China is on a mission, and it’s one that could change the face of its landscapes forever. The Gobi Desert, a vast and ever-expanding sandy expanse, has long posed a threat to the arable lands and communities on its periphery. But China has a plan—a colossal, audacious plan—to halt this relentless advance. Enter the Green Wall of China, a project as ambitious as it sounds. Similar to the Great Wall that once shielded the nation from invaders, this modern-day counterpart seeks to protect against a different kind of enemy: desertification. This living wall of trees stretches for thousands of kilometers, aiming to restore ecological balance and provide a green shield against the encroaching sands.
The Origins of the Green Wall
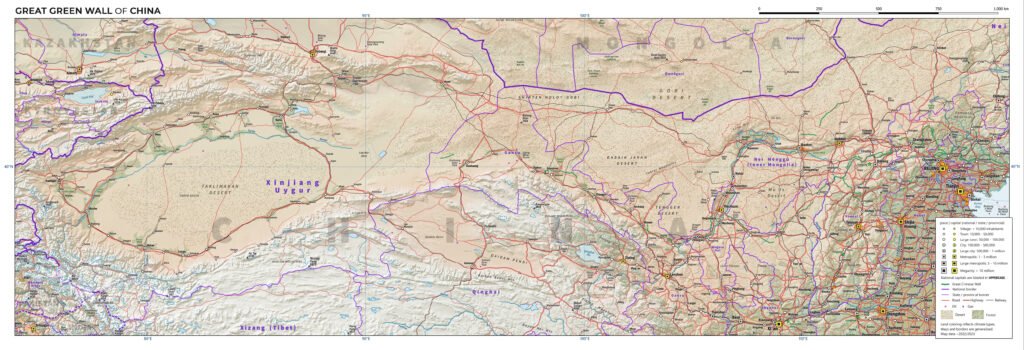
The idea of the Green Wall was born out of necessity. In the mid-20th century, China faced severe environmental challenges, with desertification among the most pressing. The relentless spread of deserts threatened agriculture, water resources, and even the air quality. The government recognized that action was needed. Thus, in the late 1970s, the Green Wall project was conceived, marking the beginning of a decades-long endeavor to reclaim the land. This initiative wasn’t just about planting trees; it was about creating a sustainable ecosystem that could withstand the harsh desert climate.
Understanding Desertification
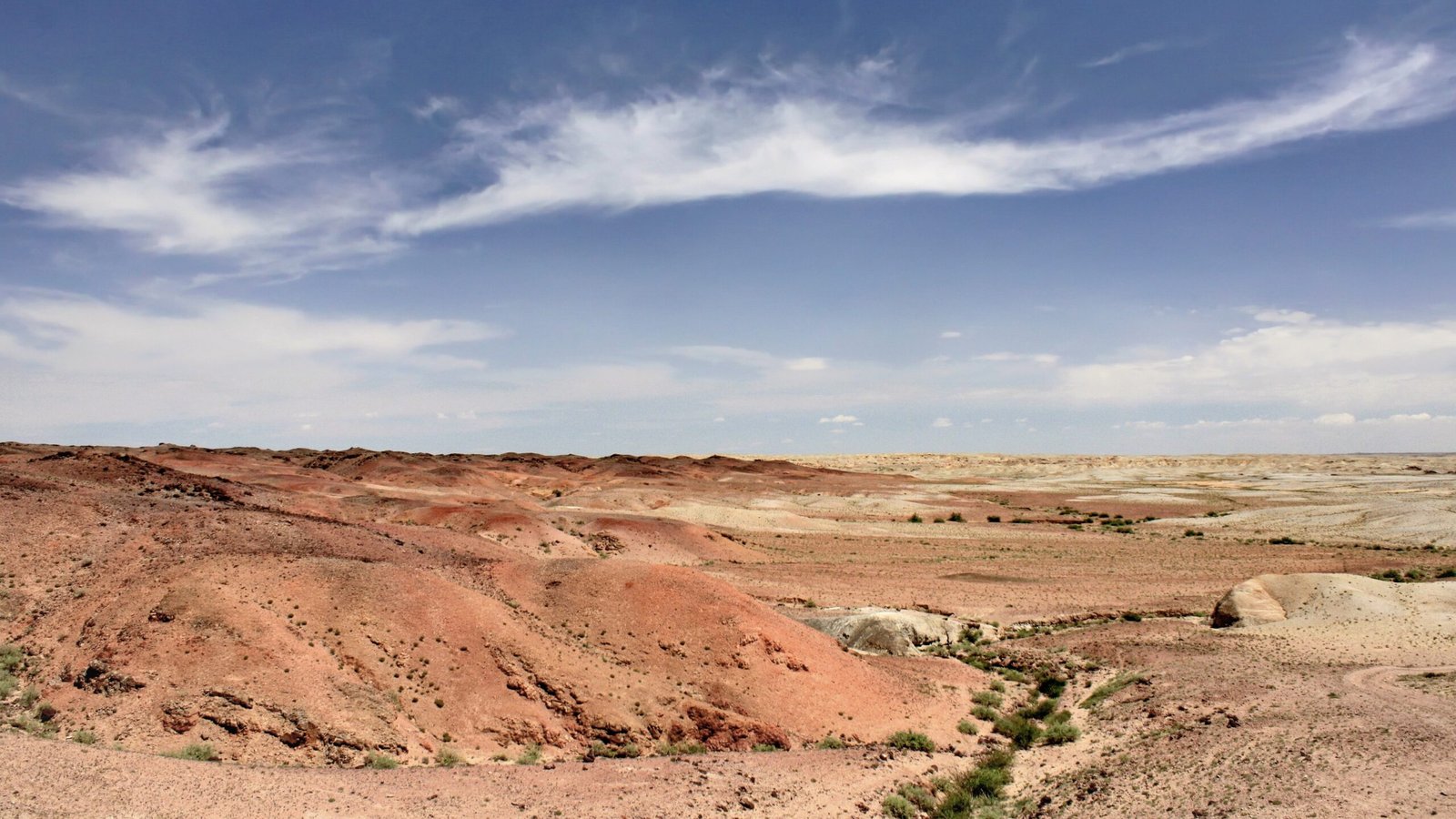

