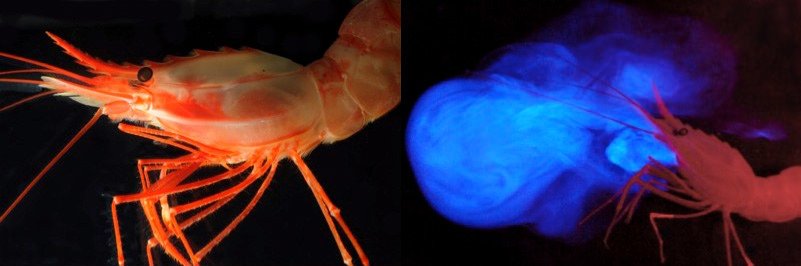
In the twilight zone, light is precious. Many creatures have turned to bioluminescence, producing their own glow through chemical reactions. Lanternfish, hatchetfish, and comb jellies flicker with blue and green lights, creating a spectacle that rivals any fireworks display. This glow isn’t just for show; it’s a tool for survival. Some animals use it to attract mates, while others create dazzling displays to confuse predators. Bioluminescence also helps creatures hide in plain sight by matching the dim light above—a tactic called counter-illumination. It’s a living light show, playing out in eternal twilight.
The Great Vertical Migration: A Daily Commute
Every night, the twilight zone comes alive with movement. Billions of fish, shrimp, and jellyfish rise toward the surface under cover of darkness to feed on plankton and other tiny organisms. As dawn approaches, they retreat back into the safety of the dim depths. This daily mass migration is the largest on the planet, outnumbering even the