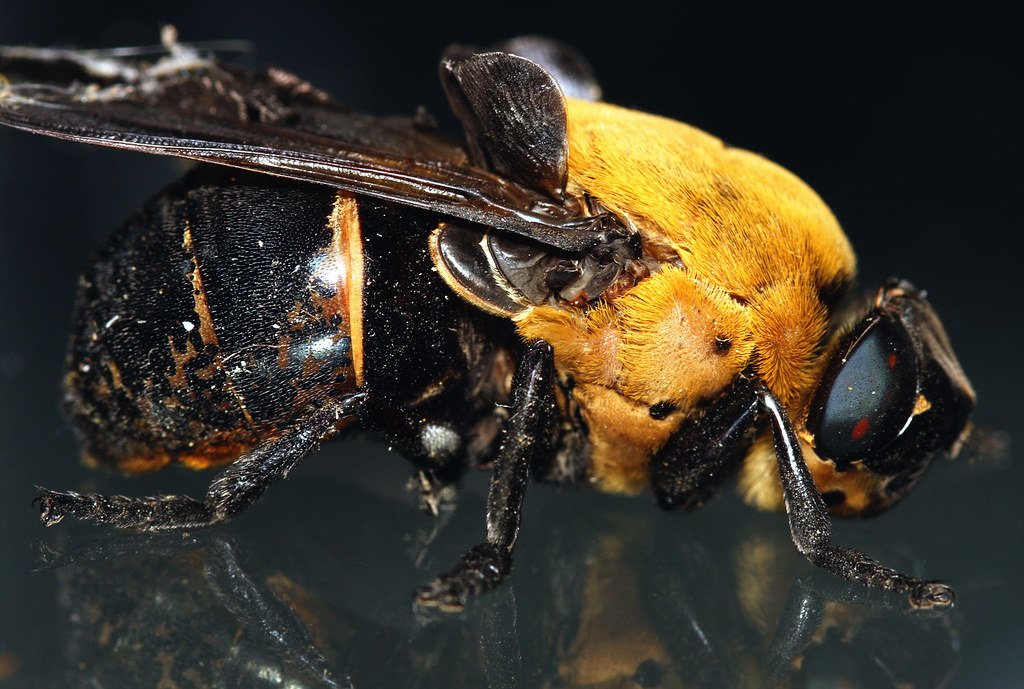
Imagine waking up one morning with an odd, itchy bump under your skin. At first, it might seem like a simple mosquito bite, but days pass and the spot becomes more painful, swollen, and disturbingly alive. You soon discover the shocking truth: something is living beneath your skin. This isn’t the plot of a horror movie—this is the real-life nightmare of a botfly infestation. The botfly, a creature both fascinating and horrifying, has mastered the art of turning unsuspecting mammals into living nurseries. Its lifecycle is a blend of science fiction and raw nature at its most bizarre, captivating the minds of scientists and sending shivers down the spines of adventurers around the world.
What Exactly Is a Botfly?
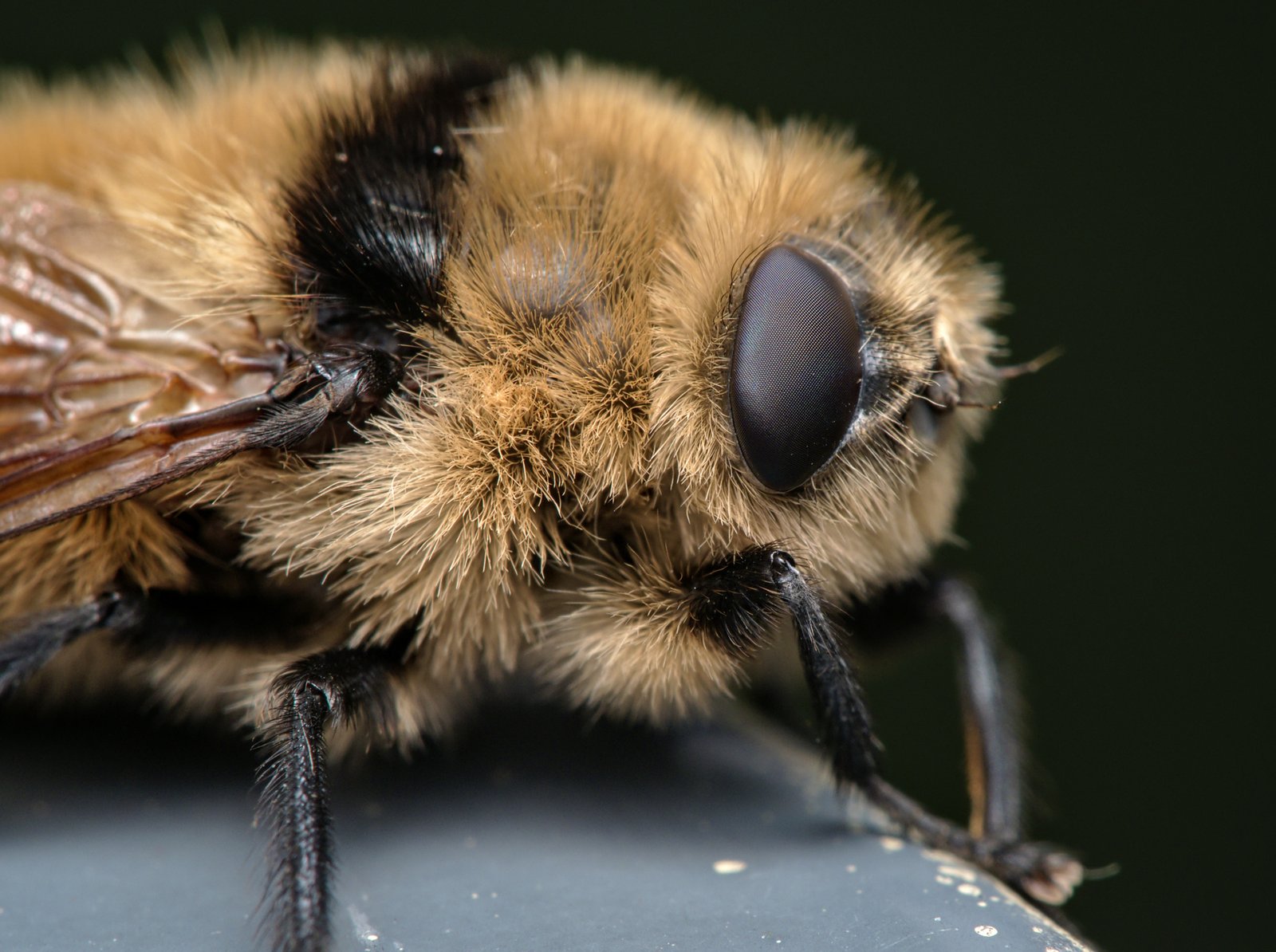

The botfly is a member of the Oestridae family, a group of flies notorious for their parasitic larvae. Unlike the harmless housefly, botflies have a unique and unsettling reproductive strategy. They lay their eggs on other insects, which then unwittingly transport these eggs to mammals—including humans. This particular behavior has earned the botfly a reputation as one of the most cunning parasites in the animal kingdom. Despite their somewhat ordinary appearance as adults, their larvae are anything but ordinary. They are perfectly designed to invade, survive, and grow inside living flesh.
The Ingenious Strategy of Egg Delivery
Botflies rarely lay their eggs directly on a host. Instead, they hijack mosquitoes, ticks, or even flies to do their dirty work. The female botfly captures these insects mid-flight, glues her eggs onto them, and releases them back into the wild. When the carrier insect lands on a warm-blooded animal to feed, the heat triggers the botfly eggs to hatch. The tiny larvae then wriggle their way into the skin through hair follicles, bites, or even unbroken skin. It’s a marvel of evolutionary engineering, using one insect as a delivery system for another.
