Imagine a world where the scarcity of organ donors no longer poses a threat to the lives of millions. Where the anxiety and uncertainty of waiting for a life-saving organ transplant become a thing of the past. This is not a scene from a science fiction movie but a tangible possibility thanks to the revolutionary field of 3D bioprinting. With the potential to transform the medical landscape, 3D-printed organs could offer a solution to the ever-growing demand for organ transplants. This article delves into the science, challenges, and future prospects of this groundbreaking technology.
The Basics of 3D Bioprinting
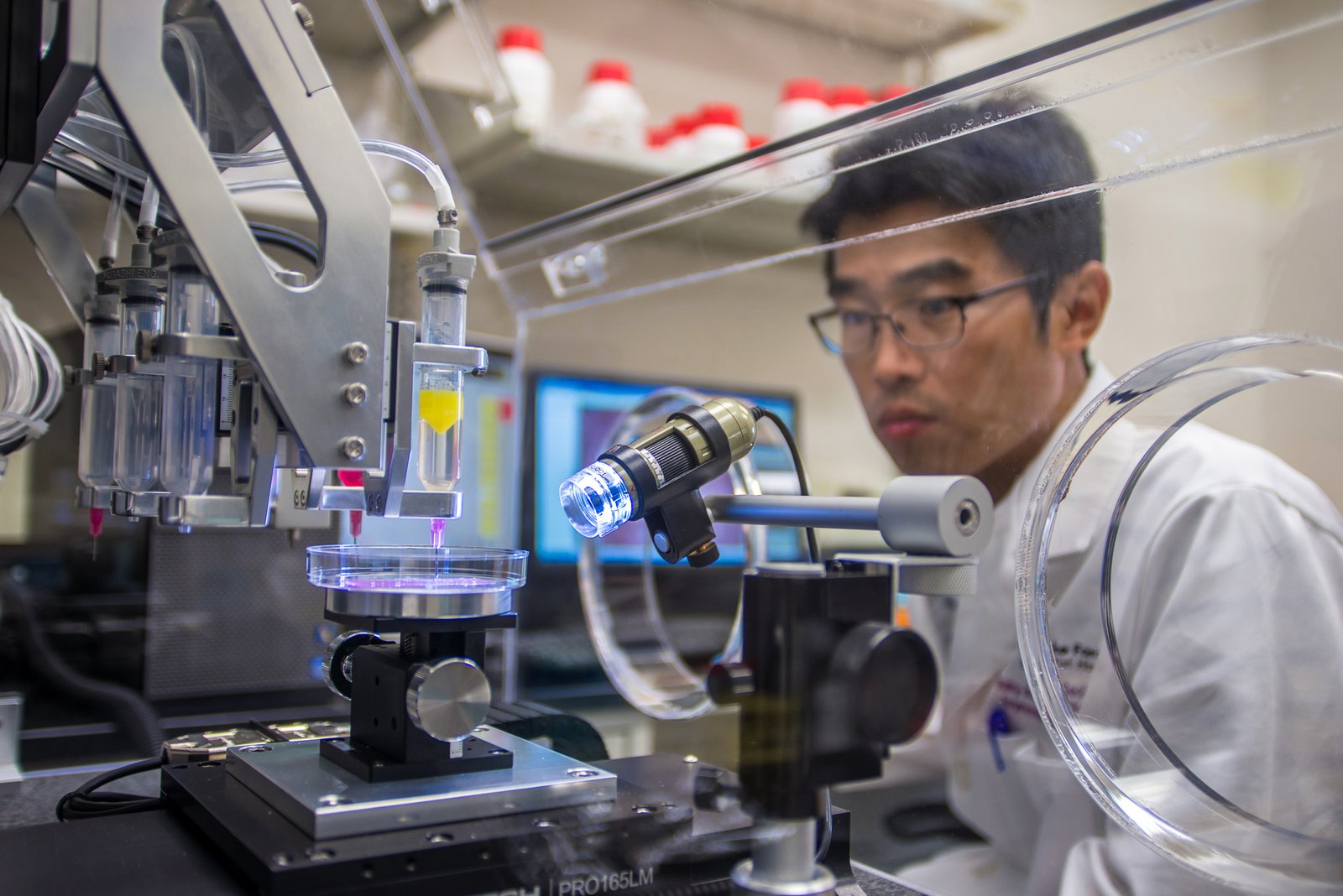

3D bioprinting is a fascinating fusion of biology and engineering that uses 3D printing technology to create living tissues. It involves the precise layering of bio-inks composed of living cells and biocompatible materials to form complex structures. This process is akin to a baker layering ingredients to create a cake, but instead, the printer layers cell-rich inks to build tissue. The technique is highly adaptable, allowing scientists to mimic the intricate architecture of human organs. By leveraging the body’s natural cellular processes, bioprinting aims to replicate the functionality of real organs, providing hope for those on transplant waiting lists.
