The enigmatic force of gravity has long intrigued scientists, inspiring them to devise innovative ways to study its effects. From dropping objects from towering heights to conducting intricate experiments in virtual worlds, the quest to understand gravity has led researchers down some truly peculiar paths. This article delves into the fascinating and sometimes bizarre methods that scientists have used to explore the fundamental force that governs our universe. Along the way, we’ll encounter experiments that stretch the imagination and open up new horizons in our understanding of the cosmos.
Galileo’s Leaning Tower of Pisa Experiment
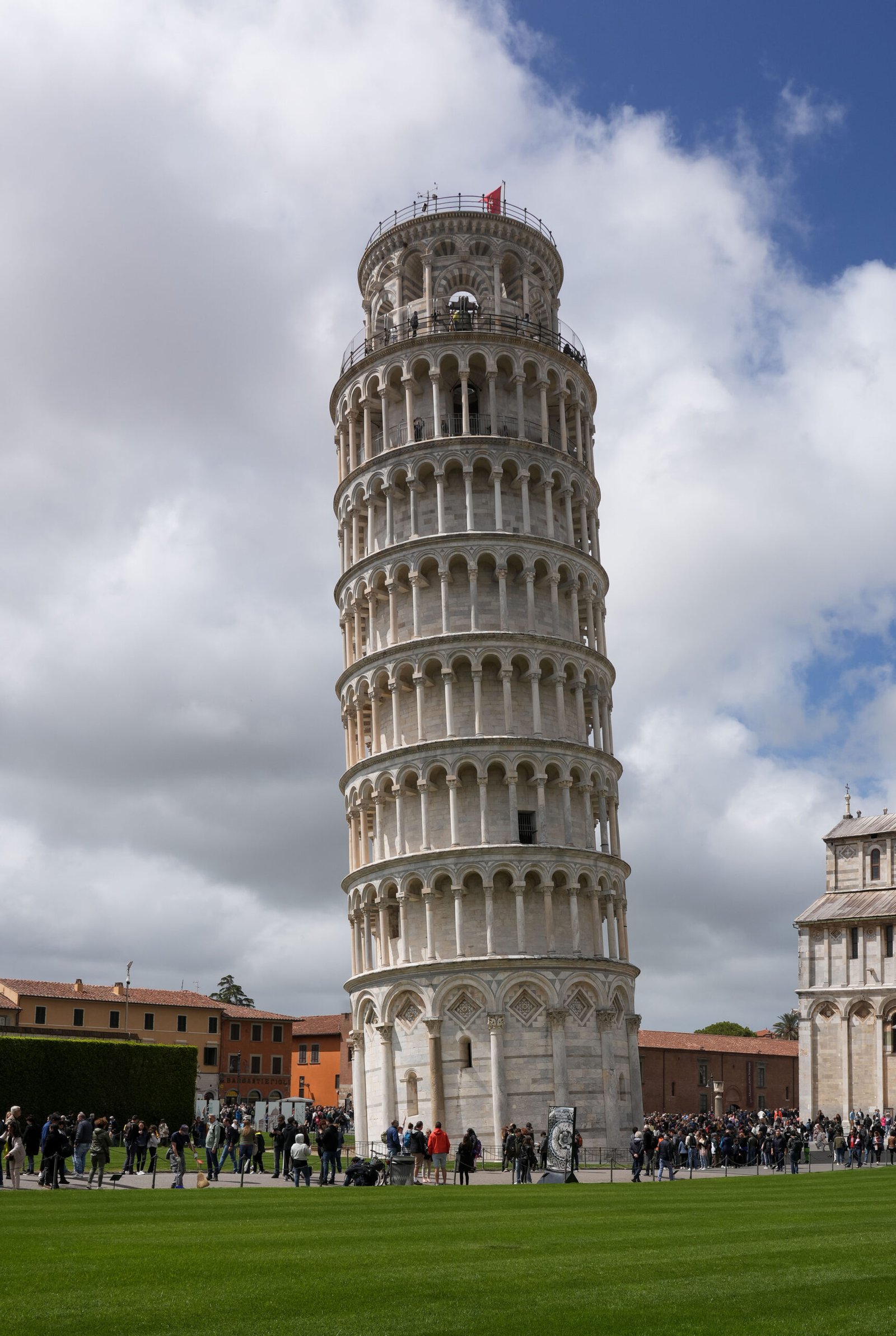

Galileo Galilei, a pioneer in the study of physics, conducted a famous experiment that challenged preconceived notions about gravity. Legend has it that he dropped two spheres of different masses from the Leaning Tower of Pisa to demonstrate that they would fall at the same rate. This simple yet revolutionary experiment helped debunk Aristotle’s long-held belief that heavier objects fall faster than lighter ones. Galileo’s findings laid the groundwork for future studies of gravity, highlighting the power of observation and experimentation in scientific discovery. While the historical accuracy of this experiment is debated, its impact on the study of gravity is undeniable.