The Shocking Life Cycle of the Botfly
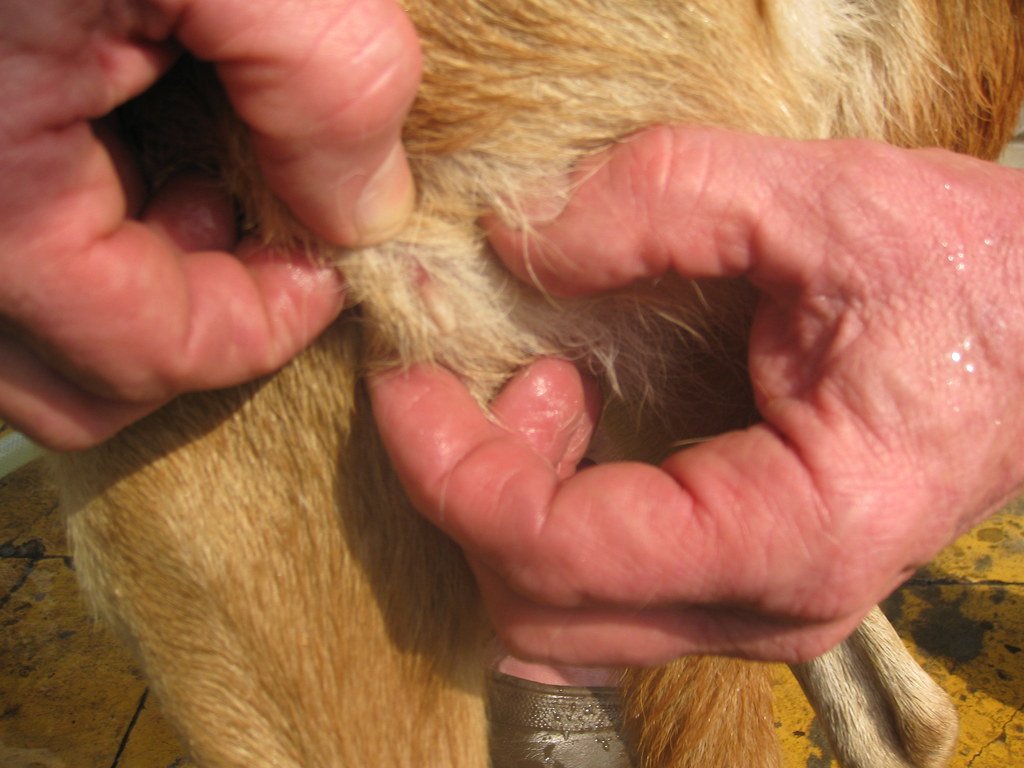
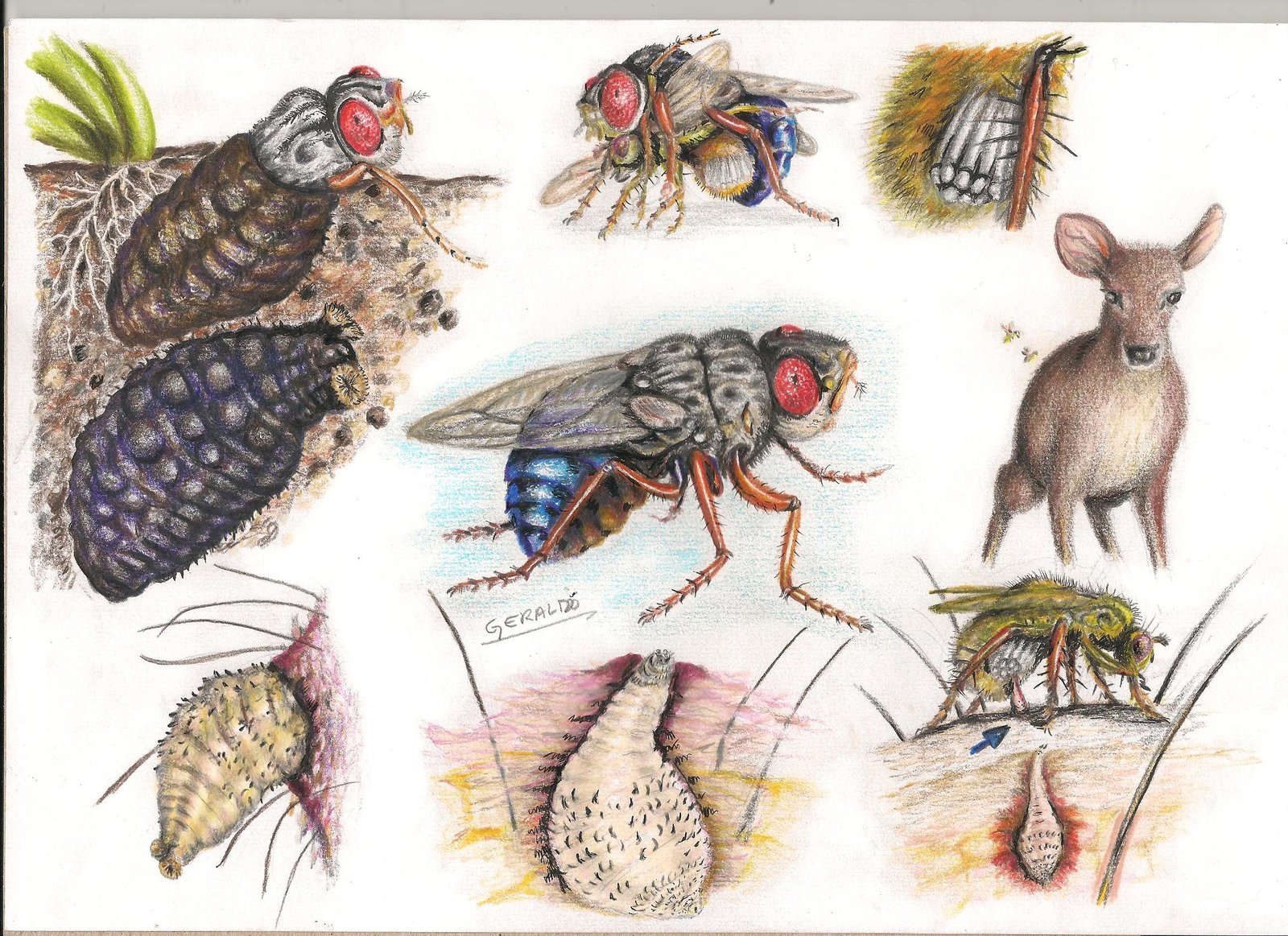
Once inside the host’s skin, the botfly larva begins its bizarre transformation. It carves out a small, air-hole-equipped chamber beneath the surface, ensuring it can breathe while it feeds. Over the course of several weeks, the larva grows, shedding its skin multiple times and increasing in size dramatically. During this stage, the host often feels itching, pain, and even movement as the larva wriggles beneath the skin. Eventually, the mature botfly larva works its way out of the host to drop into the soil, where it pupates and becomes an adult fly ready to start the cycle again.
Where in the World Do Botflies Live?
Botflies are found in various parts of the world, but the most infamous species affecting humans, Dermatobia hominis, thrives in Central and South America. Dense rainforests and humid environments provide the perfect backdrop for their lifecycle. However, botflies are not exclusive to the tropics; some species target livestock in North America, Europe, and Africa. Travelers to botfly hotspots are often warned to be extra vigilant about insect bites, especially during the rainy season when botflies are most active.