The Promise of Organ Printing
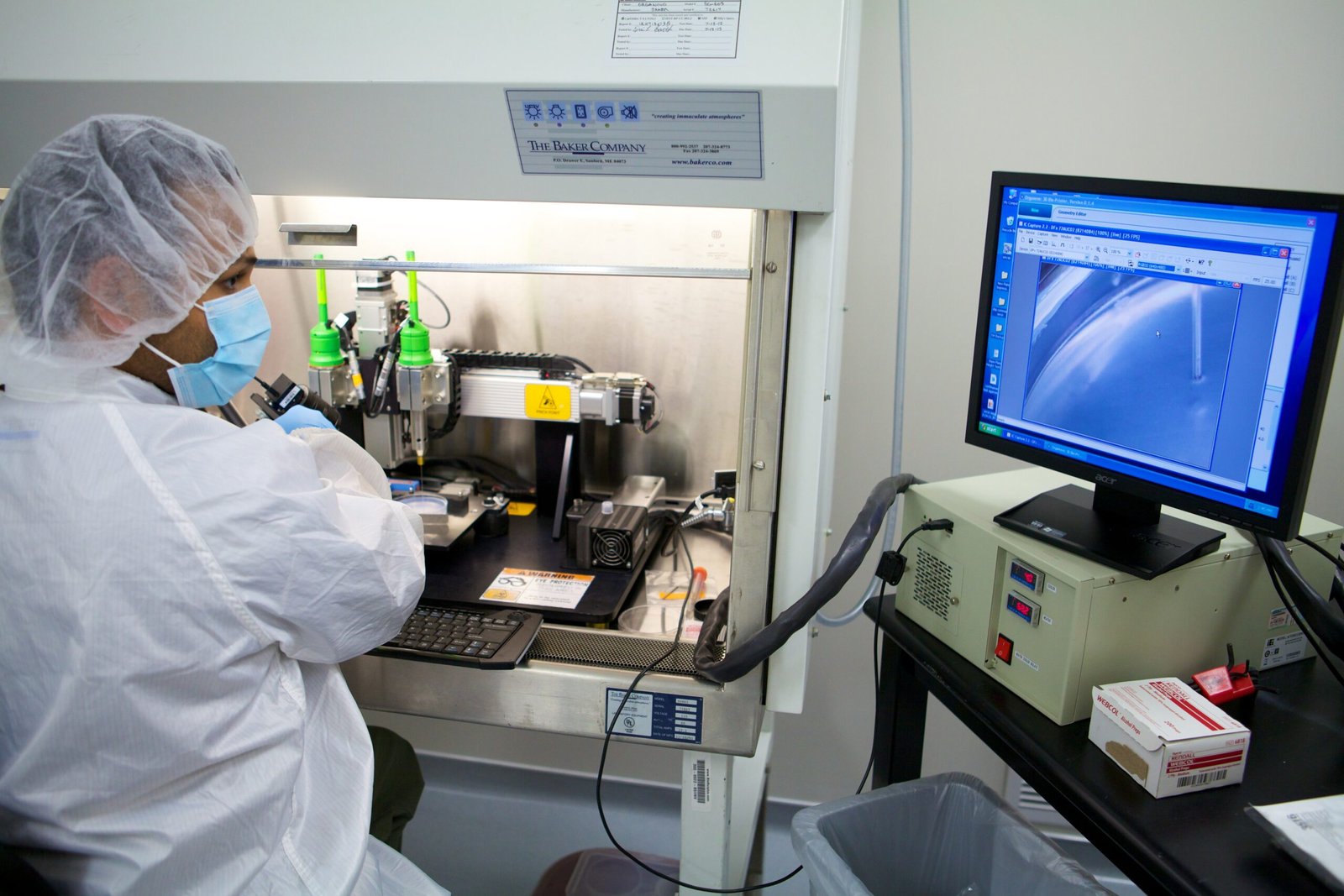

The promise of 3D-printed organs extends beyond just availability. The technology offers the potential for creating organs that are tailored to individual patients. This means that the risk of organ rejection—a significant concern in traditional organ transplants—could be significantly reduced. Imagine receiving an organ that is not only a perfect fit for your body but also made from your own cells. This customization could revolutionize the field of transplantation, making the dream of personalized medicine a reality. Furthermore, the ability to produce organs on demand could alleviate the burden on healthcare systems and improve the quality of life for countless individuals.