Newton’s Apple Tree Revelation

Sir Isaac Newton’s encounter with a falling apple is one of the most iconic stories in the history of science. This seemingly mundane event sparked Newton’s curiosity about the force that caused the apple to fall from the tree. This curiosity eventually led to the formulation of the law of universal gravitation, which describes the gravitational attraction between two masses. Newton’s groundbreaking work provided a mathematical framework for understanding gravity, influencing generations of scientists. The apple tree serves as a symbol of the profound insights that can arise from observing everyday phenomena.
Einstein’s Theory of General Relativity
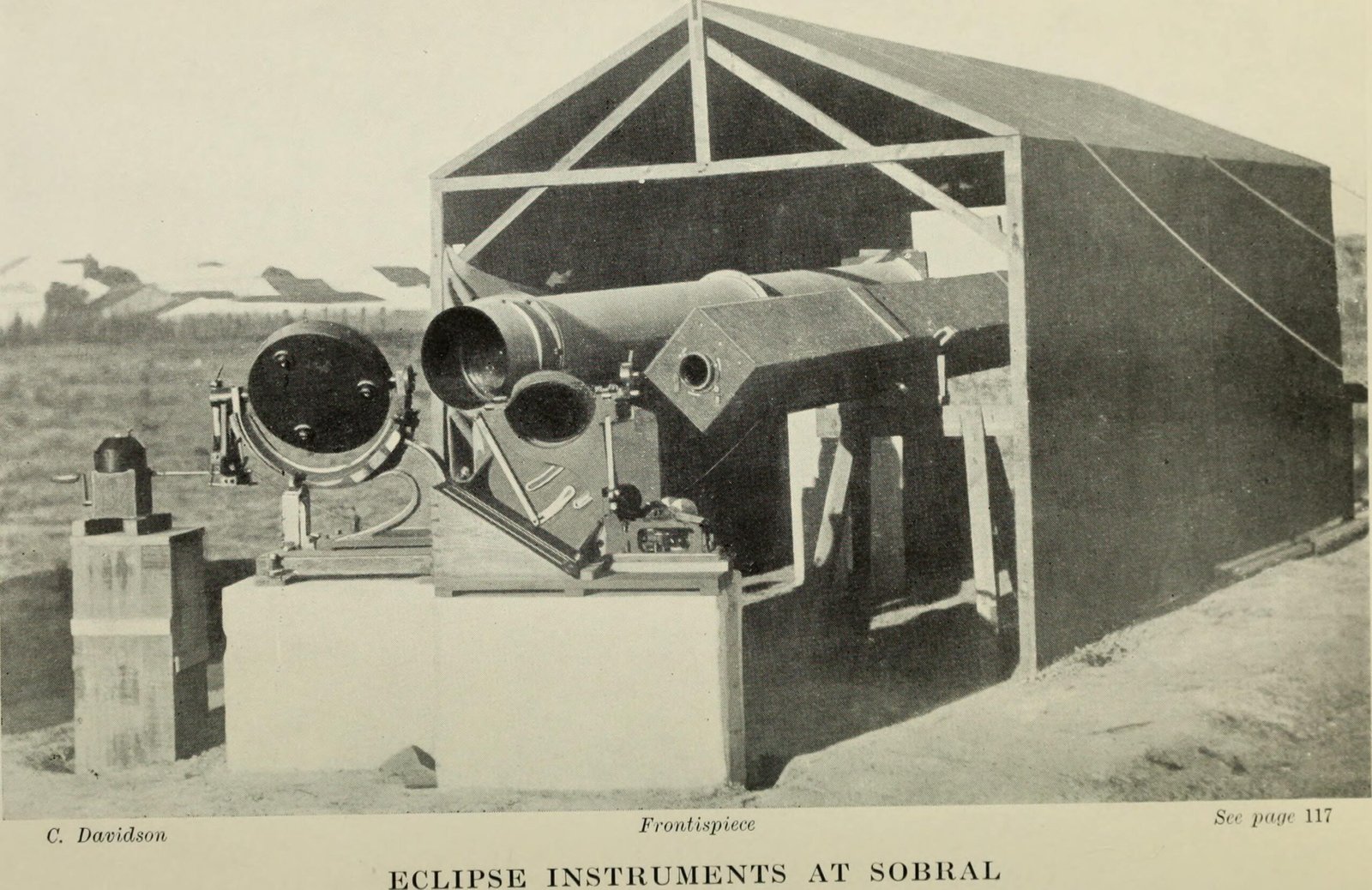
Albert Einstein revolutionized our understanding of gravity with his theory of general relativity. This theory proposed that gravity is not a force, but rather a curvature of space-time caused by massive objects. Einstein’s ideas were confirmed through the observation of light bending around the sun during a solar eclipse, a phenomenon known as gravitational lensing. This groundbreaking discovery expanded our understanding of the universe and opened up new avenues for exploring cosmic phenomena. Einstein’s theory remains a cornerstone of modern physics, guiding researchers as they explore the mysteries of black holes and the expanding universe.
The Cavendish Experiment
