The Aztecs, one of the most remarkable civilizations in history, were true masters of engineering. Despite the challenges posed by their environment, they managed to create a thriving society that was deeply intertwined with the natural world. Their cities were not just centers of culture and politics but also marvels of engineering ingenuity. The Aztecs were faced with the daunting task of managing water, navigating the threat of earthquakes, and living harmoniously with nature. In this article, we will explore how they accomplished these feats, leaving a legacy that continues to inspire awe and wonder.
The Floating Gardens: Chinampas

The Aztecs invented chinampas, a revolutionary agricultural technique that allowed them to cultivate crops on the surface of lakes. These floating gardens were essentially small, rectangular plots of fertile land constructed on shallow lake beds. The Aztecs used reeds, mud, and organic material to create these artificial islands, which were anchored by willow trees. This innovative method allowed them to maximize arable land, ensuring a steady food supply. Chinampas were highly productive and sustainable, providing a variety of crops such as maize, beans, and squash. This ingenuity in agriculture was a testament to the Aztecs’ ability to adapt to their surroundings and thrive.
Water Management: The Aqueducts and Canals

Managing water was crucial for the Aztecs, as their capital city, Tenochtitlán, was built on an island in Lake Texcoco. To address this, they constructed an elaborate system of aqueducts and canals. The aqueducts brought fresh water from nearby springs to the city, ensuring a reliable supply for drinking, irrigation, and sanitation. The canals, on the other hand, served as transportation routes, facilitating trade and communication. This sophisticated water management system not only supported the city’s population but also contributed to its economic prosperity. The Aztecs’ ability to harness and control water resources was a key factor in their success.
Earthquake Resilience: Building Techniques
Living in a region prone to earthquakes, the Aztecs developed building techniques that enhanced the resilience of their structures. They employed a method known as “floating foundations,” where structures were built on a bed of flexible materials like reeds and sand. This allowed buildings to absorb and dissipate seismic energy, reducing the risk of collapse. Moreover, Aztec architects used interlocking stones and precisely fitted masonry to create stable and durable constructions. These innovative approaches ensured that their temples, palaces, and homes could withstand the tremors of the earth, showcasing their understanding of natural forces.
Harnessing Natural Resources: Efficient Use of Materials