Challenges in 3D Organ Printing
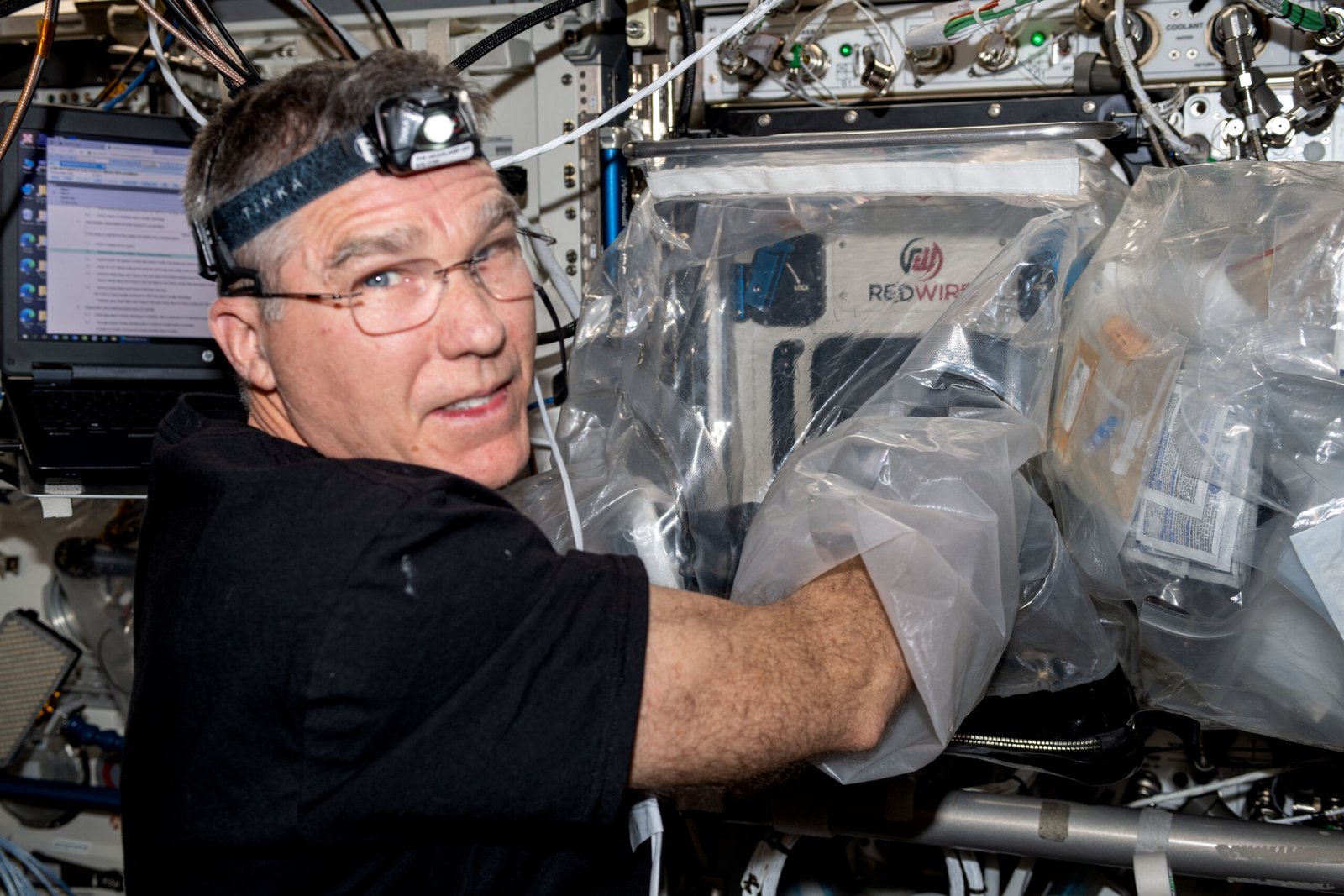

Despite the immense potential, 3D organ printing is not without its challenges. One major hurdle is replicating the complex vascular networks that supply blood and nutrients to organs. Just as roads and highways are essential for the flow of traffic in a city, intricate vascular systems are vital for maintaining organ health and functionality. Additionally, achieving the precise cellular organization and functionality of native organs remains a significant scientific challenge. Researchers are continuously exploring innovative techniques to overcome these obstacles, and while progress is being made, the road to fully functional 3D-printed organs is still under construction.