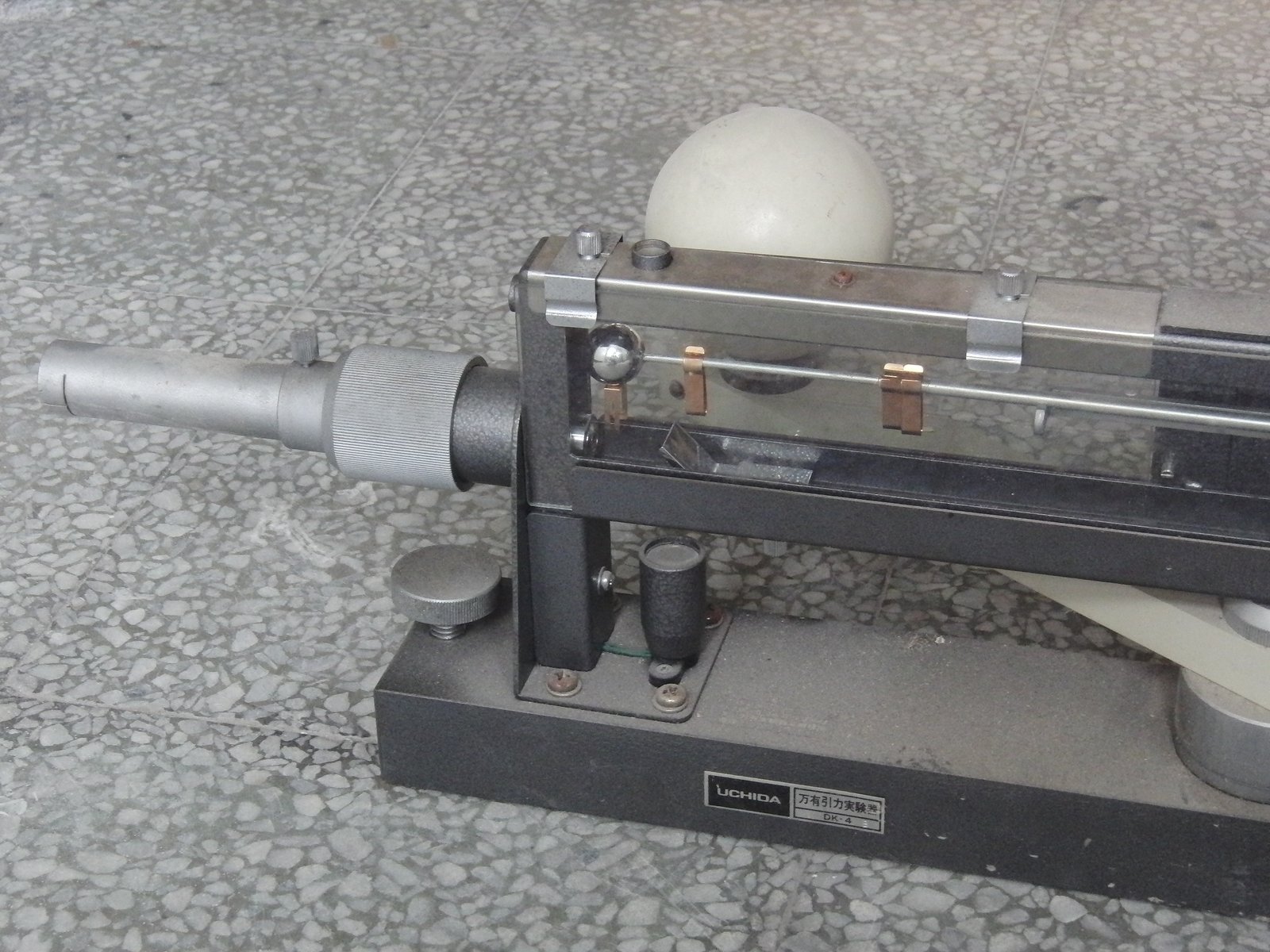

The Cavendish experiment, conducted by Henry Cavendish in the late 18th century, was a pioneering effort to measure the gravitational force between two objects. Using a delicate apparatus consisting of lead spheres and a torsion balance, Cavendish was able to calculate the gravitational constant with remarkable precision. This experiment provided the first accurate measurement of the gravitational force between masses, offering empirical support for Newton’s law of universal gravitation. The Cavendish experiment remains a classic demonstration of scientific ingenuity and precision, showcasing the power of careful measurement and analysis.