The Aztecs were adept at utilizing the natural resources available to them. They used locally sourced materials such as volcanic stone, clay, and wood to construct their buildings and infrastructure. Their understanding of these materials’ properties allowed them to design structures that were both functional and aesthetically pleasing. Additionally, they employed techniques to recycle and repurpose materials, minimizing waste and promoting sustainability. This efficient use of resources demonstrated the Aztecs’ commitment to living in harmony with their environment, a principle that is increasingly relevant today.
Urban Planning: The Layout of Tenochtitlán
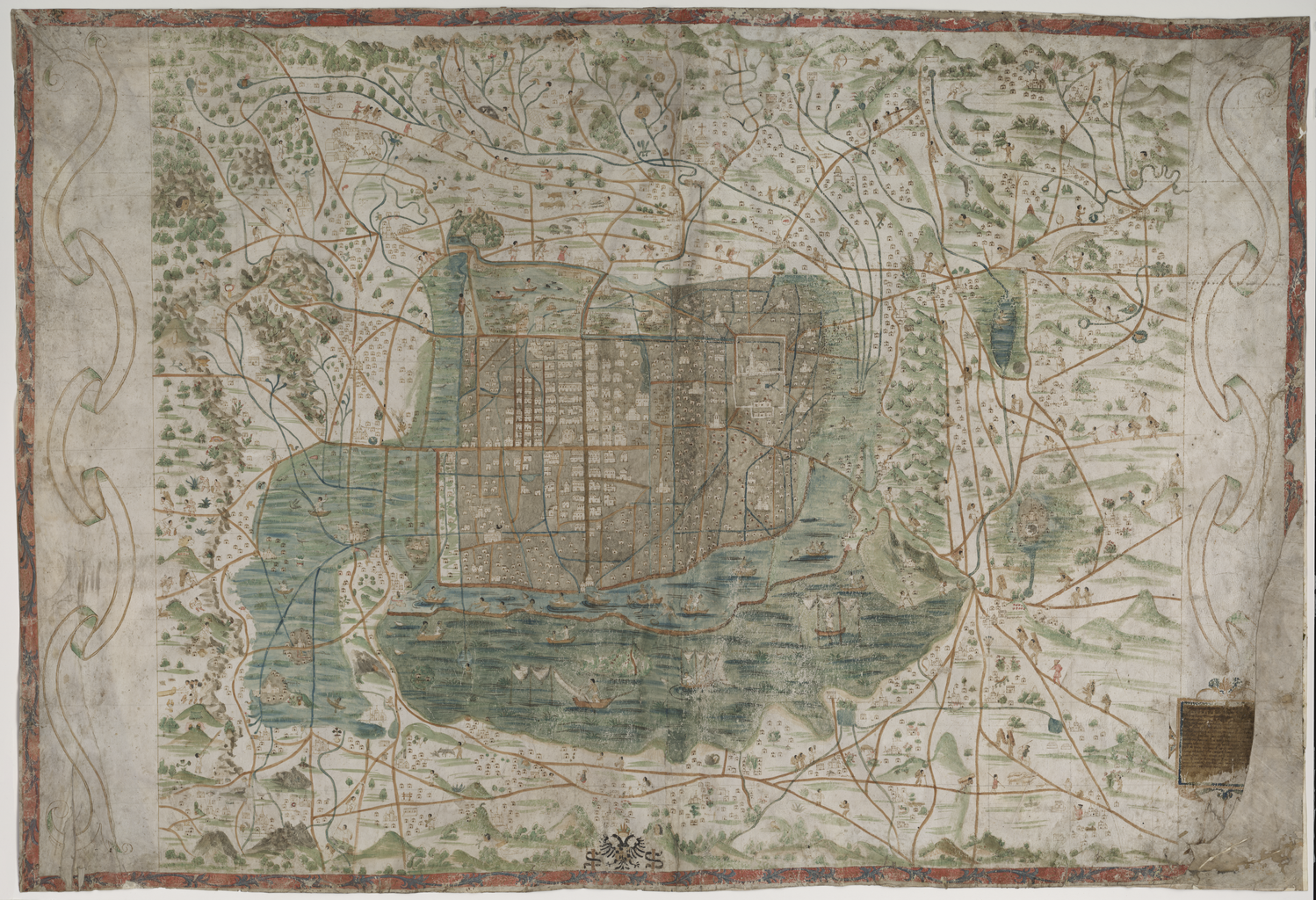
The layout of Tenochtitlán was a testament to Aztec urban planning and engineering prowess. The city was meticulously organized, with a grid-like pattern of streets and canals that facilitated movement and trade. The central plaza, known as the Templo Mayor, was the heart of the city, surrounded by important religious and administrative buildings. This strategic layout ensured efficient communication and commerce while promoting a sense of community and cohesion. The Aztecs’ ability to plan and execute such a complex urban design speaks to their advanced understanding of infrastructure and society.
Adapting to the Environment: Terracing and Agriculture