Desertification is more than just the spread of sand; it’s a complex process that involves the degradation of land in arid regions. Factors such as climate change, deforestation, and unsustainable agricultural practices contribute to this phenomenon. In the case of the Gobi Desert, a combination of natural and human-induced factors has accelerated its growth. As a result, fertile lands turn barren, water sources dry up, and biodiversity declines. Addressing these underlying causes is crucial to stopping the desert’s expansion, and the Green Wall is a strategic response to these challenges.
The Science Behind the Green Wall

The Green Wall isn’t just about planting any trees; it’s about planting the right trees in the right places. Scientists and ecologists have carefully selected species that are drought-resistant and suitable for the local soil and climate. This scientific approach ensures that the trees not only survive but thrive, creating a self-sustaining ecosystem. Additionally, the project incorporates modern technology to monitor growth patterns, soil conditions, and climatic changes. This data-driven approach allows for adjustments and improvements, making the Green Wall a dynamic and adaptive solution to desertification.
Community Involvement and Economic Impact
One of the key aspects of the Green Wall project is the involvement of local communities. By engaging farmers, herders, and residents in tree-planting efforts, the project fosters a sense of ownership and responsibility. This grassroots approach not only empowers communities but also provides economic benefits. The planting and maintenance of the Green Wall have created jobs, boosted local economies, and improved living standards. Moreover, the increased vegetation has enhanced agricultural productivity, providing a more stable food supply for the surrounding areas.
Challenges and Setbacks
The road to building the Green Wall has not been without obstacles. Harsh climatic conditions, such as extreme temperatures and limited rainfall, pose significant challenges to tree survival. Additionally, logistical issues, such as transporting water and materials to remote areas, complicate the project. There’s also the concern of maintaining biodiversity and preventing monocultures, which could lead to ecological imbalances. Despite these challenges, China remains committed to overcoming these hurdles through innovation, adaptation, and perseverance.
Success Stories and Milestones