The Dropping of Atomic Clocks
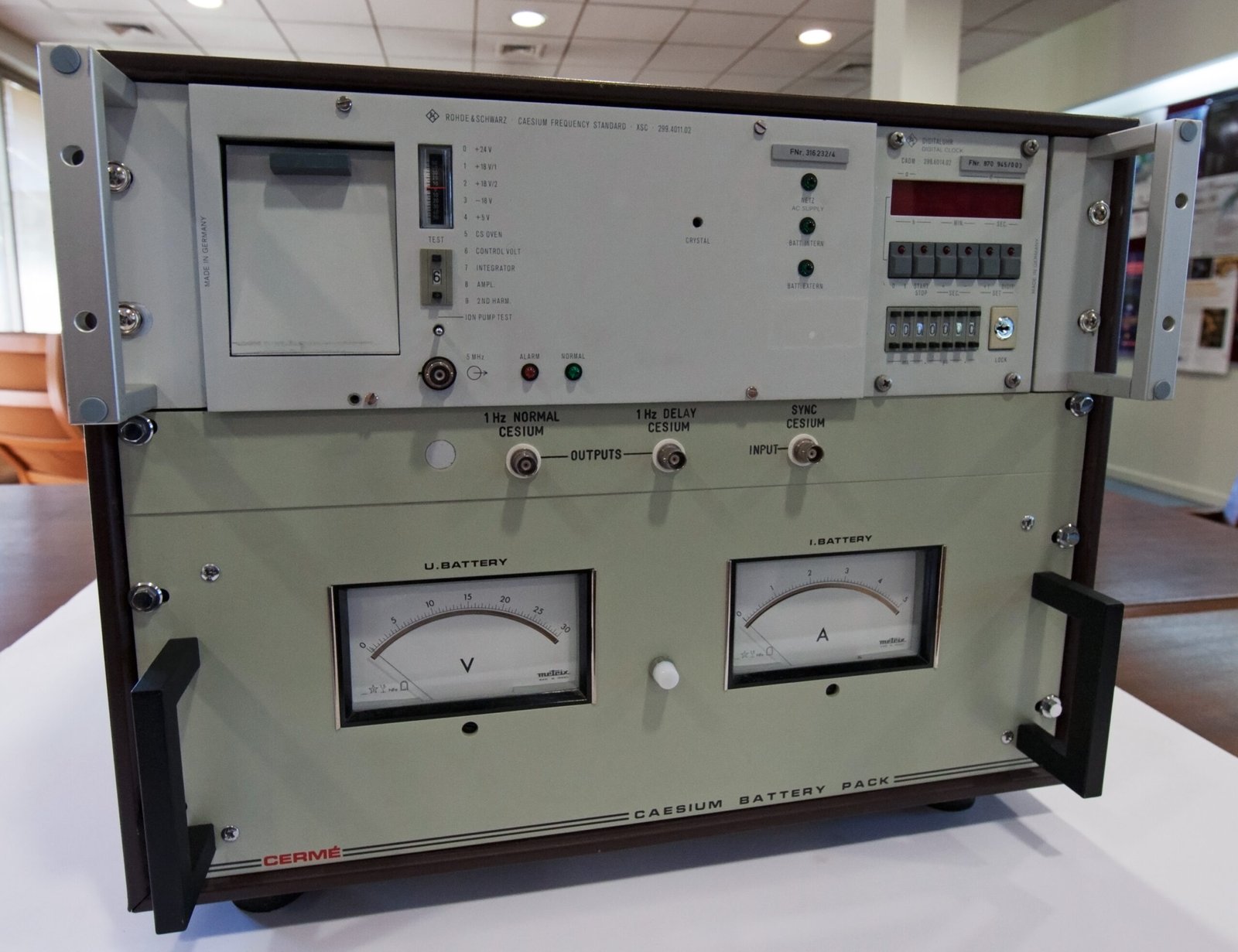

In a more modern exploration of gravity, scientists have conducted experiments involving the precise measurement of time using atomic clocks. By placing these highly accurate timepieces at different altitudes, researchers have observed the effects of gravity on time, a concept predicted by Einstein’s theory of general relativity. This phenomenon, known as gravitational time dilation, demonstrates that time passes more slowly in stronger gravitational fields. Experiments with atomic clocks have provided compelling evidence for the theory of general relativity and have practical applications in technologies such as GPS. These findings underscore the interconnectedness of gravity, space, and time.
