The olive tree, a symbol of peace and prosperity, has stood resilient through the ages, from ancient civilizations to modern times. For generations, these trees have been a source of livelihood, tradition, and culinary delight across Europe, particularly in the Mediterranean region. However, this age-old icon now faces a grave threat. The silent enemy, a bacterial disease, is stealthily ravaging the olive groves, leaving desolate landscapes in its wake. This disease, known as Xylella fastidiosa, is reshaping the fate of olive cultivation in Europe, leading to economic loss and cultural disruption.
Understanding Xylella Fastidiosa
Xylella fastidiosa is a deadly bacterium that attacks the vascular system of plants, blocking the flow of water and nutrients. This blockage leads to the wilting and eventual death of the plant. Originating in the Americas, it has now found its way to Europe, primarily affecting olive trees in Italy, Spain, and France. The bacterium is spread by sap-feeding insects, known as vectors, which are difficult to control, making the disease even more challenging to manage. Its impact on olive trees is particularly devastating, as these trees are not only economically valuable but also hold significant cultural importance.
The Spread Across Europe

The disease was first detected in Europe in 2013 in the Apulia region of Italy. Since then, it has rapidly spread across Southern Europe, threatening millions of olive trees. The warm and humid Mediterranean climate provides the perfect breeding ground for the bacterium and its insect vectors. As the disease spreads, entire groves have been quarantined, and thousands of trees have been uprooted and destroyed in an attempt to contain the outbreak. This has led to a severe economic impact on farmers whose livelihoods depend on olive production.
The Economic Impact
The olive oil industry is a significant economic driver in Europe, contributing billions to the economy annually. Olive oil is not just a staple in European kitchens but is also exported worldwide. With the spread of Xylella fastidiosa, olive production has seen a dramatic decline, leading to increased prices and scarcity of olive oil. For many farmers, the loss of olive trees means the loss of generations of hard work and heritage. The financial burden extends to local economies that rely on agriculture, affecting jobs, tourism, and related industries.
Cultural and Historical Significance

Olive trees are deeply rooted in the cultural and historical fabric of the Mediterranean. They have been cultivated for over 6,000 years and are often associated with peace, wisdom, and victory. The loss of these trees is not just a biological issue but a cultural one. Entire landscapes that have been shaped by olive groves for millennia are changing. This transformation affects local traditions, festivals, and the identity of communities that have lived in harmony with these trees for centuries.
Scientific Efforts and Research
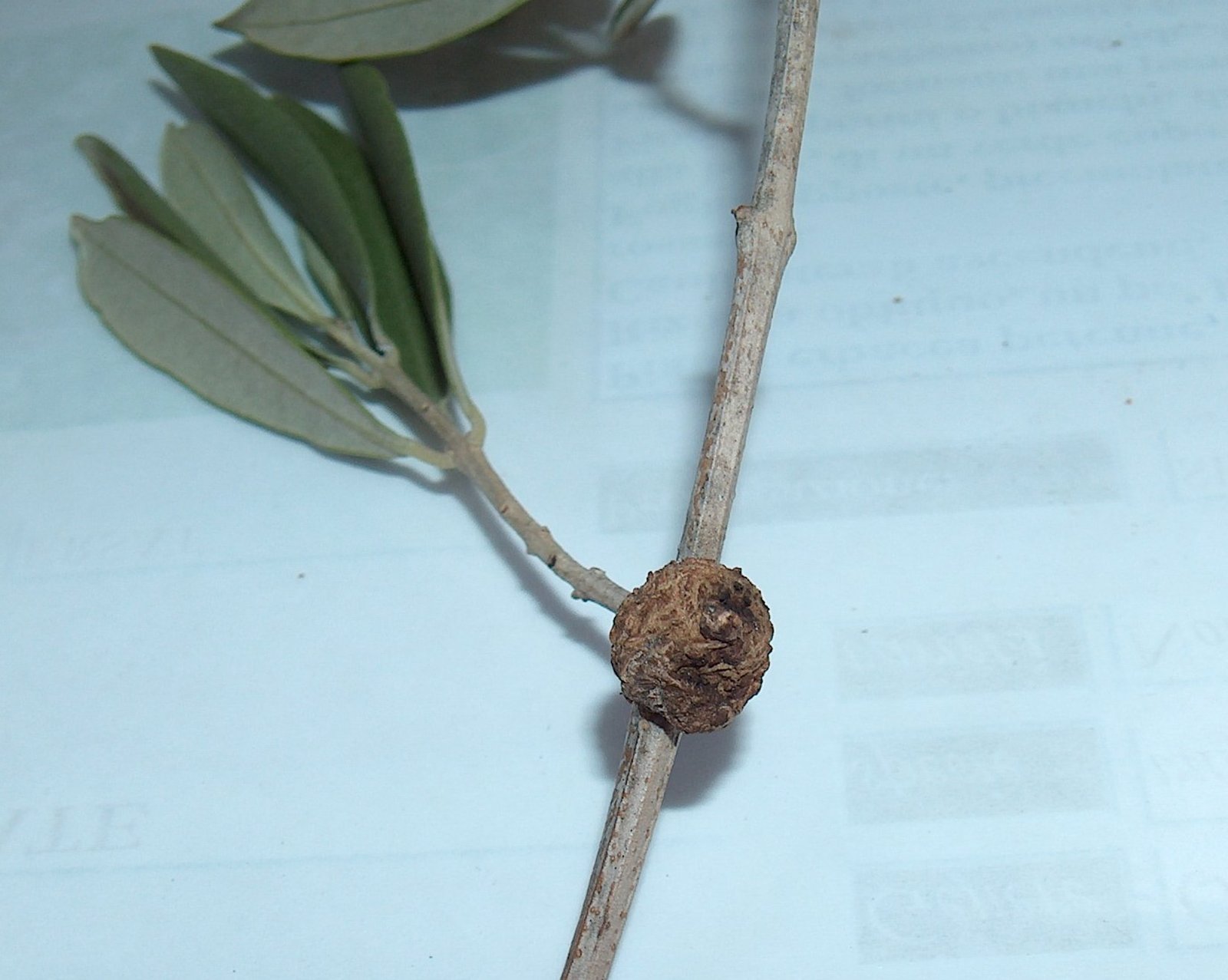