Despite the challenges, the Green Wall project has achieved remarkable successes. Satellite images have shown a significant reduction in desert expansion in certain regions. Areas that were once barren are now lush with greenery, providing habitats for wildlife and improving air quality. The project has also successfully mitigated sandstorms, which once plagued cities and agricultural lands. These milestones demonstrate the potential of large-scale ecological restoration projects and serve as an inspiration for other nations facing similar challenges.
The Global Implications of China’s Green Wall
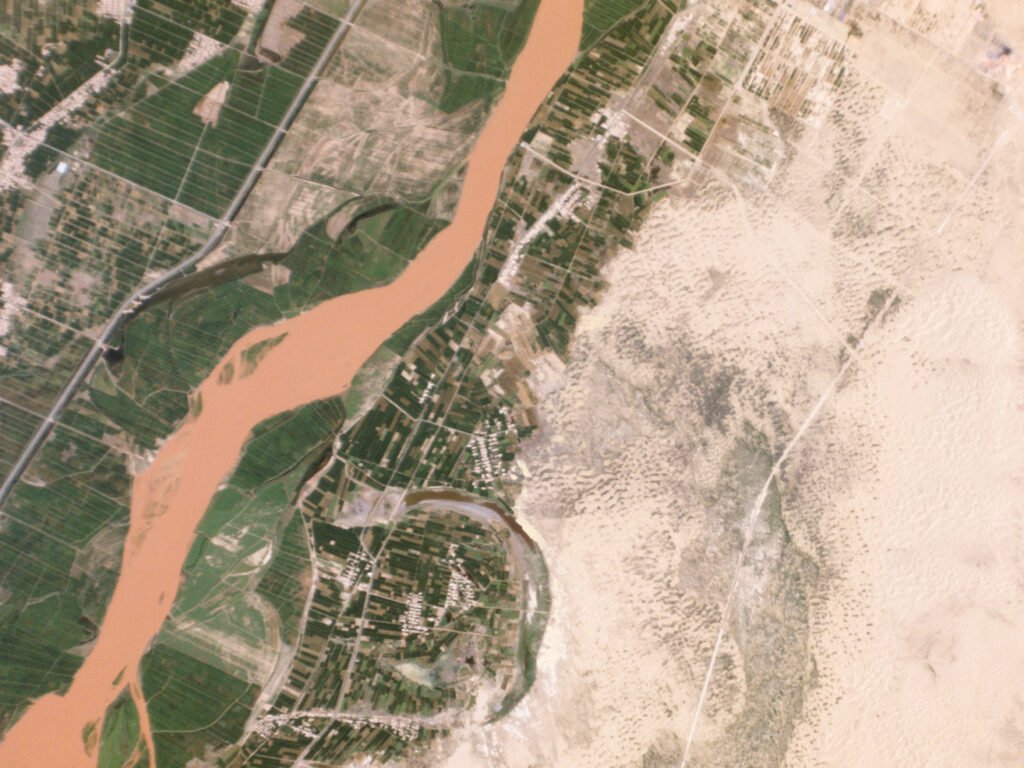

China’s Green Wall project has garnered international attention, serving as a model for other countries battling desertification. Its success highlights the importance of collaborative efforts in combating environmental issues, as desertification is a global problem requiring global solutions. The project also underscores the potential of large-scale reforestation efforts in mitigating climate change, as trees absorb carbon dioxide and contribute to cooling the planet. As such, China’s Green Wall is not only a national endeavor but a global beacon of hope.
Looking to the Future
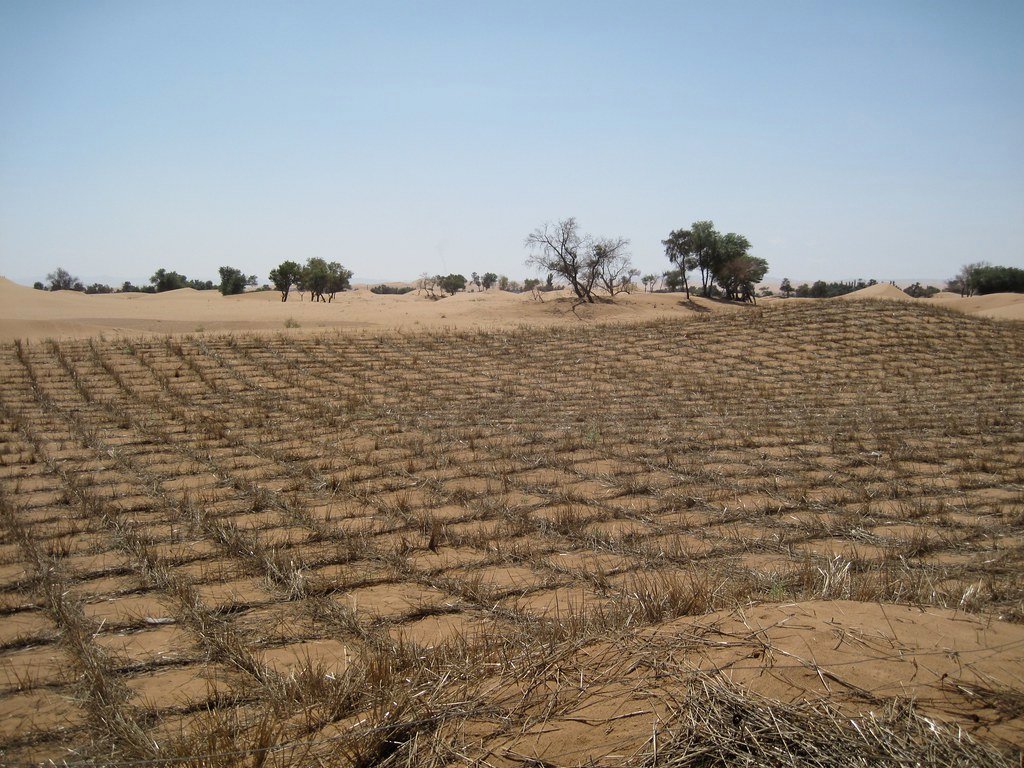

