In the vast tapestry of nature, relationships between species are woven with threads of mutual dependence. Among these intricate connections, few are as captivating as the bond between a bee and an orchid. Imagine an orchid that blooms in vibrant hues, its petals shaped to perfection, yet its partner, the bee, is no longer there to visit. This story is not just a tale of loss but a testament to the resilience of nature and the enduring legacy of the creatures that once were.
The Symbiosis of Bees and Orchids
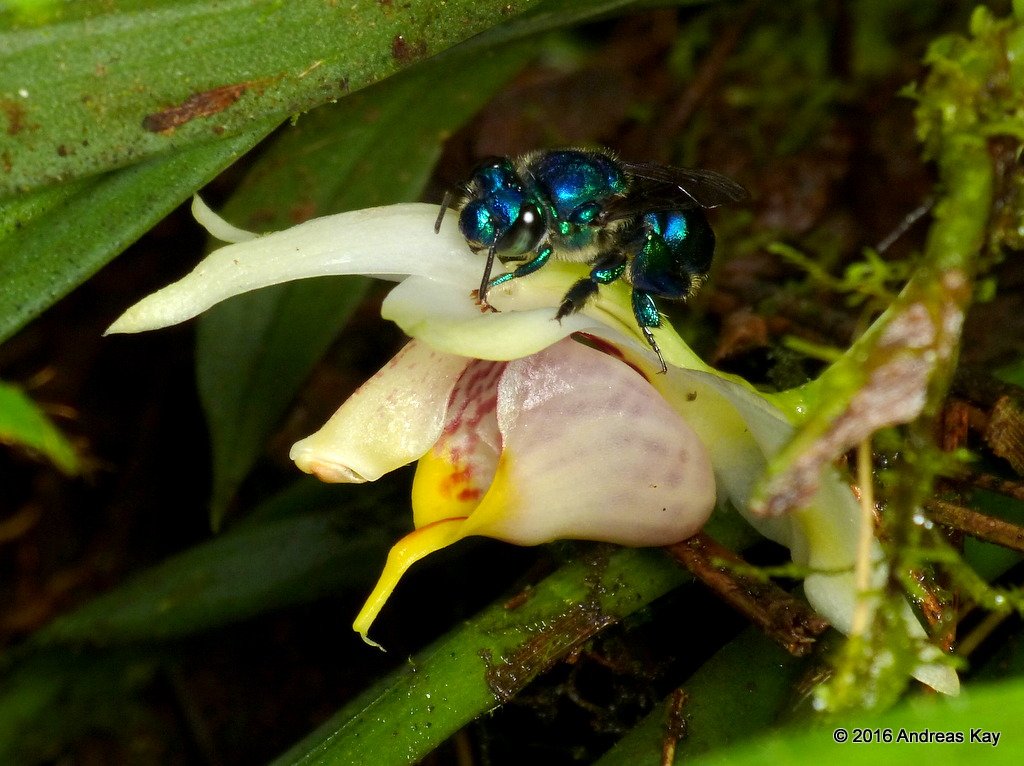
Bees and orchids share a mutualistic relationship, which means they both benefit from each other’s presence. The bee, in search of nectar, visits the orchid, inadvertently picking up pollen and transferring it to the next flower. This process is crucial for the reproduction of orchids. In return, the bee receives nourishment. It’s a perfect dance of give and take, a symbiotic relationship that has evolved over millions of years. In this delicate balance, both species thrive, highlighting the beauty and complexity of nature’s interconnected web.
The Disappearance of the Pollinator Bee
However, in some ecosystems, the bee that once played this vital role has vanished, leaving the orchid seemingly stranded. This disappearance can be attributed to various factors such as habitat loss, pesticide use, and climate change. As the environment shifts, the delicate equilibrium is disrupted, and the once-plentiful pollinators become scarce. The absence of the bee is a poignant reminder of the fragility of these relationships and the impact human activities have on ecosystems.