In addition to chinampas, the Aztecs employed terracing techniques to cultivate crops on hilly terrain. By creating stepped platforms on slopes, they were able to prevent soil erosion and optimize water usage. This allowed them to grow a diverse range of crops, supporting their growing population. The terraces also helped to regulate temperature and microclimates, further enhancing agricultural productivity. The Aztecs’ ability to adapt their farming methods to different environments ensured their food security and contributed to their civilization’s resilience.
The Role of Religion: Integrating Nature and Belief
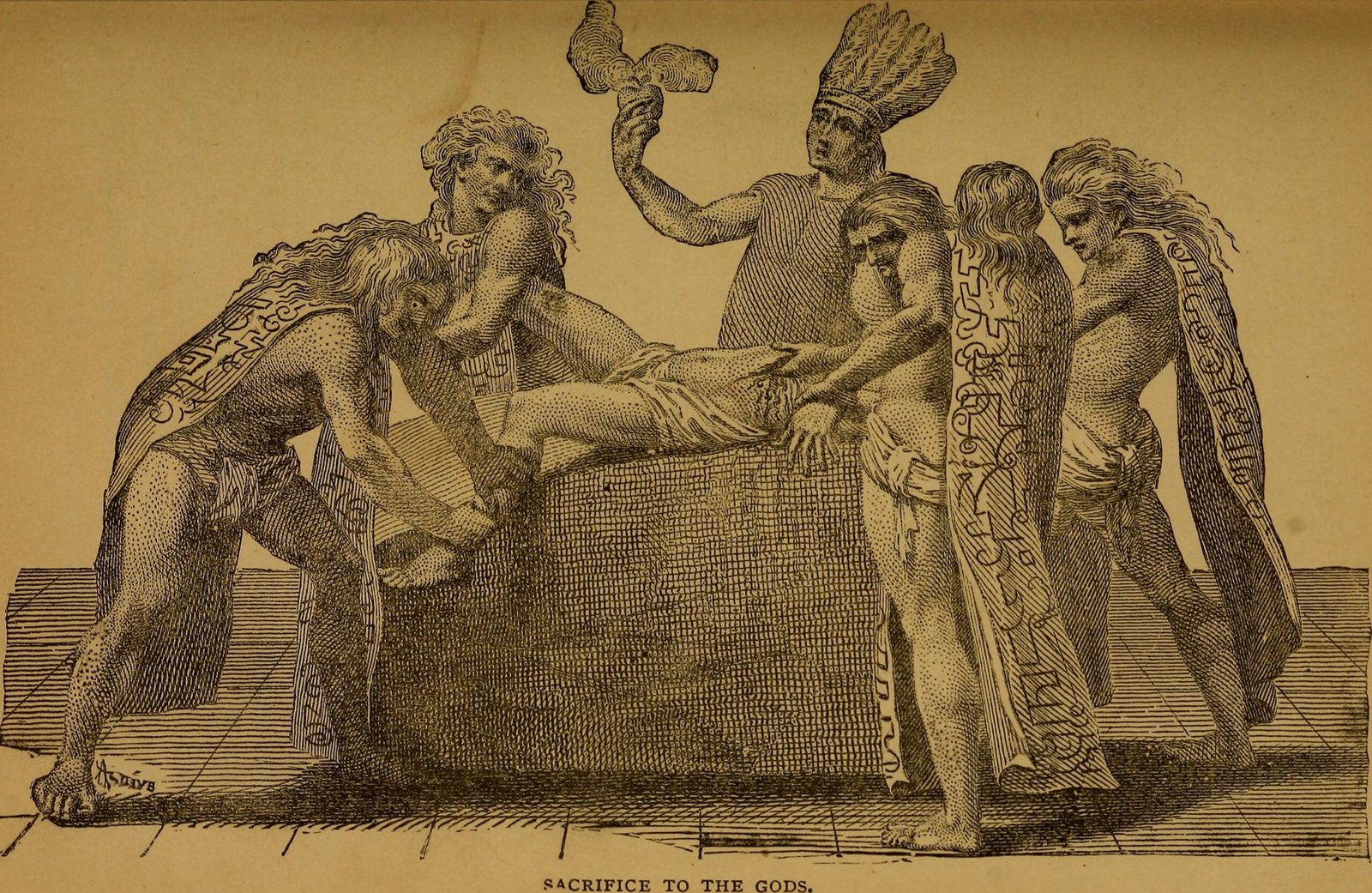

Religion played a significant role in Aztec society, and their engineering achievements were often intertwined with their beliefs. The Aztecs viewed nature as sacred and sought to maintain a harmonious relationship with it. This reverence for nature was reflected in their architectural designs, which often incorporated religious symbolism and aligned with celestial events. Temples were built to honor deities associated with natural elements, such as Tlaloc, the rain god. The integration of religion and engineering not only reinforced the Aztecs’ cultural identity but also provided a framework for understanding and interacting with the natural world.
Communication and Trade: The Role of Causeways

The Aztecs constructed an extensive network of causeways that connected Tenochtitlán to the mainland, facilitating trade and communication. These raised roads were built using stone and earth, allowing for the movement of goods and people across the lake. The causeways were equipped with drawbridges to control access to the city, providing both security and convenience. This infrastructure was crucial for maintaining the economic and political stability of the Aztec Empire. The causeways exemplified the Aztecs’ strategic thinking and their ability to integrate engineering with social and economic needs.
Art and Architecture: The Aesthetic Legacy
Aztec art and architecture were not only functional but also highly aesthetic, leaving a lasting legacy that continues to inspire. Their buildings were adorned with intricate carvings, sculptures, and murals that depicted religious and cultural themes. The use of vibrant colors and elaborate designs reflected the Aztecs’ appreciation for beauty and creativity. This artistic expression extended to their engineering projects, where form and function were seamlessly integrated. The Aztecs’ ability to combine practicality with artistry set a standard for architectural excellence that resonates with modern designers and architects.
A Legacy of Innovation: Lessons for the Modern World

The Aztecs’ engineering marvels offer valuable lessons for the modern world. Their ability to adapt to their environment, utilize natural resources efficiently, and integrate technology with culture and belief systems is a testament to their ingenuity and foresight. As we face challenges such as climate change, resource scarcity, and urbanization, the Aztecs’ approach to sustainable living and harmonious interaction with nature serves as a model for future generations. Their legacy challenges us to rethink our relationship with the environment and inspires us to innovate in ways that honor both our past and our planet’s future.