As the Green Wall continues to grow, the future looks promising. China is committed to expanding the project, with plans to increase the number of trees and extend the wall’s reach. The focus is also on enhancing biodiversity by introducing a wider variety of plant and animal species. With continuous research and innovation, the Green Wall is poised to become a resilient and sustainable solution to desertification. The hope is that it will not only stop the Gobi Desert in its tracks but also restore the land to its former glory.
The Role of Individuals and Communities
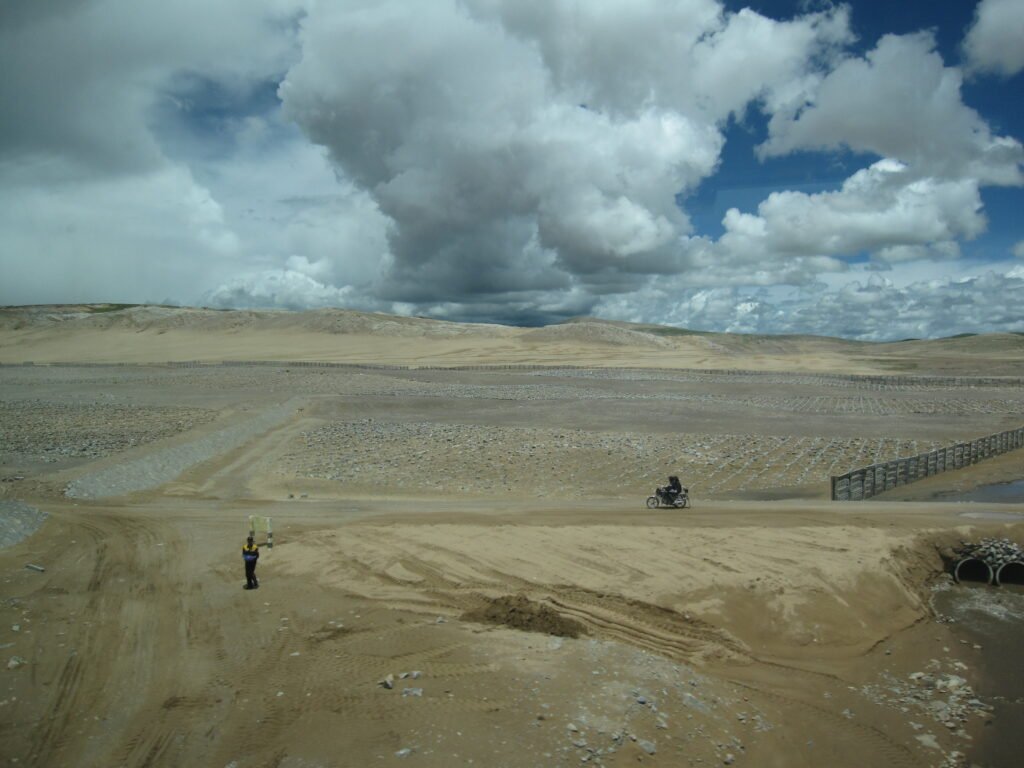

While the Green Wall is a monumental undertaking, its success also relies on the actions of individuals and communities. Every tree planted, every piece of land restored, contributes to the larger goal. Education and awareness campaigns are essential in promoting sustainable practices and encouraging active participation. By working together, people can make a significant impact, proving that when it comes to environmental preservation, every effort counts.
A Call to Action

The story of China’s Green Wall is a testament to human ingenuity and resilience in the face of environmental challenges. It serves as a reminder that with determination, collaboration, and innovation, seemingly insurmountable problems can be tackled. As the Green Wall continues to grow, it invites the world to reflect on our collective responsibility to protect and preserve our planet. The time to act is now, and every step taken today paves the way for a greener, more sustainable tomorrow.