In the intricate tapestry of nature, few relationships are as intriguing and complex as the one between the butterfly and the ant. Among the many wonders of the natural world, there exists a butterfly that has mastered the art of deception, persuading ants to nurture it as one of their own. This phenomenon, both fascinating and perplexing, showcases the adaptive brilliance of this butterfly species, offering a glimpse into the subtle and often unseen strategies employed by creatures to survive and thrive.
The Marvel of Mimicry
Mimicry is a common survival strategy in the animal kingdom, but the relationship between certain butterflies and ants takes it to an extraordinary level. These butterflies, specifically the Lycaenidae family, have evolved to mimic the larvae of ants in both appearance and behavior. This clever disguise allows the butterfly larvae to blend seamlessly into the ant colony. The ants, fooled by this mimicry, tend to the caterpillars as if they were their own, providing them with food and protection. This remarkable adaptation highlights the butterfly’s ability to exploit the ants’ nurturing instincts for its own survival.
The Science Behind the Deception
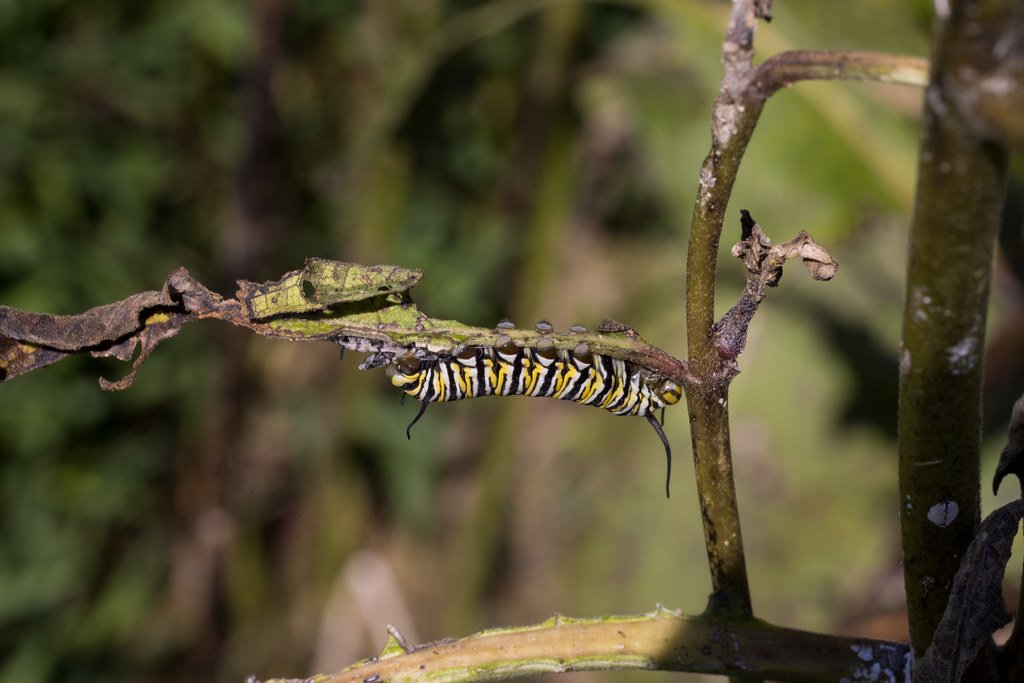

The deception is more than skin deep. Some butterfly larvae have developed the ability to produce chemical signals similar to those of ant larvae. These chemical cues, known as pheromones, are crucial in ant communication. By emitting these signals, the butterfly larvae effectively “speak” the language of the ants, further solidifying their place within the colony. This chemical mimicry is a testament to the intricate evolutionary arms race between species, where survival often depends on the ability to outsmart predators and competitors.
A Masterclass in Survival
Surviving in the wild requires more than just physical strength; it demands ingenuity and adaptability. The butterfly’s trickery is a masterclass in survival, demonstrating how species can evolve not just to endure but to thrive in specific ecological niches. By leveraging the ants’ resources and protection, the butterfly larvae can develop in a safe environment, free from many of the dangers they would face alone. This symbiotic relationship, albeit one-sided, underscores the complexity of ecological interactions and the lengths to which species will go to ensure their continuation.
