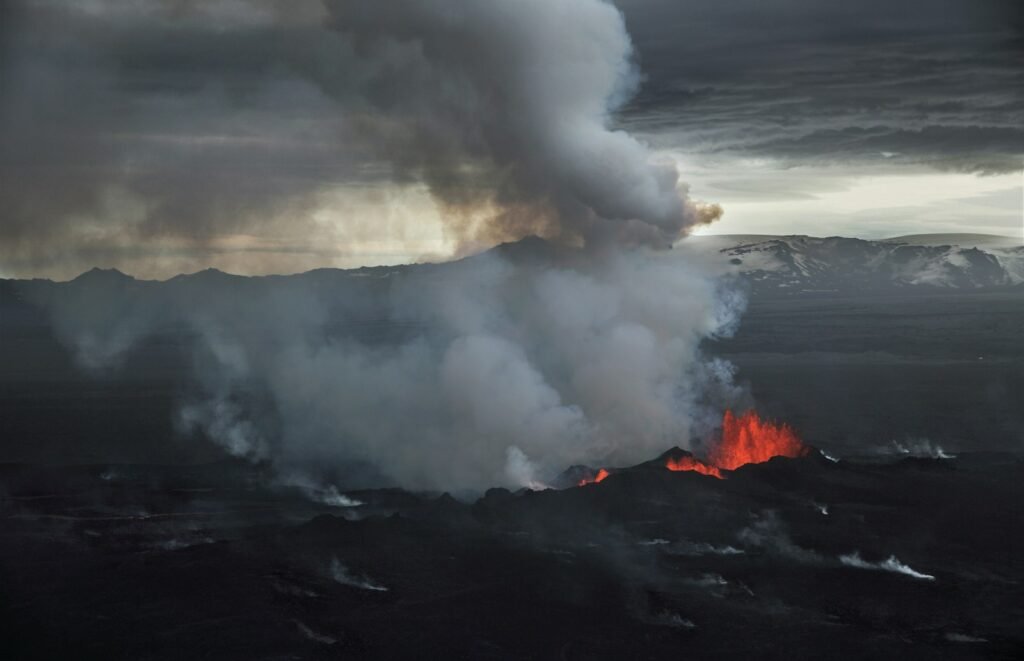
Imagine a world where the very ground beneath your feet could erupt without warning, altering landscapes and reshaping human history. This isn’t a tale from a fantasy novel but a reality in El Salvador, a country marked by its volatile volcanic past. The “lost” craters of El Salvador tell a story of fiery blasts and monumental changes that have left indelible marks on the planet and its people. These craters, remnants of ancient volcanic eruptions, hold secrets of the past that continue to captivate scientists and history enthusiasts alike. As we delve into this fascinating topic, we uncover how these natural phenomena have sculpted the land and influenced human civilization in profound ways.
The Volcanic Backbone of El Salvador

El Salvador, a small yet vibrant nation in Central America, is home to an impressive array of volcanoes. Known as the “Land of Volcanoes,” it boasts over 20 active volcanoes, each with its own unique history and character. These geological wonders form a volcanic backbone that stretches across the country, shaping its landscape and influencing its climate. The volcanic activity in this region is a result of the Pacific Ring of Fire, a horseshoe-shaped area known for its seismic activity. This geological feature has given rise to the numerous craters that dot the Salvadoran terrain, each a testament to the earth’s fiery past.