Current Successes in Bioprinting
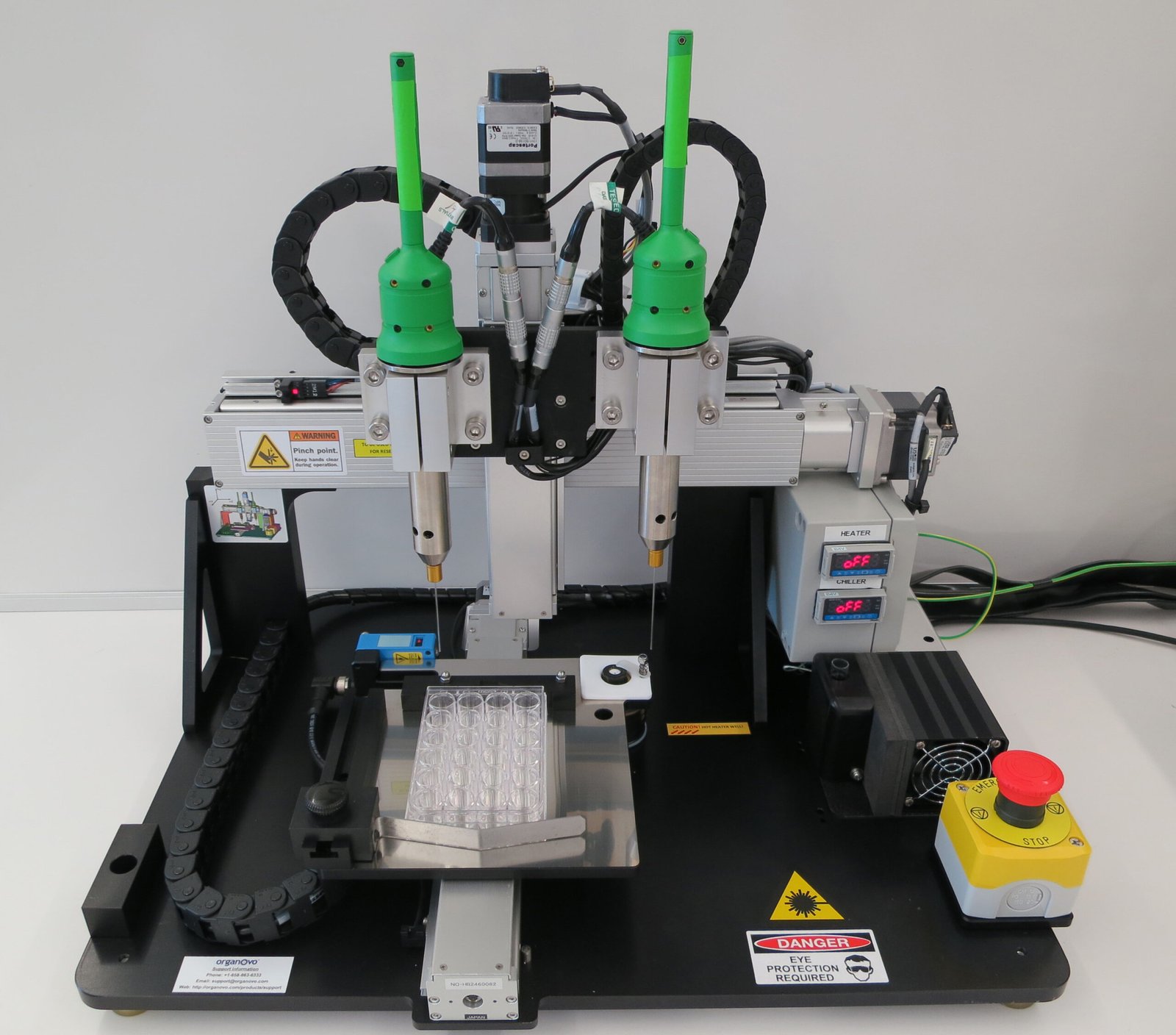

The field of 3D bioprinting has witnessed remarkable successes in recent years. Researchers have successfully printed simple tissues such as skin, cartilage, and bone, marking significant milestones in regenerative medicine. For instance, printed skin can be used for grafts to treat burn victims, while bioprinted cartilage offers hope for those suffering from joint disorders. These developments serve as stepping stones toward more complex organ printing. Moreover, advancements in bio-inks and printer technology have led to improved cell viability and precision, bringing us closer to the dream of fully functional printed organs.
