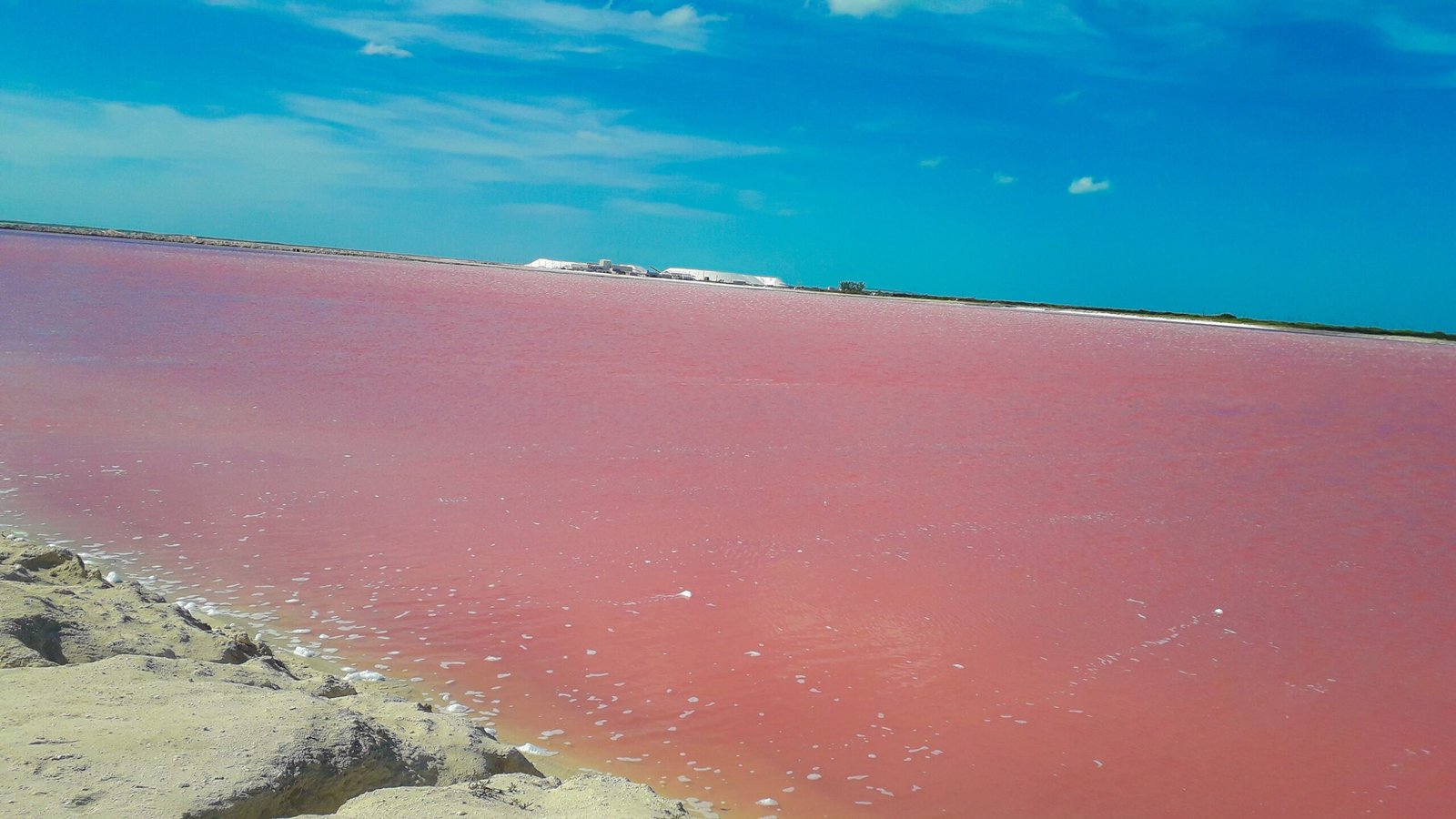
Have you ever wondered why some lakes are a vibrant shade of pink? The phenomenon is as captivating as it is perplexing, drawing in curious minds and nature enthusiasts alike. In Mexico, the pink lakes are not just a feast for the eyes but a testament to the wonders of nature’s microbial ecosystems. These lakes, with their bubblegum hues, are more than just a pretty sight—they are a complex interplay of biology, chemistry, and environmental factors. But what exactly causes these lakes to turn pink, and why are they so special? Let’s delve into the fascinating world of Mexico’s pink lakes.