great herds of Africa. It’s a journey fraught with danger, but essential for survival. By moving up and down, these animals help cycle nutrients throughout the ocean and even play a role in regulating the planet’s climate by moving carbon away from the atmosphere.
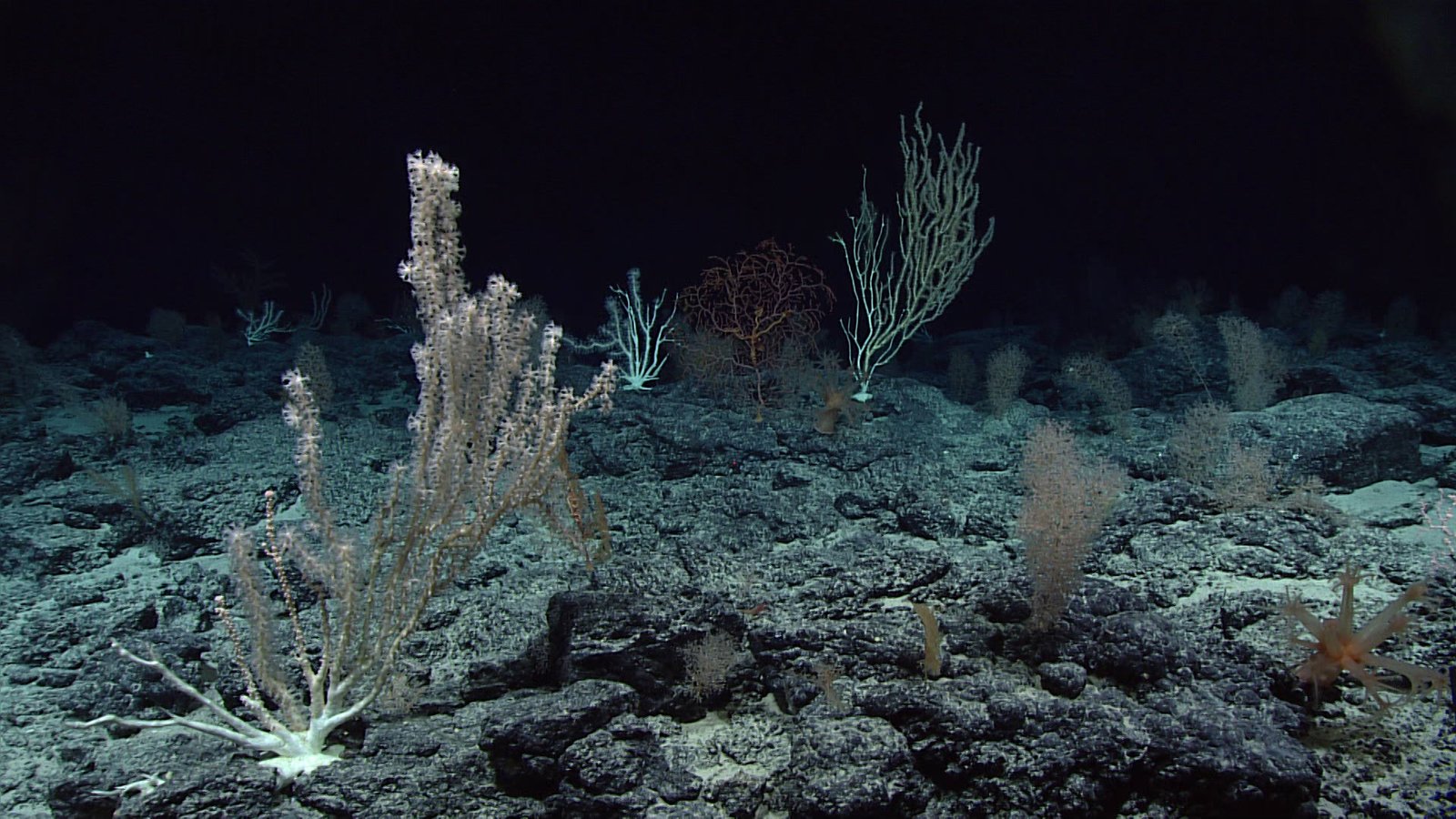
Strange and Fascinating Creatures
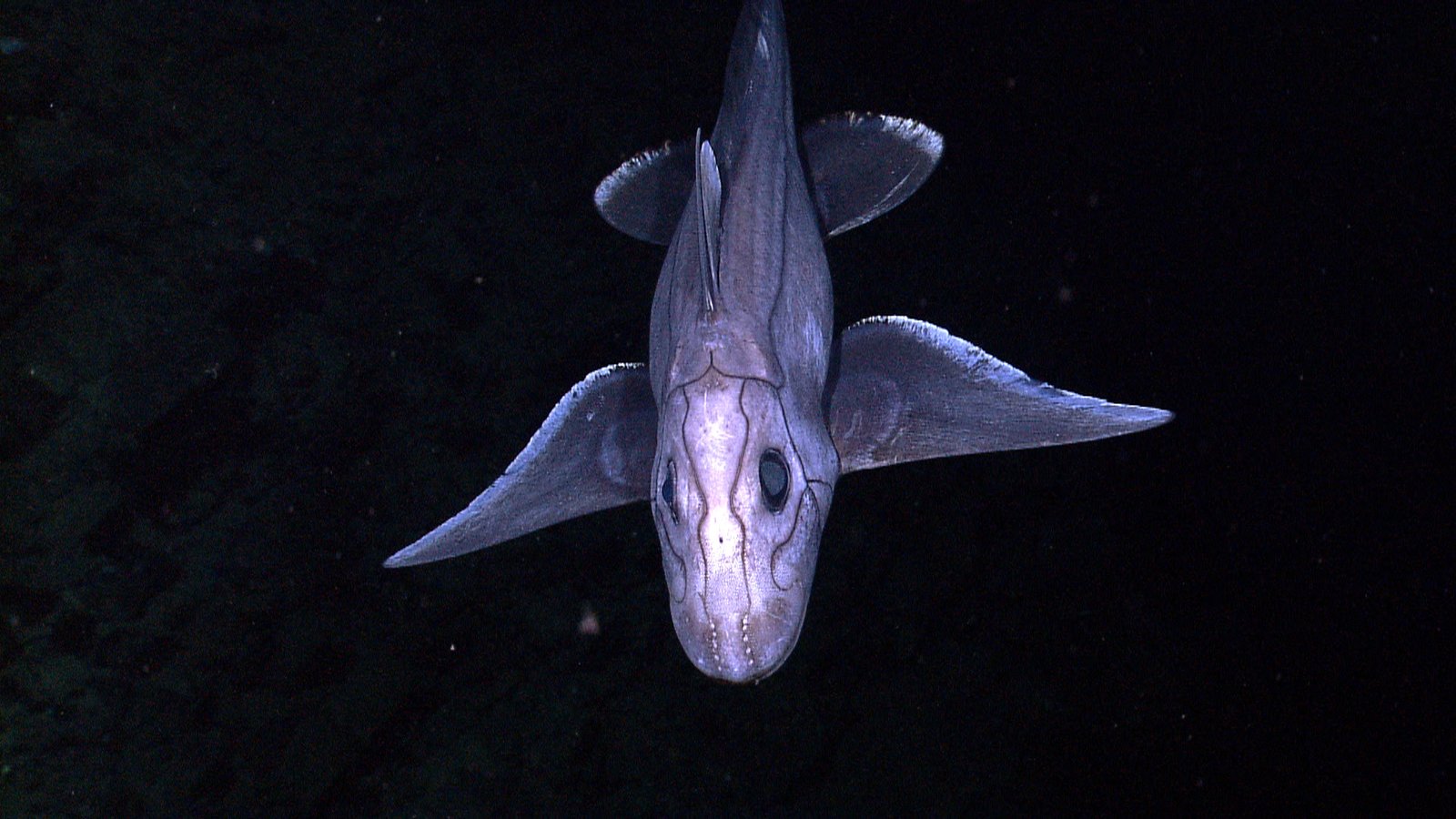
The twilight zone is home to some of the weirdest and most wonderful animals on Earth. The anglerfish, with its glowing lure and monstrous teeth, is a legend of the deep. Hatchetfish have bodies so thin they look almost invisible from the side, helping them evade predators. The gulper eel can unhinge its jaw to swallow prey much larger than itself, while the glass squid is nearly transparent, blending seamlessly into the water. These oddities aren’t just curiosities—they’re masterpieces of evolution, perfectly adapted to a world of darkness and danger.
Food Webs in the Shadows
Life in the twilight zone revolves around a delicate food web. Since photosynthesis is impossible here, most creatures depend on organic matter drifting down from above—what scientists call “marine snow.” This snow is a constant rain of dead plankton, fecal pellets, and debris. Tiny copepods and krill feed on it, while larger fish and squid hunt these smaller animals. Predators like dragonfish and squid rule the upper reaches, while strange gelatinous creatures drift below. The food web is intricate, with each creature playing a role in keeping the zone alive.
Carbon Cycling and Climate Impact
The twilight zone is a silent player in the fight against climate change. As animals feed and migrate, they transport carbon deeper into the ocean, locking it away for centuries. This process, known as the biological pump, helps regulate the amount of carbon dioxide in Earth’s atmosphere. Without this hidden army of swimmers, our planet would heat up much faster. Scientists are only beginning to understand how vital the twilight zone is for global climate stability, making it even more important to protect and study.