Ethical and Regulatory Considerations
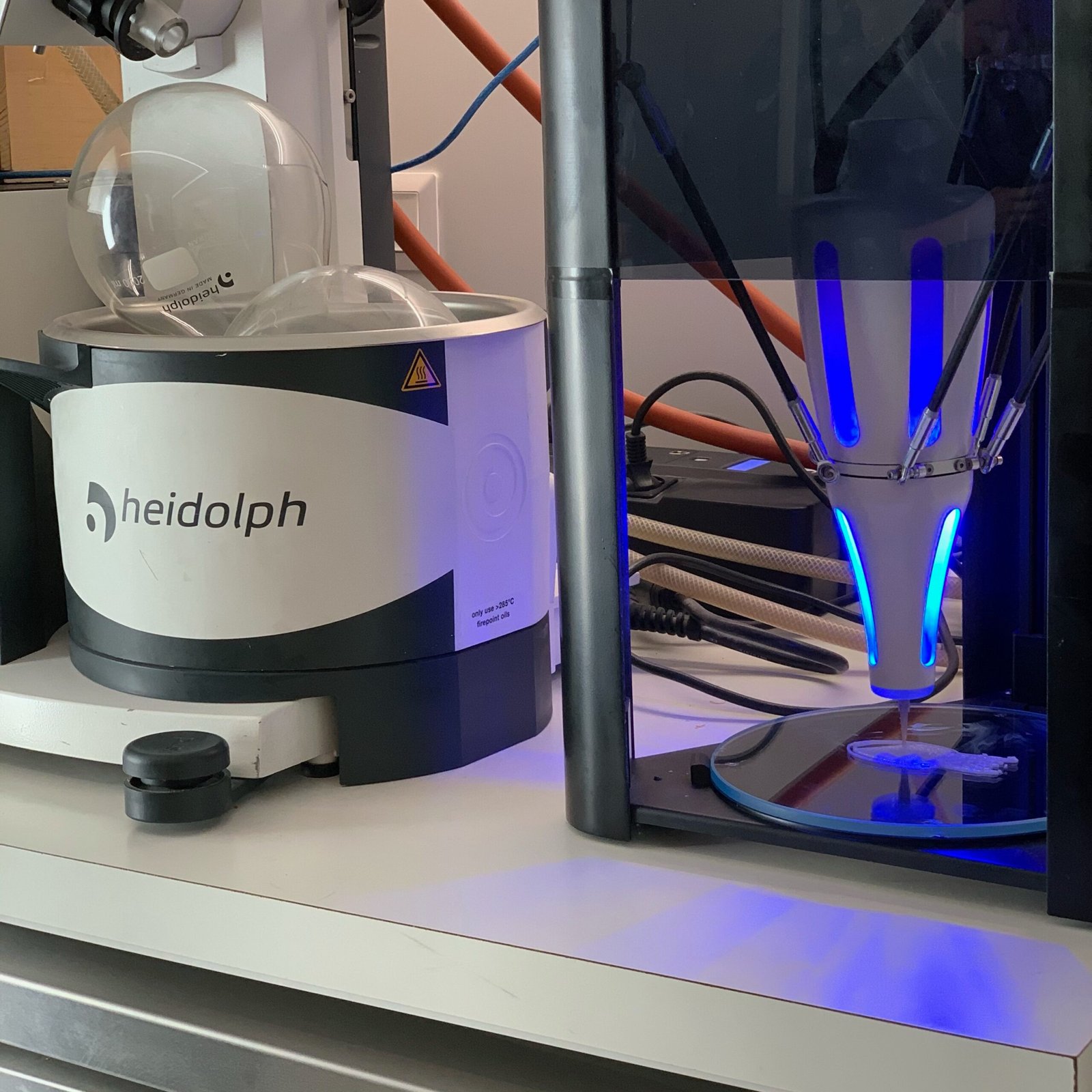

As with any groundbreaking technology, 3D organ printing raises important ethical and regulatory questions. The idea of creating life-like organs in a laboratory prompts discussions about the moral implications of such practices. There are concerns about the potential misuse of this technology, as well as issues related to consent and ownership of bioprinted tissues. Moreover, regulatory frameworks must be established to ensure the safety and efficacy of 3D-printed organs before they can be used in clinical settings. These considerations highlight the need for ongoing dialogue and collaboration between scientists, ethicists, regulators, and the public.