The Orchid’s Remarkable Adaptability

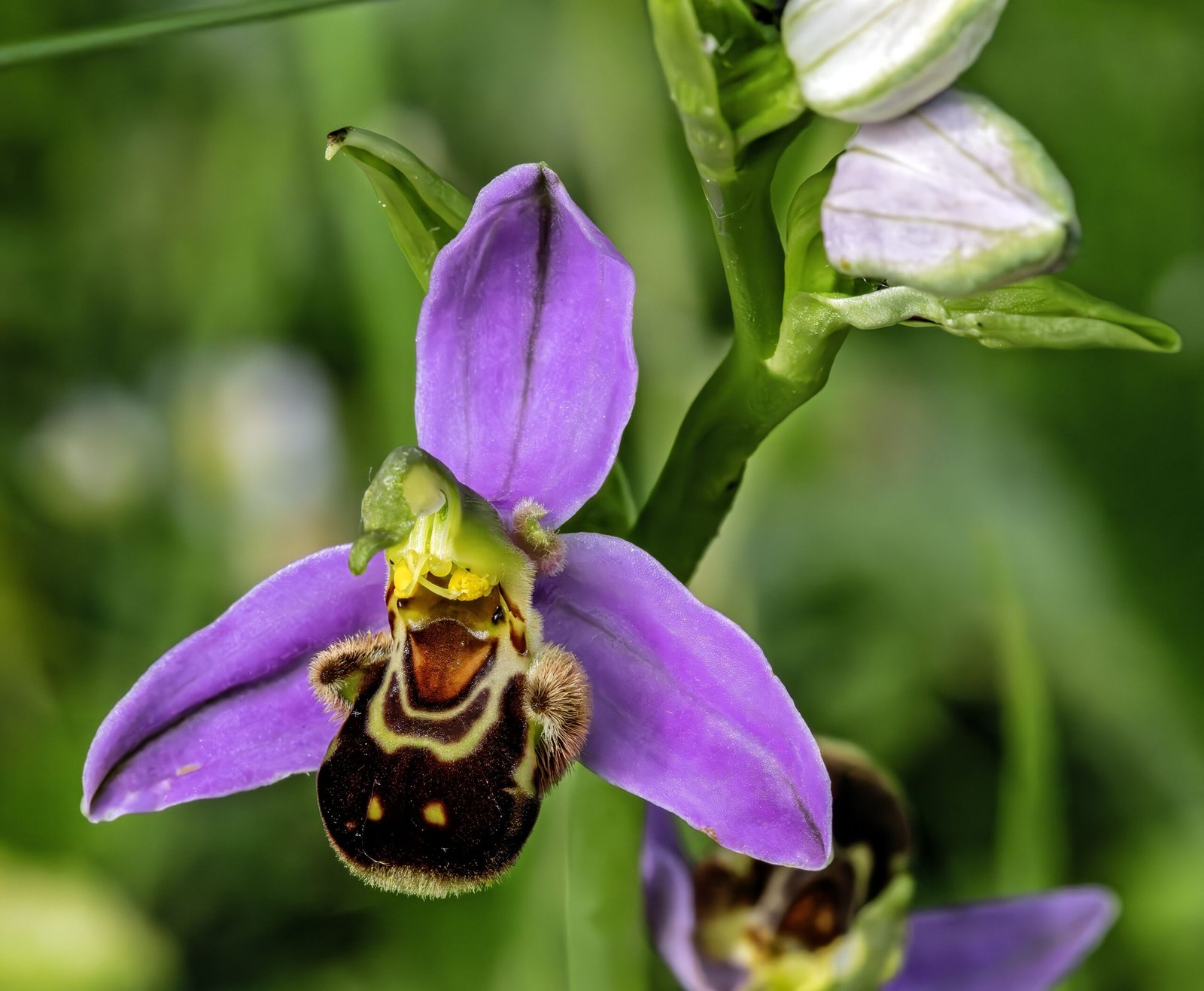
Despite the disappearance of its partner, the orchid continues to bloom, its petals still shaped to attract the long-gone bee. This enduring form is a testament to the orchid’s adaptability. Over time, some orchids have evolved to attract other pollinators, like moths or hummingbirds, ensuring their survival. Others may rely on wind or self-pollination. The orchid’s resilience is a remarkable example of nature’s ability to adapt and persevere in the face of adversity.
The Role of Memory in Nature
The orchid’s unchanged form is often described as a “memory” of the bee that once pollinated it. This memory is not conscious but rather a genetic imprint, a blueprint passed down through generations. It serves as a record of past interactions, a history embedded in the orchid’s very being. This concept of memory in nature is fascinating, as it highlights the persistence of evolutionary adaptations long after the original conditions have changed.
Legacy of the Lost Bee

The story of the bee and the orchid is a poignant reminder of the enduring legacy of extinct species. Even in absence, the bee’s influence lives on in the orchid. This legacy is a testament to the interconnectedness of life on Earth. Every species, no matter how small, leaves a mark on its environment. The lost bee’s legacy serves as a call to action to protect and preserve the remaining pollinators that play such crucial roles in our ecosystems.
Exploring Orchid Diversity
Orchids are one of the most diverse plant families, with over 25,000 species. Each species has unique adaptations that enable it to survive in different environments. Some orchids have developed intricate mechanisms to attract specific pollinators, while others are more generalist in their approach. This diversity is a testament to the orchid’s ability to adapt and thrive in a wide range of conditions. It also underscores the importance of preserving diverse habitats to support these remarkable plants.
The Importance of Pollinators in Ecosystems
Pollinators like bees play a critical role in ecosystems by facilitating plant reproduction. They are essential for the production of fruits, seeds, and the continuation of plant species. Without pollinators, many plants would struggle to survive, leading to a cascade of effects throughout the food chain. The decline of pollinator populations is a pressing concern for ecosystems worldwide, underscoring the need for conservation efforts to protect these vital creatures.