Challenges of Exploration
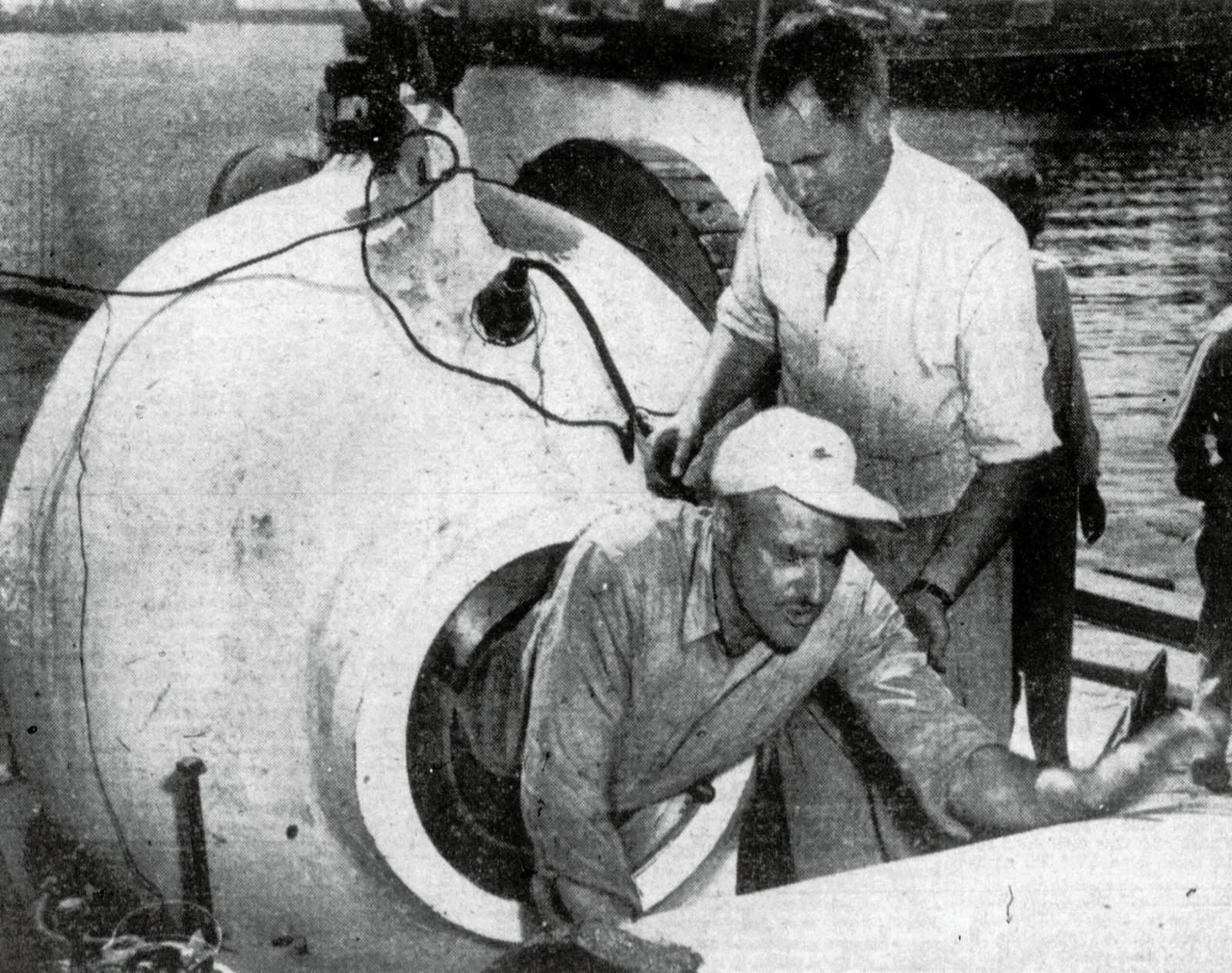
Exploring the twilight zone is like trying to study the dark side of the moon. Crushing pressure, frigid temperatures, and perpetual darkness make it a nightmare for traditional research tools. Remotely operated vehicles (ROVs), submersibles, and new generations of deep-sea drones are slowly unlocking its secrets. Even so, much of what we know comes from fleeting glimpses or creatures caught in nets. The twilight zone’s vastness and remoteness mean that every expedition is a high-stakes adventure, with discoveries waiting at every turn.