The Birth of the “Lost” Craters

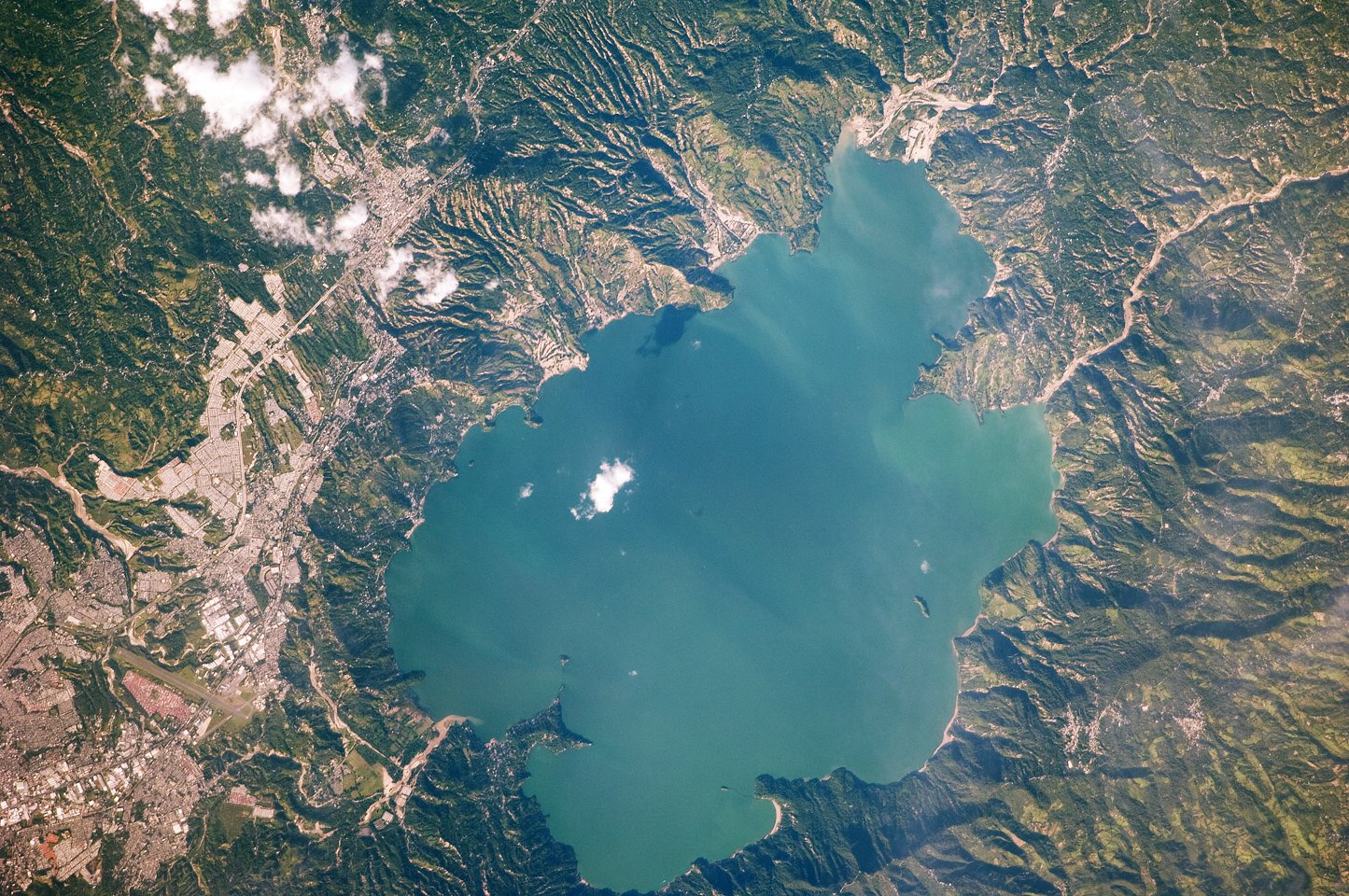
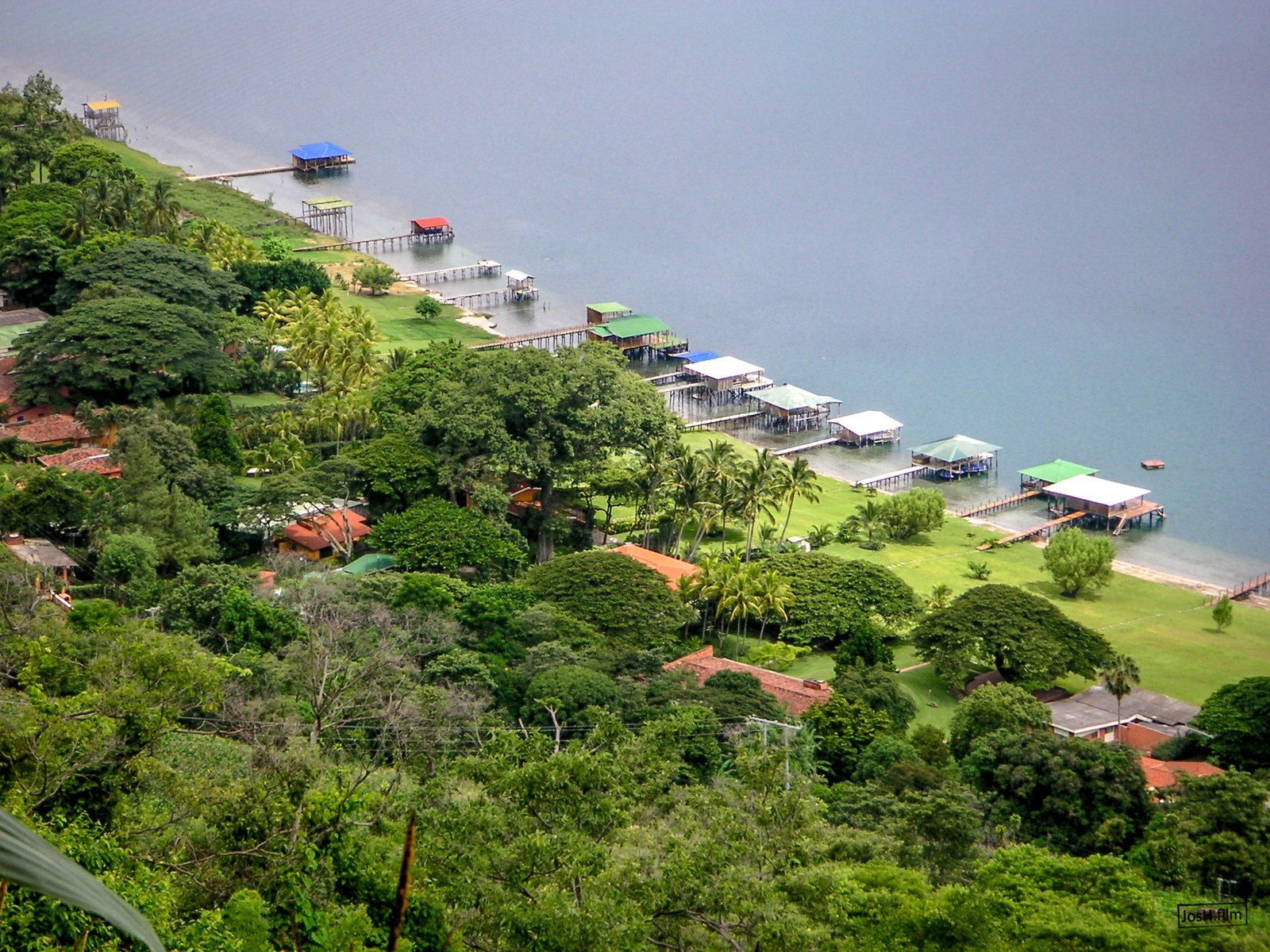
The “lost” craters of El Salvador are a result of massive volcanic eruptions that occurred thousands of years ago. These eruptions were so powerful that they left behind vast calderas, or large volcanic craters, that have since been obscured by time and vegetation. One of the most significant eruptions was that of the Ilopango volcano, which erupted around 1,500 years ago. This cataclysmic event spewed ash and lava across the region, creating a massive caldera that is now filled by Lake Ilopango. Such eruptions have played a pivotal role in shaping the geography of El Salvador, leaving behind a legacy of craters that intrigue geologists and historians alike.