The Role of Ants in the Equation
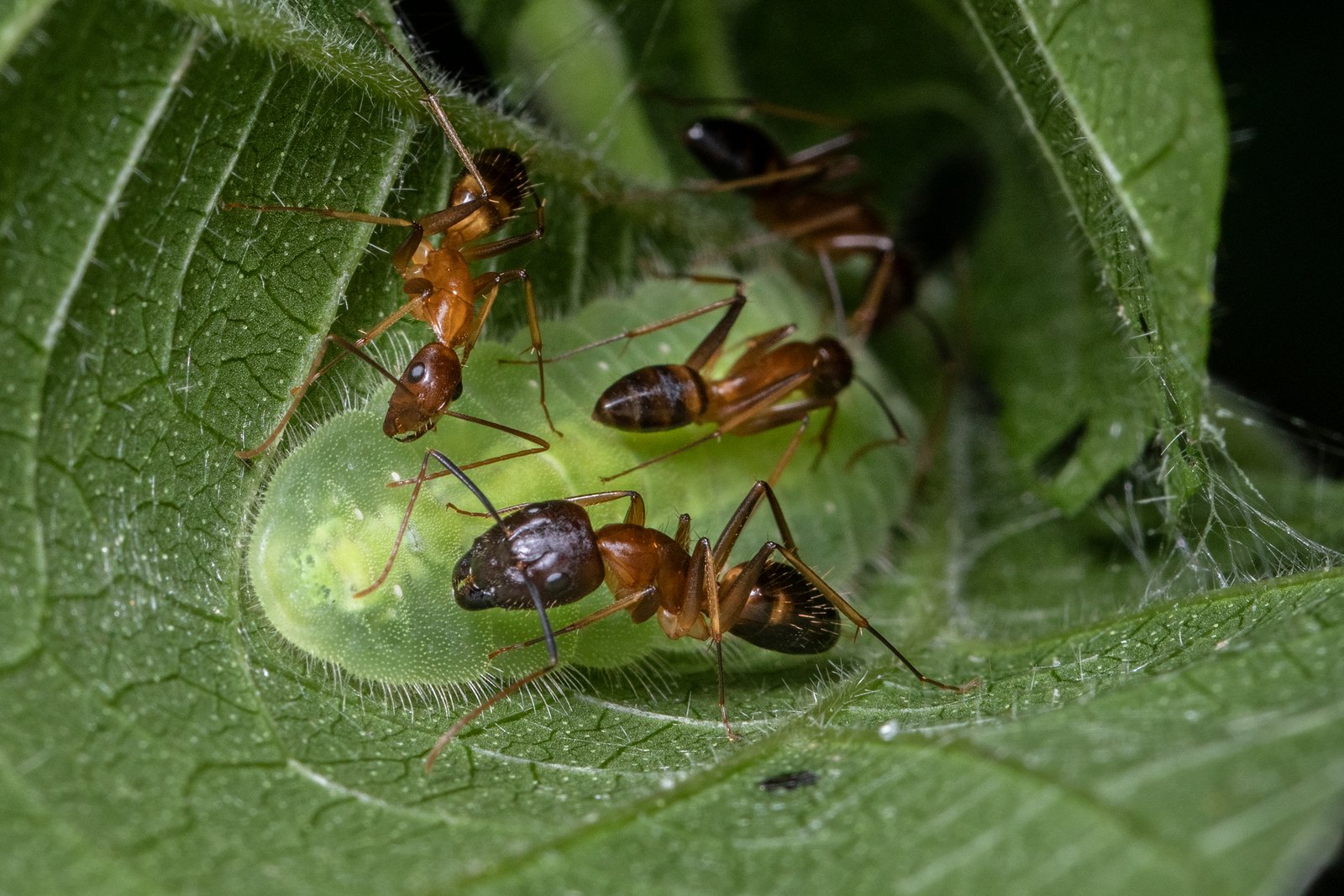

Ants, often regarded as the diligent workers of the insect world, play an unwitting yet crucial role in this elaborate ruse. Their highly organized social structure and strong protective instincts make them ideal caretakers for the butterfly larvae. The ants’ commitment to their colony drives them to nurture what they perceive as their kin, underscoring the power of instinctual behavior. This interaction, while beneficial for the butterflies, poses an interesting question about the costs to the ant colony. The resources spent on the imposters may have implications for the colony’s overall health and success.
The Evolutionary Dance
The relationship between the butterfly and the ant is a prime example of coevolution, where two or more species influence each other’s evolutionary trajectory. This dance of adaptation and counter-adaptation has led to the development of increasingly sophisticated methods of deception and detection. As butterflies refine their mimicry, ants may develop better ways to identify imposters, leading to an ongoing evolutionary arms race. This dynamic interplay illustrates the ever-changing nature of ecosystems and the delicate balance of survival strategies.
The Butterfly’s Lifecycle
Understanding the lifecycle of these butterflies provides insight into the timing and execution of their deceptive strategies. The process begins with the female butterfly laying her eggs near an ant colony. Once hatched, the larvae instinctively make their way to the ants, relying on their mimicry to be accepted into the colony. As they grow, the larvae continue to mimic the ant larvae, ensuring they remain under the ants’ care. Eventually, the larvae metamorphose into butterflies, emerging from the colony to begin the cycle anew. This lifecycle highlights the precision and timing required for the butterfly’s deception to succeed.
The Impact on Biodiversity
This unique interaction between butterflies and ants is a testament to the complexity of biodiversity. Such relationships contribute to the rich tapestry of life, showcasing the interconnectedness of species within ecosystems. While the butterfly benefits from the ants’ care, the broader ecological implications are profound. These interactions can influence the distribution and abundance of species, affecting the overall health of ecosystems. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for conservation efforts, as it highlights the importance of preserving the delicate balance of natural habitats.