The Role of Technology in Discovery

New technologies are revolutionizing our understanding of the twilight zone. High-definition cameras, environmental DNA samplers, and autonomous underwater vehicles now allow scientists to observe life without disturbing it. These tools can spend months drifting through the zone, capturing data that was impossible to obtain a decade ago. Artificial intelligence is helping sort through mountains of footage to identify species and behaviors. The technological leap is like handing a magnifying glass to a detective in a dimly lit room—suddenly, hidden details come into sharp focus.
Human Impact and Threats to the Twilight Zone

Despite its remoteness, the twilight zone is not immune to human activities. Commercial fishing is starting to target mesopelagic fish as surface stocks dwindle, raising concerns about overexploitation. Pollution—especially plastics—can drift down and accumulate in the zone, threatening delicate food webs. Climate change is altering temperature and oxygen levels, forcing creatures to adapt or perish. These threats are largely invisible to the public, making it urgent to raise awareness and protect this vulnerable ecosystem before damage becomes irreversible.
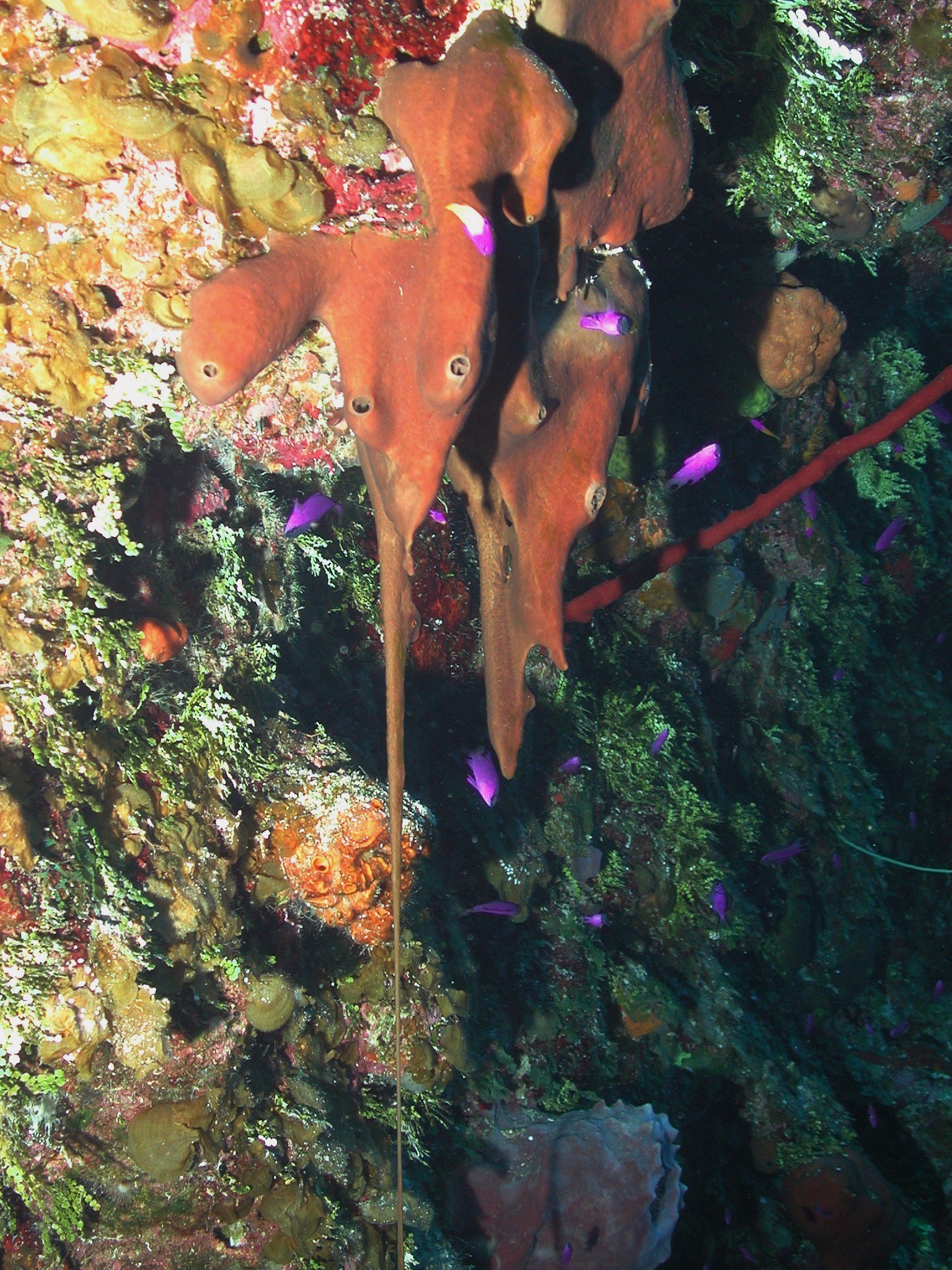
The Promise of New Medicines

Some of the twilight zone’s strangest inhabitants could hold the key to future medical breakthroughs. Deep-sea bacteria and sponges produce unique compounds to survive extreme conditions, some of which show promise as antibiotics or cancer treatments. Scientists are just scratching the surface, but already, molecules found in these depths are inspiring new drugs and biotechnologies. The next wonder drug might not come from a rainforest or a laboratory—it could come from a creature glowing in the darkness hundreds of meters below the waves.
Myths, Legends, and Pop Culture
For centuries, the twilight zone has inspired tales of sea monsters, glowing serpents, and ghostly ships. Sailors feared what lurked beneath the waves, often spinning wild stories after glimpsing strange lights or shadowy shapes. Today, this mysterious zone still sparks the imagination, appearing in movies, books, and documentaries as a place of adventure and danger. The truth, as we’re learning, is even stranger than fiction—real-life monsters, glowing wonders, and alien-like landscapes exist just out of sight.
The Importance of Preserving the Twilight Zone