Human Impact on Pollinator Populations
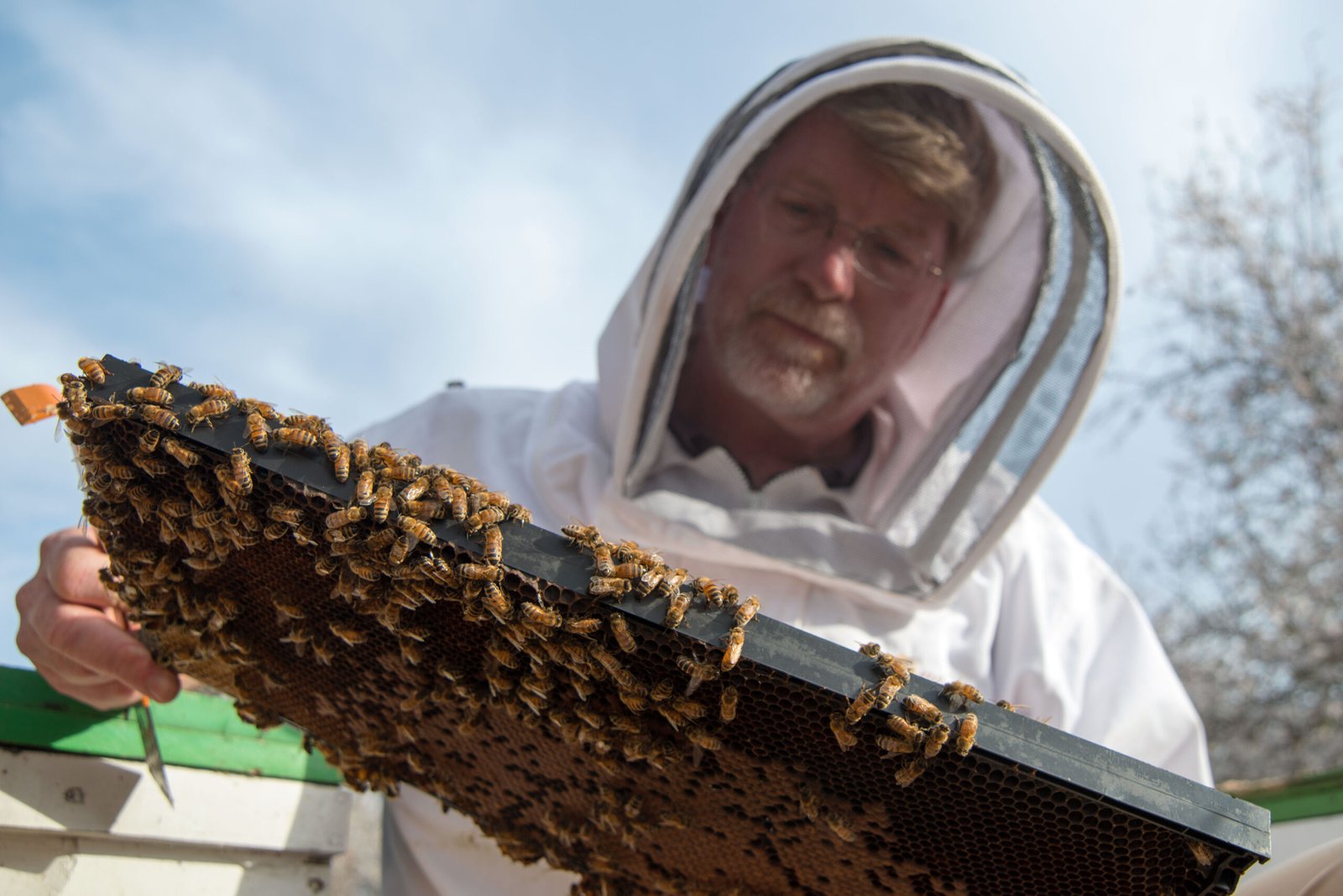

Human activities have significantly impacted pollinator populations. Urbanization, agriculture, and pesticide use have contributed to habitat loss and fragmentation. Climate change further exacerbates these challenges by altering the availability and distribution of resources. These pressures threaten the delicate balance of ecosystems, highlighting the urgent need for sustainable practices that prioritize biodiversity and environmental health.
Conservation Efforts and Future Prospects

Efforts to conserve pollinator populations are crucial for maintaining ecosystem health. Initiatives such as creating pollinator-friendly habitats, reducing pesticide use, and supporting organic agriculture can help mitigate the decline of these essential species. Public awareness and education are also vital in fostering a culture of conservation. By working together, we can ensure a future where pollinators and the plants they sustain continue to thrive.
The Resilience of Nature
The story of the bee and the orchid is a testament to the resilience of nature. Despite challenges and losses, ecosystems have an incredible capacity to adapt and recover. This resilience offers hope and inspiration as we navigate the complexities of biodiversity conservation. By understanding and respecting the intricate relationships within nature, we can work towards a more harmonious coexistence with the natural world.