Zero Gravity Flights
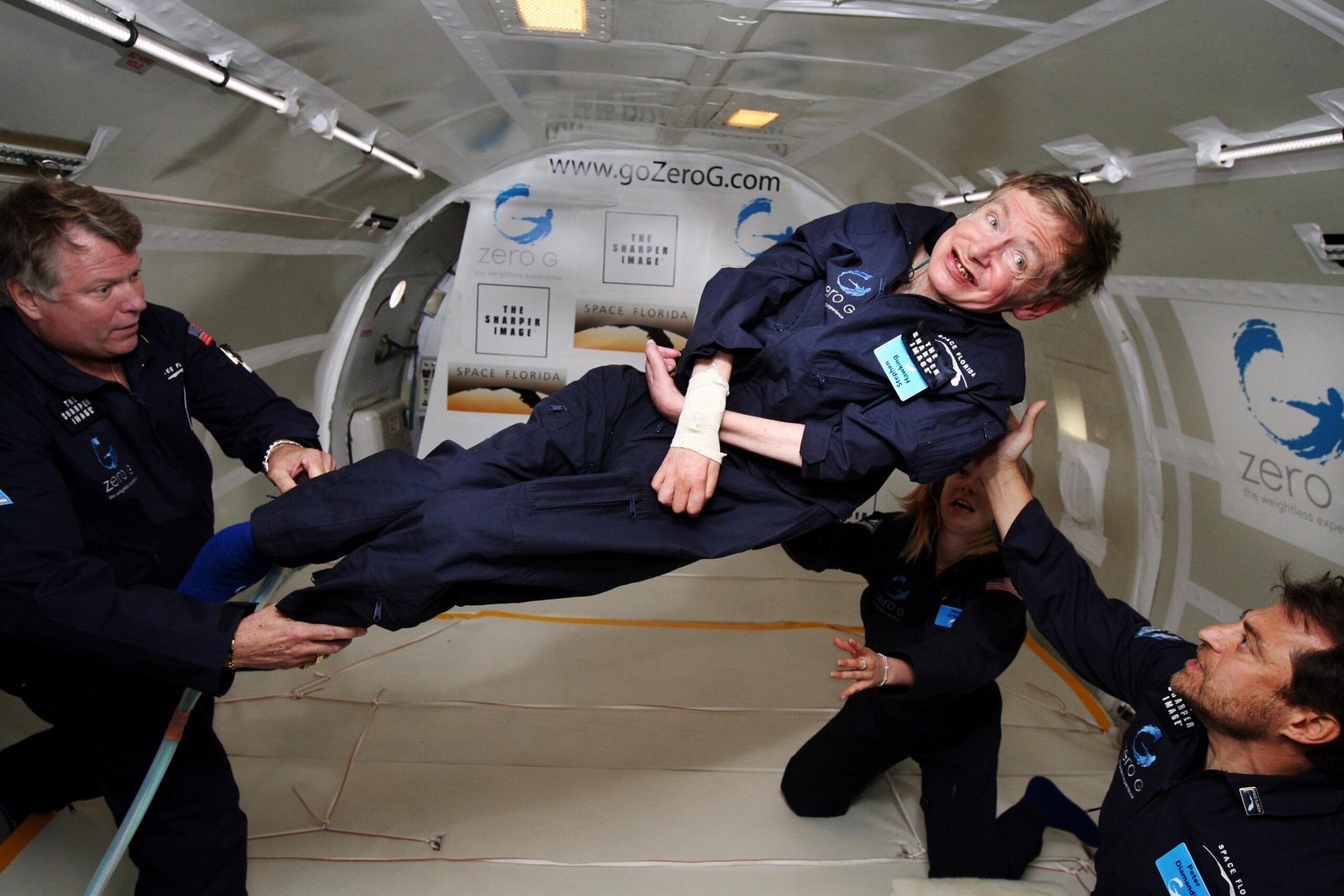

To study the effects of gravity on the human body and various materials, scientists often turn to zero gravity flights, sometimes referred to as “vomit comets.” These flights involve aircraft flying in parabolic arcs that create brief periods of weightlessness. Researchers use these flights to conduct experiments that would be difficult or impossible to perform on Earth. From studying fluid dynamics to testing the behavior of materials in microgravity, these flights provide valuable insights into the challenges of space exploration. Zero gravity flights offer a unique platform for experimentation, pushing the boundaries of scientific knowledge.