Scientists and researchers across Europe are working tirelessly to understand and combat Xylella fastidiosa. Efforts are being made to identify resistant olive tree varieties and develop effective management strategies. Research is also focused on understanding the biology of the bacterium and its vectors to devise targeted control methods. Collaborative efforts between countries, research institutions, and farmers are crucial in this fight. However, the complexity of the disease and the rapid spread of the bacterium make it a formidable challenge.
Prevention and Control Measures
Preventing the spread of Xylella fastidiosa requires rigorous monitoring and management practices. Farmers are encouraged to regularly inspect their groves for signs of infection and report any suspicious symptoms. Quarantine measures are essential to prevent the movement of infected plants and vectors. Control efforts also include the use of insecticides to manage vector populations and the removal of infected trees to prevent further spread. Public awareness campaigns are vital to educate farmers and the general public on the importance of these measures.
The Role of Climate Change

Climate change plays a significant role in the spread of plant diseases, including Xylella fastidiosa. Warmer temperatures and altered rainfall patterns create favorable conditions for the bacterium and its vectors. As climate change continues to impact global ecosystems, the spread of plant diseases is likely to increase. Understanding the link between climate change and plant health is crucial for developing long-term strategies to protect crops and ecosystems. This adds an additional layer of complexity to the challenges faced by olive growers.
International Cooperation and Policies

The fight against Xylella fastidiosa requires international cooperation and effective policies. The European Union has implemented strict regulations to prevent the spread of the disease, including restrictions on the movement of plants and plant products from affected areas. Cross-border collaborations are essential for sharing knowledge, resources, and best practices. International organizations and governments must work together to support research and provide financial assistance to affected regions. Global cooperation is key to addressing this crisis and safeguarding the future of olive cultivation.
The Future of Olive Trees in Europe

The future of olive trees in Europe hangs in the balance as scientists, farmers, and policymakers grapple with the challenges posed by Xylella fastidiosa. While the situation is dire, there is hope. Advances in research and technology offer potential solutions, and the resilience of farmers and communities is a testament to the enduring relationship between humans and nature. Protecting olive trees requires a collective effort and a commitment to preserving our natural heritage. As we face this challenge, it is vital to remember the cultural, economic, and ecological importance of olive trees and the need to protect them for future generations.