The Role of Stem Cells in Bioprinting
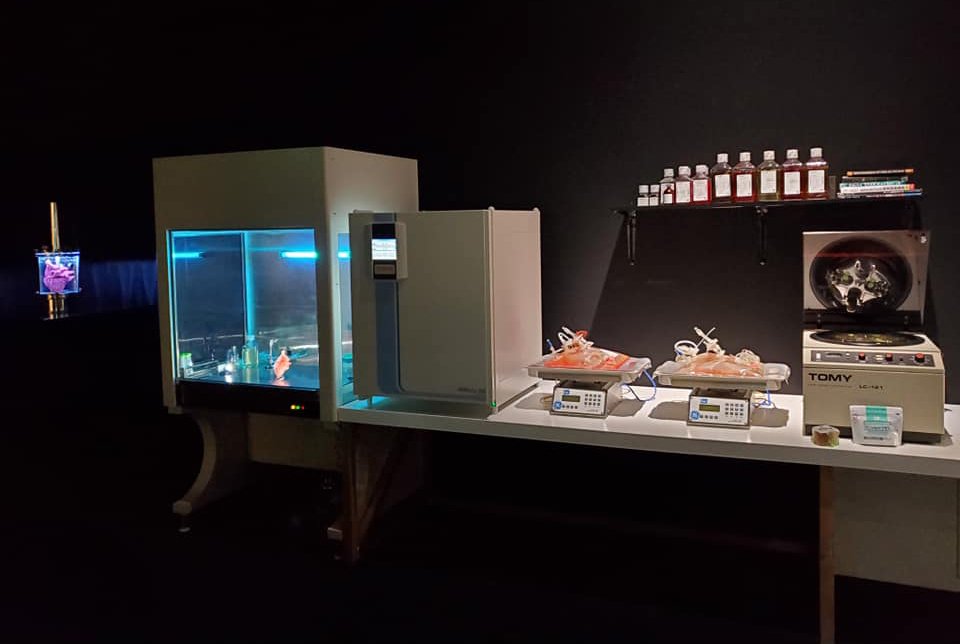

Stem cells play a pivotal role in the field of 3D bioprinting. These remarkable cells have the ability to differentiate into various cell types, making them ideal candidates for creating diverse tissue structures. Imagine stem cells as the seeds of a garden, capable of growing into different types of plants depending on the conditions provided. By harnessing the potential of stem cells, scientists can create tissues with the necessary cellular diversity to mimic real organs. This ability to guide stem cells into specific tissue types is a crucial aspect of advancing 3D organ printing technology.