The Lunar Laser Ranging Experiment
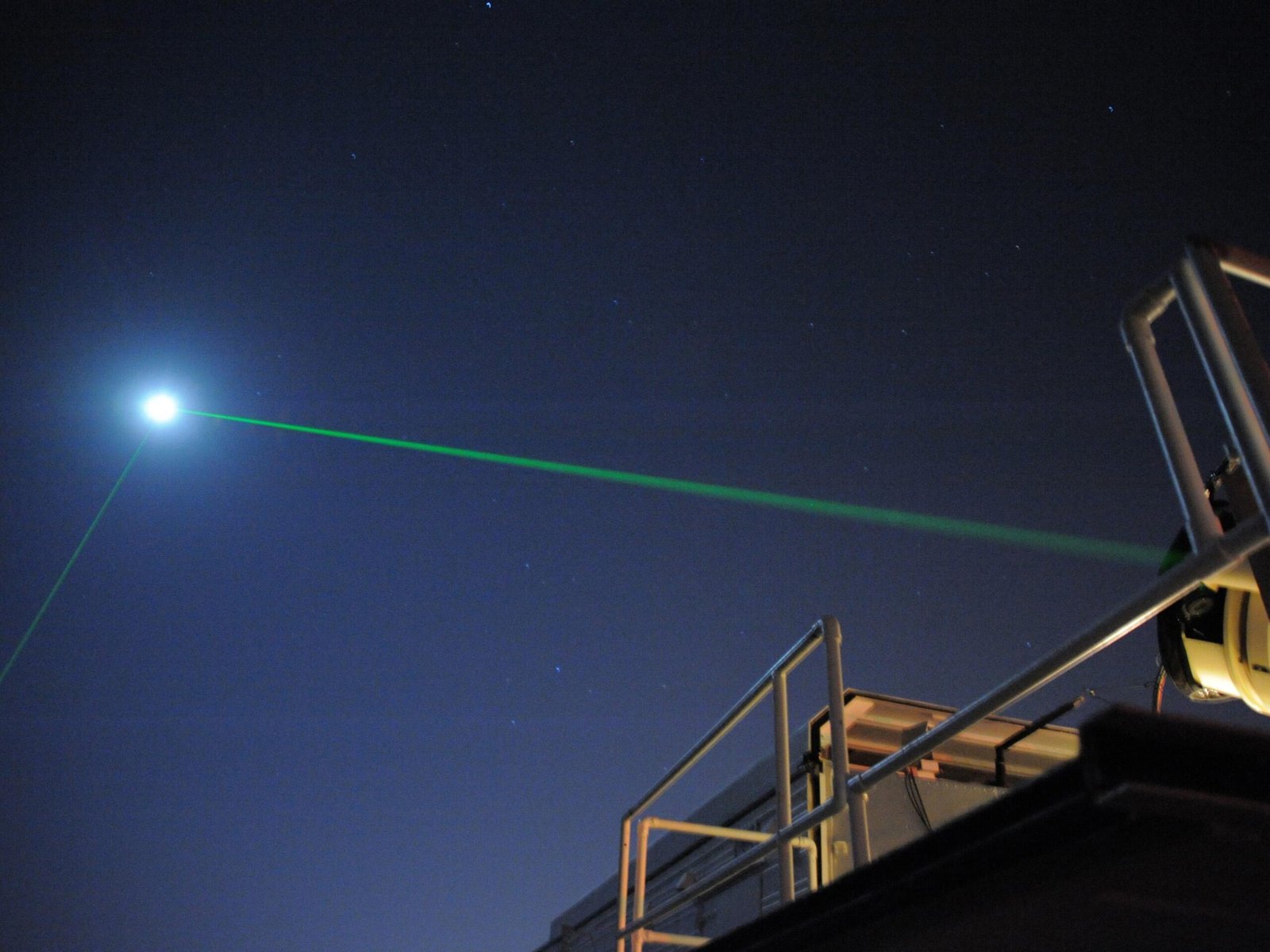

The Lunar Laser Ranging Experiment, initiated during the Apollo missions, involves bouncing laser beams off retroreflectors left on the moon’s surface. By measuring the time it takes for the laser light to return to Earth, scientists can track the moon’s distance with incredible accuracy. This experiment has provided valuable data on the Earth-moon system, revealing insights into the gravitational interactions between celestial bodies. The Lunar Laser Ranging Experiment continues to yield important information about the dynamics of our solar system, highlighting the enduring legacy of human exploration on the moon.