The Human Botfly: Dermatobia hominis
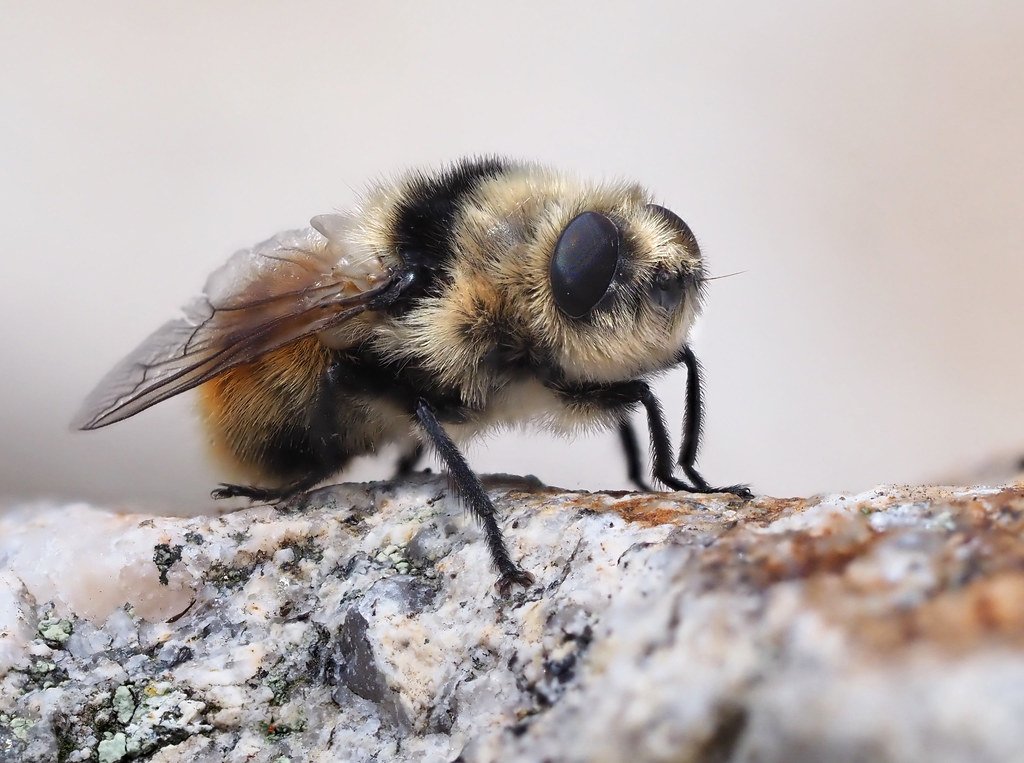

Dermatobia hominis is the primary culprit behind human botfly infestations. Unlike its relatives that target cattle or rodents, this species has evolved to use humans as one of its preferred hosts. The larvae can grow up to two centimeters long under the skin, causing considerable discomfort and sometimes secondary infections. While rarely life-threatening, an encounter with Dermatobia hominis is unforgettable and can leave lasting scars—both physical and psychological. The experience is often described as both fascinating and deeply unsettling.
How Does It Feel to Host a Botfly Larva?
People who have hosted botfly larvae often report a strange mix of sensations. It may start as an itchy bump, but as the larva grows, the area becomes swollen and tender. Some individuals describe a “creeping” sensation as the larva moves. In rare cases, you might even see a part of the larva poking out, using its tail end to breathe. The wound can become red, oozy, and painful if left unattended. The psychological impact can be just as profound, with feelings of disgust, anxiety, and even fascination.