Innovative Techniques in Organ Printing
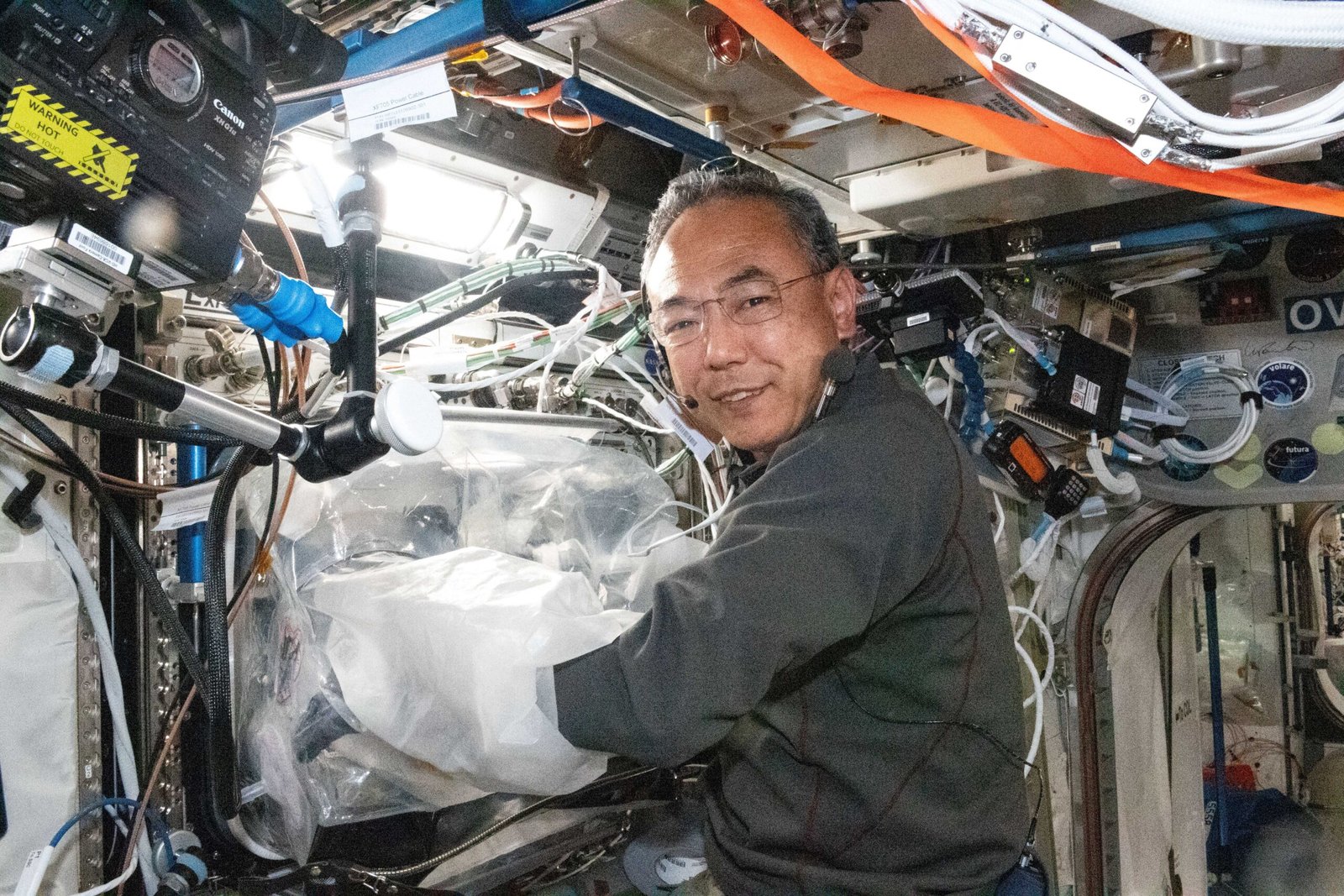

Innovative techniques are continually being developed to enhance the precision and efficiency of 3D organ printing. One such technique involves the use of microfluidic devices, which allow for the controlled deposition of bio-inks to create intricate structures. Another promising approach is the integration of artificial intelligence to optimize printing parameters and improve the fidelity of printed tissues. These advancements are akin to refining the tools of an artist, allowing for greater creativity and accuracy in the creation of complex tissue structures. As technology evolves, the potential for printing fully functional organs becomes increasingly attainable.