Impact on Human Civilization
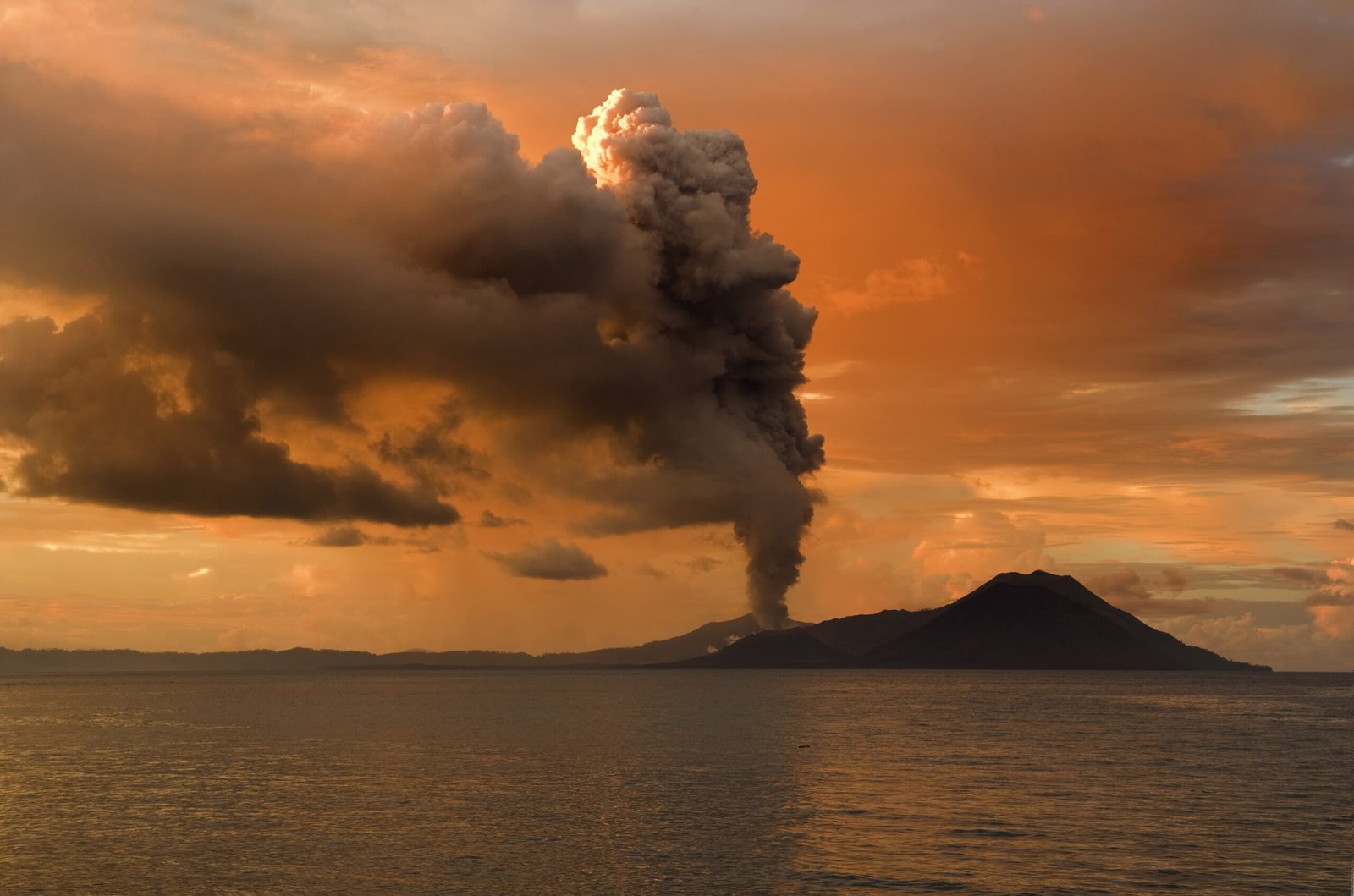

The volcanic activity in El Salvador has had a profound impact on human civilization. The eruption of the Ilopango volcano, for instance, is believed to have had far-reaching effects on the Mayan civilization, leading to significant cultural and societal changes. The ash and debris from the eruption would have caused widespread devastation, disrupting agriculture and forcing communities to adapt to new environmental conditions. Such events remind us of the delicate balance between nature and human society, highlighting the resilience and adaptability of our ancestors in the face of natural disasters.