Gravitational Wave Detection
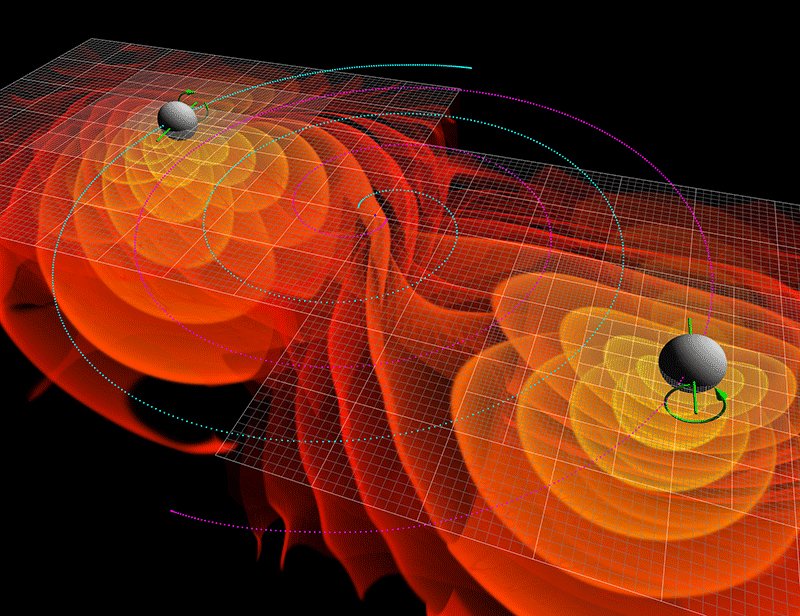
The detection of gravitational waves represents one of the most significant breakthroughs in the study of gravity. These ripples in space-time, caused by cataclysmic events like colliding black holes, were first observed by the LIGO observatory in 2015. Gravitational wave detection has opened up a new realm of astrophysics, allowing scientists to observe cosmic events that were previously hidden from view. This groundbreaking achievement has expanded our understanding of the universe and confirmed key predictions of Einstein’s theory of general relativity. The study of gravitational waves continues to reveal new insights into the fundamental nature of gravity and the cosmos.
Testing Gravity in Virtual Worlds: Minecraft
In a surprising twist, the popular video game Minecraft has become a platform for exploring the concept of gravity. Players in the game can manipulate blocks and create structures that defy the laws of physics in the real world. This virtual sandbox allows for creative experimentation with gravitational concepts, offering a unique perspective on the interplay between virtual and physical realities. While Minecraft is primarily a form of entertainment, its potential as an educational tool for exploring scientific principles is gaining recognition. By engaging with gravity in a digital environment, players can develop a deeper appreciation for the complexities of the physical world.
Conclusion: The Ever-Evolving Study of Gravity

The exploration of gravity has taken scientists on a fascinating journey, from ancient observations to cutting-edge experiments. Each method, whether rooted in historical legend or digital innovation, contributes to our understanding of this fundamental force. Gravity, with its mysterious and pervasive influence, continues to captivate the human imagination, driving researchers to seek new ways to unravel its secrets. As we look to the future, the study of gravity promises to reveal even more about the universe we inhabit, challenging us to rethink our place within it.