The Removal Process: Not for the Faint of Heart

Extracting a botfly larva is not a task for the squeamish. Traditionally, people have used bacon, petroleum jelly, or even nail polish to block the larva’s air hole, forcing it to emerge in search of oxygen. Once the larva surfaces, it can be carefully pulled out with tweezers. Medical professionals may use surgical techniques for larger or deeper larvae. The process must be done carefully to avoid breaking the larva, which can lead to infection. Despite the horror of the act, many people feel an odd sense of relief and triumph once the creature is gone.
Risks and Complications of Botfly Infestation
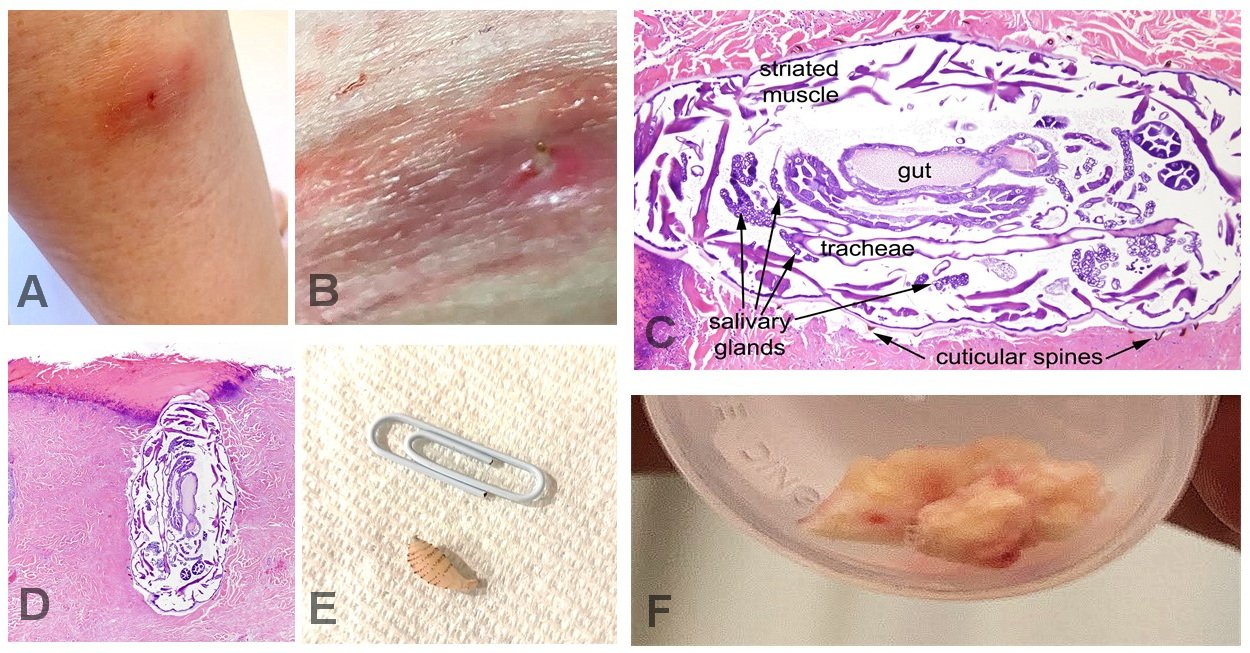
Although botfly infestations rarely cause serious health problems, complications can occur. If the larva dies inside the skin or is improperly removed, the wound can become infected. Some people may develop allergic reactions, while others might experience prolonged pain or scarring. Secondary bacterial infections are a particular concern in tropical environments where hygiene may be difficult to maintain. Timely and careful removal is crucial for minimizing these risks.