Scientific Exploration and Discoveries

In recent years, scientific exploration has shed new light on the “lost” craters of El Salvador. Advances in technology have allowed researchers to study these volcanic formations in greater detail, uncovering clues about past eruptions and their impact on the environment. Techniques such as remote sensing and geochemical analysis have provided valuable insights into the composition and history of these craters, helping scientists piece together the puzzle of El Salvador’s volcanic past. These discoveries not only enhance our understanding of the region’s geology but also contribute to our broader knowledge of volcanic activity and its effects on the planet.
The Role of Volcanoes in Biodiversity
Volcanoes, despite their destructive power, play a crucial role in fostering biodiversity. The nutrient-rich soils created by volcanic eruptions provide an ideal environment for a wide variety of plant and animal species to thrive. In El Salvador, the “lost” craters have become habitats for diverse ecosystems, supporting an array of flora and fauna unique to the region. These natural sanctuaries offer a glimpse into the resilience of life, demonstrating how ecosystems can adapt and flourish in the wake of volcanic activity. The interplay between destruction and creation is a testament to the dynamic nature of our planet.
Volcanoes and Climate Change
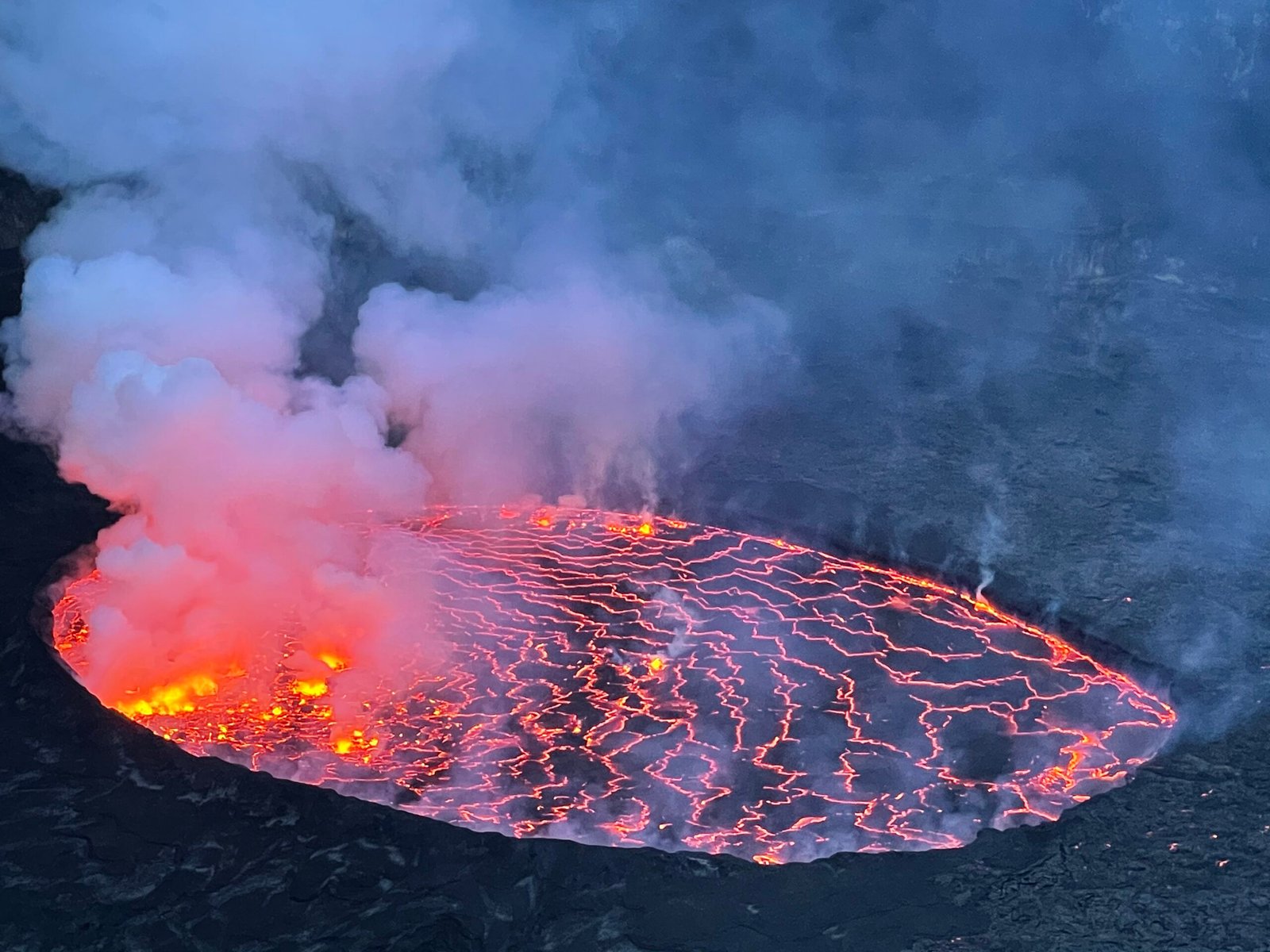

The eruptions of El Salvador’s volcanoes have also had implications for global climate patterns. The release of volcanic ash and gases into the atmosphere can lead to temporary cooling effects, as sunlight is blocked from reaching the earth’s surface. This phenomenon, known as volcanic winter, can have significant consequences for weather patterns and agricultural productivity. While the “lost” craters of El Salvador are remnants of ancient eruptions, they serve as a reminder of the interconnectedness of our planet’s systems and the potential impact of volcanic activity on climate change.