Protecting the twilight zone is more critical than ever. Its creatures are vital links in ocean food webs, and its processes help stabilize the planet’s climate. Yet, the zone’s remoteness makes it easy to ignore or exploit. Conservationists are calling for international agreements to manage fishing, mining, and pollution threats. By valuing the twilight zone not just as a resource, but as a living treasure, we can safeguard its wonders for future generations.
The Search for Alien Life Begins at Home
Astrobiologists—scientists who hunt for life beyond Earth—often look to the twilight zone for clues. Its extreme conditions mimic those found on icy moons like Europa or Enceladus. Studying how life thrives here helps us imagine what might be possible elsewhere in the universe. If life can survive crushing pressure, freezing temperatures, and eternal darkness in our own oceans, who knows what might exist beneath the ice of distant worlds?
Citizen Science and Public Involvement

You don’t need a PhD or a submarine to help explore the twilight zone. Citizen science projects invite people from all walks of life to help identify species in underwater photos, track migration patterns, or monitor ocean health. With every click and observation, the public becomes part of the greatest exploration of our time. It’s a reminder that curiosity and wonder belong to everyone, not just scientists.
What’s Next for Twilight Zone Research?

The future holds exciting possibilities for twilight zone exploration. Planned missions will send fleets of autonomous vehicles to map and monitor vast areas. Scientists hope to decode the region’s complex food webs and uncover the full impact of human activities. International collaborations are growing, uniting countries in the quest to understand and protect this enigmatic layer. Each new discovery brings us closer to understanding our planet’s most mysterious frontier.
The Last Frontier Beneath the Waves
Standing on a beach, it’s hard to imagine the teeming world that lies just a short distance offshore and hundreds of meters down. The twilight zone is a place where science meets wonder, where every answer leads to more questions. As we push deeper into its shadows, we are reminded of how much we have yet to learn—and how much we stand to lose. The twilight zone is not just a scientific curiosity; it’s a vital, living part of our planet, waiting for us to uncover its secrets.