The Science Behind the Pink Hue
The enchanting pink color of these lakes is primarily due to the presence of microorganisms that thrive in high-salinity environments. One of the main contributors is a type of algae known as Dunaliella salina. This microalga produces carotenoids, particularly beta-carotene, which gives the water its pinkish hue. Additionally, halophilic bacteria, or salt-loving bacteria, such as Halobacteria, also contribute to the color with their reddish pigments. These organisms have adapted to survive in extreme conditions, where most life forms would perish, making the pink lakes a unique ecological niche.
Environmental Conditions Favoring Pink Lakes
The formation of pink lakes is not a random occurrence; it requires a specific set of environmental conditions. High salinity is a crucial factor, often resulting from the evaporation of water in arid climates. This concentration of salt creates an inhospitable environment for most organisms, allowing specialized microbes to flourish. The intense sunlight typical of these regions enhances the production of pigments in the microorganisms, further intensifying the pink color. Moreover, the shallow nature of these lakes means that sunlight can penetrate easily, promoting photosynthesis and the growth of pigment-producing algae and bacteria.
The Role of Salt Production
Interestingly, many of Mexico’s pink lakes are also sites for salt production. The process involves the evaporation of seawater, leaving behind salt crystals. As the water evaporates, the concentration of microorganisms increases, amplifying the pink color. This dual role of the lakes as both natural wonders and economic resources highlights their significance. The salt harvested from these lakes is not only a vital commodity but also a testament to the harmonious coexistence of nature and human industry. It’s a delicate balance that requires careful management to preserve the ecological integrity of the lakes.
A Haven for Unique Wildlife
The pink lakes are not just home to microorganisms; they also support a diverse range of wildlife. Flamingos are particularly drawn to these areas, attracted by the abundance of food. The carotenoids in the algae and bacteria are ingested by the flamingos, contributing to their distinctive pink plumage. This vibrant ecosystem provides a sanctuary for various bird species, making it a hotspot for birdwatchers and photographers. The interplay between the organisms in the lake and the wildlife it supports is a fascinating example of nature’s interconnectedness.
Tourism and Its Impact
The striking beauty of the pink lakes has not gone unnoticed, and they have become popular tourist destinations. While tourism can boost local economies, it also poses challenges. Increased human activity can disrupt the delicate balance of the ecosystem, impacting the very features that make these lakes so special. Responsible tourism practices are essential to ensure that visitors can enjoy the lakes without causing harm. This includes regulating access, educating tourists about the ecological importance of the lakes, and implementing measures to minimize environmental impact.
Conservation Efforts
Given their ecological significance and vulnerability, conservation efforts are crucial to protect Mexico’s pink lakes. These efforts focus on preserving the unique microbial communities and the overall health of the ecosystem. Initiatives include monitoring water quality, regulating salt production, and conducting research to better understand the dynamics of these ecosystems. Collaboration between scientists, local communities, and policymakers is essential to develop and implement effective conservation strategies. By safeguarding these natural wonders, we ensure that future generations can continue to marvel at their beauty and complexity.
The Cultural Significance

Beyond their ecological and economic roles, the pink lakes hold cultural significance for local communities. They are often steeped in folklore and tradition, serving as symbols of natural beauty and resilience. The lakes have inspired art, literature, and music, reflecting their deep connection to the cultural identity of the region. This cultural heritage adds another layer of value to the lakes, emphasizing the need to preserve them not just as ecological treasures but as cultural landmarks.
Scientific Research Opportunities
The unique conditions of the pink lakes provide a valuable opportunity for scientific research. Studying these ecosystems can offer insights into extremophiles—organisms that thrive in extreme environments—and their potential applications in biotechnology. Research into the adaptive mechanisms of these microorganisms could lead to breakthroughs in fields such as medicine, agriculture, and environmental science. The pink lakes serve as natural laboratories, offering a glimpse into the resilience and adaptability of life in the face of challenging conditions.
A Call to Action

The pink lakes of Mexico are a reminder of the wonders of the natural world and the importance of preserving it. As stewards of the planet, it is our responsibility to protect these unique ecosystems. This involves raising awareness, supporting conservation efforts, and advocating for sustainable practices. By doing so, we ensure that the pink lakes continue to inspire awe and wonder for generations to come. The question remains: How can we balance human interests with the preservation of such natural marvels?