Cultural Significance and Myths
Volcanoes have long held a place in the cultural and spiritual beliefs of the people of El Salvador. Throughout history, these majestic formations have been revered and feared, inspiring myths and legends that reflect the awe and respect they command. In Salvadoran folklore, volcanoes are often seen as powerful deities, capable of both creation and destruction. These stories, passed down through generations, offer a glimpse into the cultural significance of volcanoes and their role in shaping the identity of the Salvadoran people.
Preserving the Craters for Future Generations
Preserving the “lost” craters of El Salvador is essential for future generations to appreciate and learn from these natural wonders. Conservation efforts are underway to protect these sites from human encroachment and environmental degradation. By safeguarding these geological treasures, we ensure that they continue to serve as valuable educational resources and sources of inspiration for years to come. The preservation of these craters is not only a testament to the importance of protecting our natural heritage but also a commitment to understanding the forces that have shaped our world.
The Call to Action

The “lost” craters of El Salvador offer a fascinating glimpse into the dynamic history of our planet. They remind us of the power and unpredictability of nature, as well as the resilience of human civilization in the face of adversity. As we continue to explore and study these volcanic formations, we are called to reflect on our relationship with the natural world and the importance of preserving it for future generations. What lessons can we learn from the past, and how can we apply them to create a more sustainable future? The answers lie within the craters themselves, waiting to be discovered.