Lessons from Nature’s Tricksters
The butterfly’s ability to deceive ants offers valuable lessons for scientists and nature enthusiasts alike. It serves as a reminder of the ingenuity and adaptability inherent in the natural world. This phenomenon encourages us to look beyond the surface and appreciate the complex strategies that species employ to survive. It also prompts questions about the ethical implications of deception in nature and how these strategies can inform human understanding of communication and relationships.
The Future of Butterfly and Ant Interactions
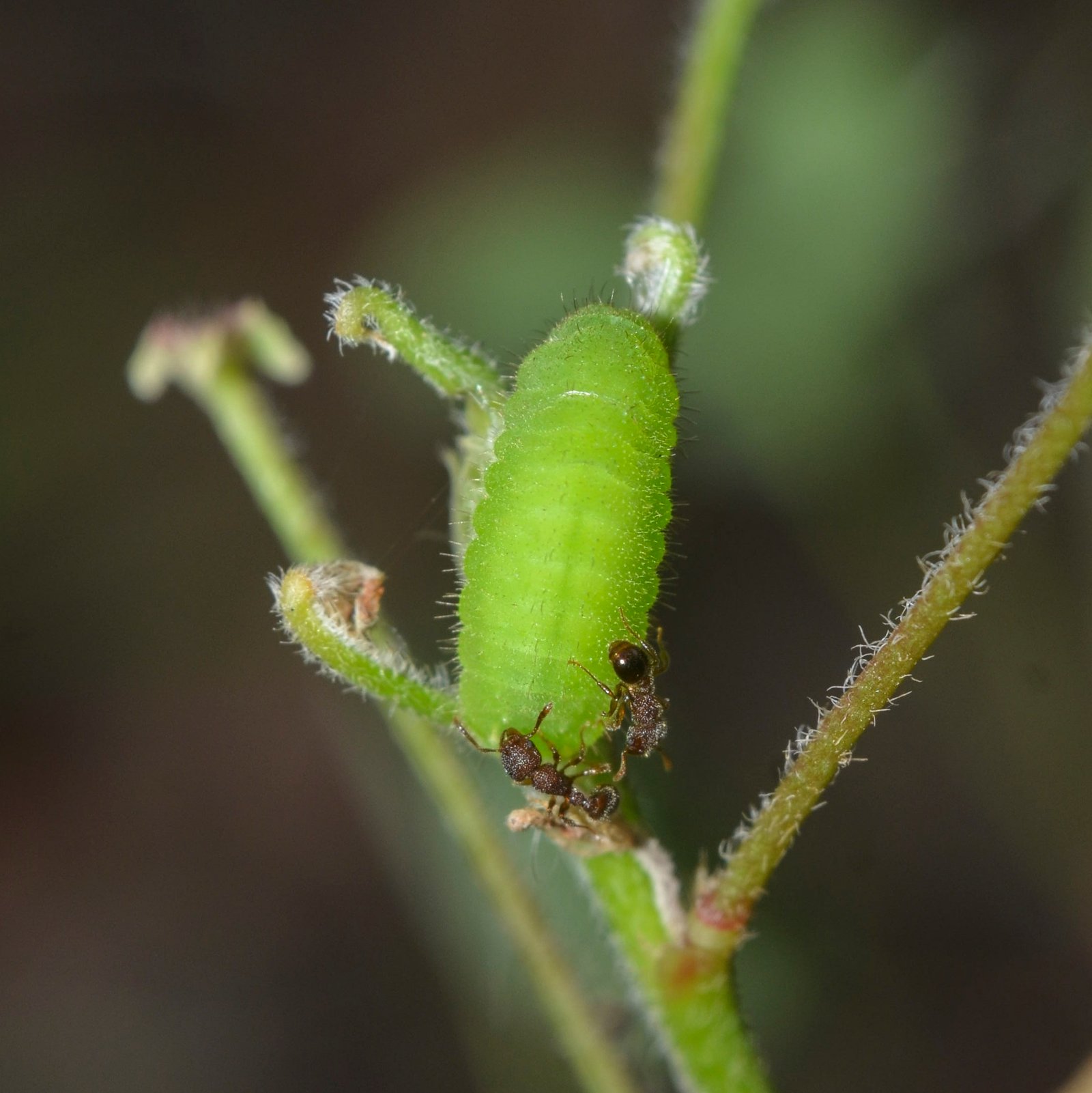

As environmental conditions change, the future of the butterfly-ant relationship remains uncertain. Climate change, habitat loss, and human activities pose significant threats to these delicate interactions. Scientists are keenly interested in how these factors may alter the balance between the butterflies and ants, potentially leading to shifts in their behaviors and evolutionary paths. Research into these interactions not only enhances our understanding of ecological dynamics but also informs conservation strategies aimed at preserving these intricate relationships for future generations.
Concluding Thoughts
The butterfly that tricks ants into raising it like one of their own is a fascinating example of nature’s ingenuity. This complex interaction showcases the extraordinary lengths to which species will go to ensure survival. By delving into the science behind this relationship, we gain a deeper appreciation for the intricacies of the natural world. As we continue to explore these connections, we are reminded of the importance of preserving the delicate balance of ecosystems and the remarkable adaptations that arise within them.