Botflies in Animals: A Hidden Epidemic
Botflies don’t just target humans—they’re a persistent problem for a variety of animals. Livestock, such as cattle and horses, often suffer from botfly infestations that can cause weight loss, discomfort, and even death in severe cases. Wild mammals, including rabbits and rodents, are also frequent hosts. In some regions, botflies play a significant role in local ecosystems by controlling animal populations and serving as food for other predators once they leave their hosts.
Evolutionary Wonders: Why Botflies Thrive

Botflies have evolved some of the most complex and effective reproductive strategies in the insect world. Their use of intermediate vectors, ability to sense host body heat, and adaptations for breathing under the skin are all products of millions of years of evolution. These adaptations have made botflies remarkably resilient and successful, allowing them to persist in diverse environments and exploit a wide range of hosts.
Botflies in Popular Culture and Folklore

The botfly’s bizarre life cycle has captured the human imagination for centuries. In some cultures, botflies are seen as symbols of persistence or resilience. In others, they are feared as omens of disease or misfortune. Television documentaries and viral internet videos have further fueled fascination, often highlighting the horror and spectacle of botfly removal. Despite their unsettling nature, botflies have found a strange place in the world of human storytelling.
How to Avoid Botfly Infestation
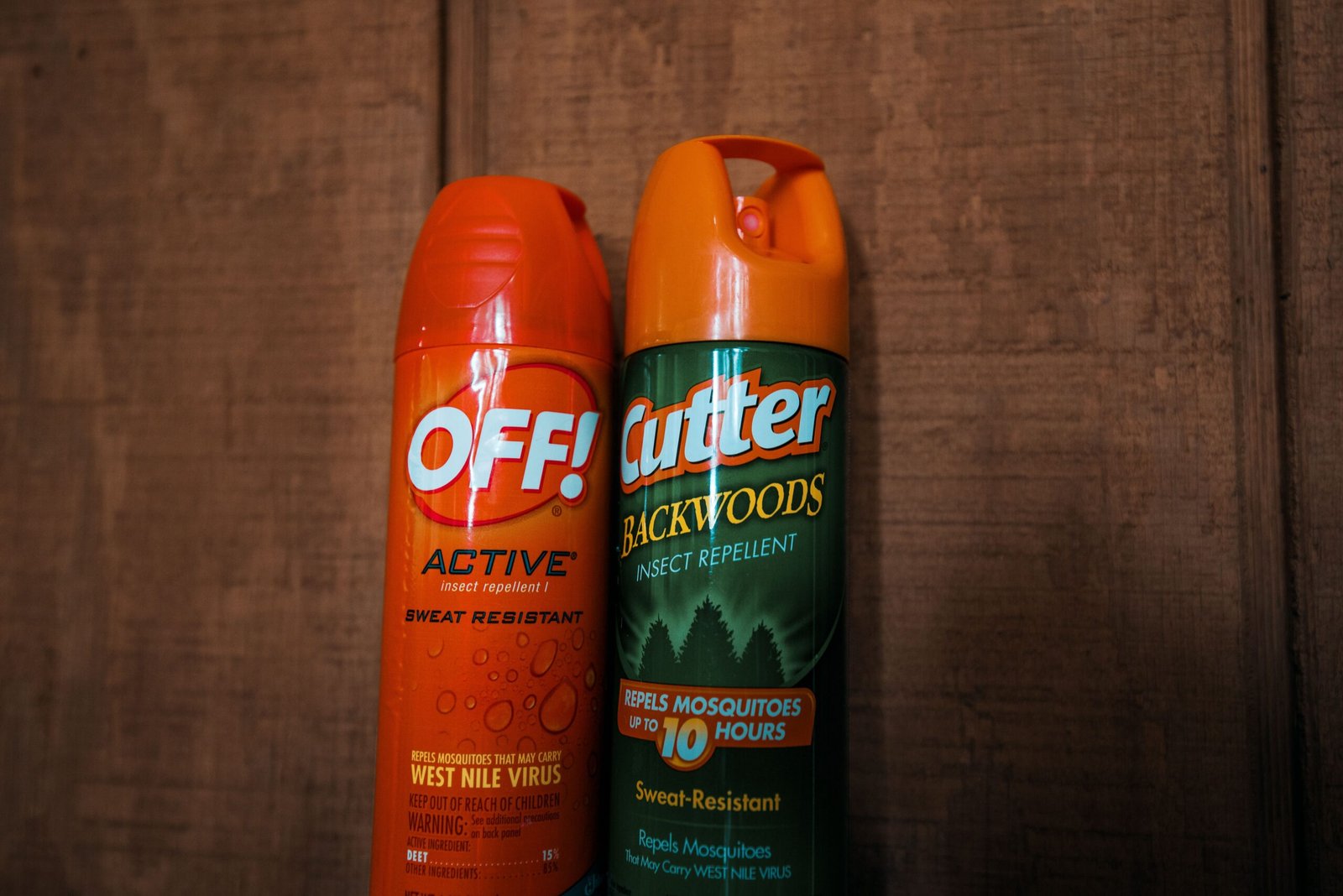

Travelers to botfly-prone areas can take several steps to reduce their risk. Wearing long sleeves and pants, using insect repellent, and sleeping under mosquito nets are effective defenses. Checking your skin regularly for insect bites and promptly treating any wounds can help detect larvae early. It’s also wise to avoid sitting or lying directly on the ground in endemic areas. Awareness and prevention are your best allies when exploring botfly territory.
Medical Advances in Treatment and Prevention
Modern medicine has improved the diagnosis and treatment of botfly infestations. Physicians use ultrasound imaging to locate larvae and specialized tools for extraction. Antibiotics may be prescribed to prevent secondary infections. Research continues into vaccines and repellents that could offer even greater protection, especially for livestock populations. These advancements are helping to reduce the burden of botflies on both humans and animals.
The Role of Botflies in Ecosystems

Botflies, as gruesome as they seem, play important roles in their native ecosystems. By parasitizing certain animal populations, they help maintain ecological balance. Their larvae serve as food for birds and other predators once they leave their hosts. Even the wounds they cause can provide entry points for decomposer organisms, aiding in nutrient cycling. The botfly’s existence is a reminder of nature’s interconnected complexity.
Personal Encounters: Tales of the Unexpected

Many travelers and locals alike have stories about botfly encounters. Some recount the initial confusion and mounting horror as they realize what’s living beneath their skin. Others speak of the strange bond they feel with the creature after weeks of coexistence. It’s not uncommon to feel a mix of disgust, curiosity, and even awe at the resilience of both host and parasite. These stories often become the stuff of legend, shared around campfires and family gatherings.
Botflies and Human Curiosity

Despite their fearsome reputation, botflies have inspired curiosity and scientific inquiry. Entomologists study their lifecycles to better understand parasitism and host behavior. Adventurers seek out botfly hotspots for the thrill of encountering one firsthand. The botfly challenges our notions of comfort and safety, forcing us to confront the wildness that still exists in the natural world. In a way, they are a living reminder of the planet’s enduring mysteries.
The Unexpected Upside: What Botflies Teach Us

As unsettling as botflies are, they offer valuable lessons about adaptation, survival, and the interconnectedness of life. They remind us that every creature has a role, however uncomfortable it may be for us. Observing the botfly’s lifecycle can deepen our appreciation for nature’s creativity and resilience. In a world increasingly sanitized and controlled, encounters with creatures like the botfly pull us back into the raw reality of the natural world.