The Impact on Transplant Waiting Lists
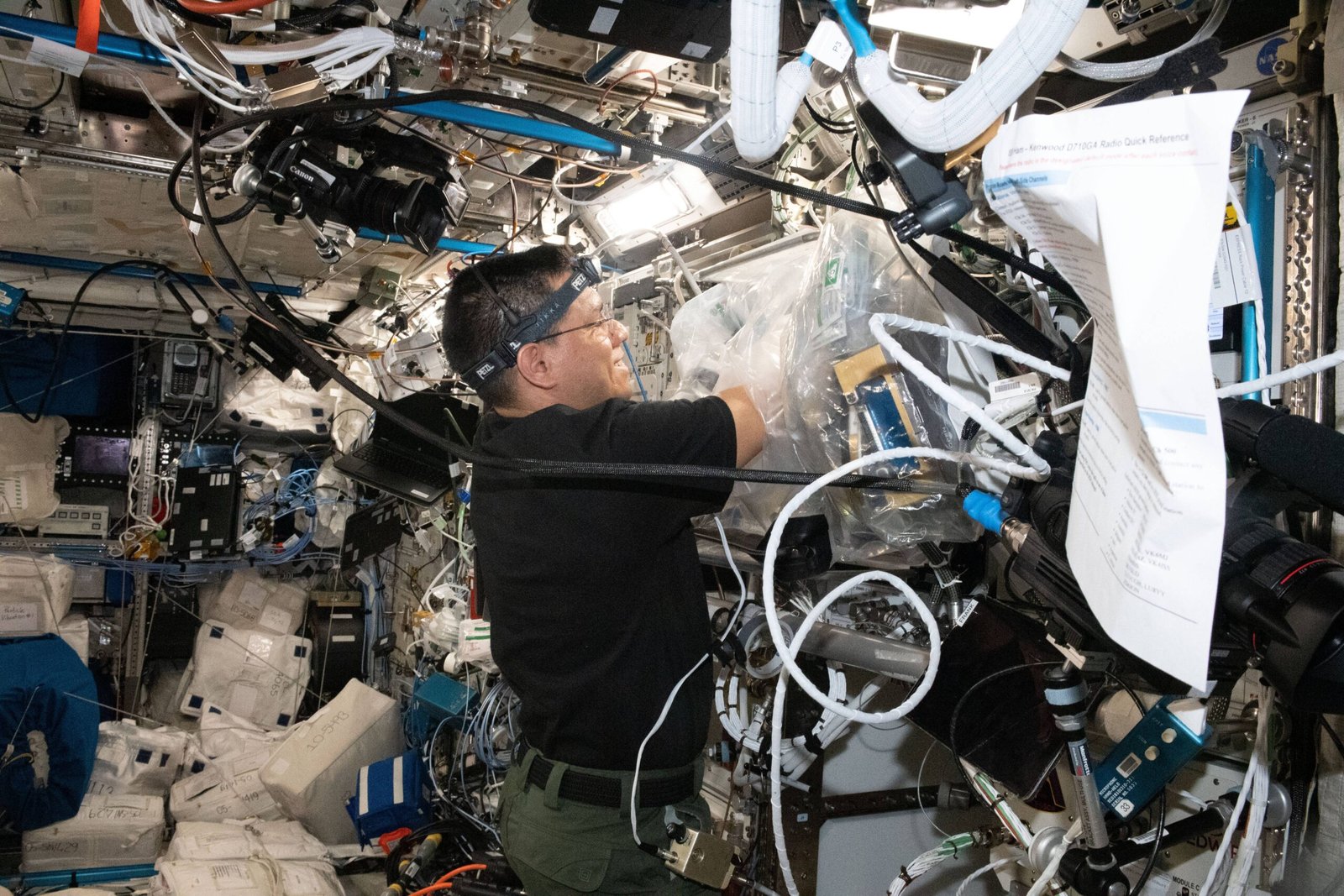

The impact of 3D-printed organs on transplant waiting lists could be transformative. Currently, thousands of patients worldwide face long and uncertain waits for life-saving organ transplants. The ability to produce organs on demand could drastically reduce these waiting times, saving lives and improving patient outcomes. Additionally, the reduced risk of rejection and complications associated with personalized organs could lead to more successful transplant procedures. This shift could alleviate the burden on healthcare systems and provide a new lease on life for countless individuals in need of transplants.
Future Prospects and Research Directions
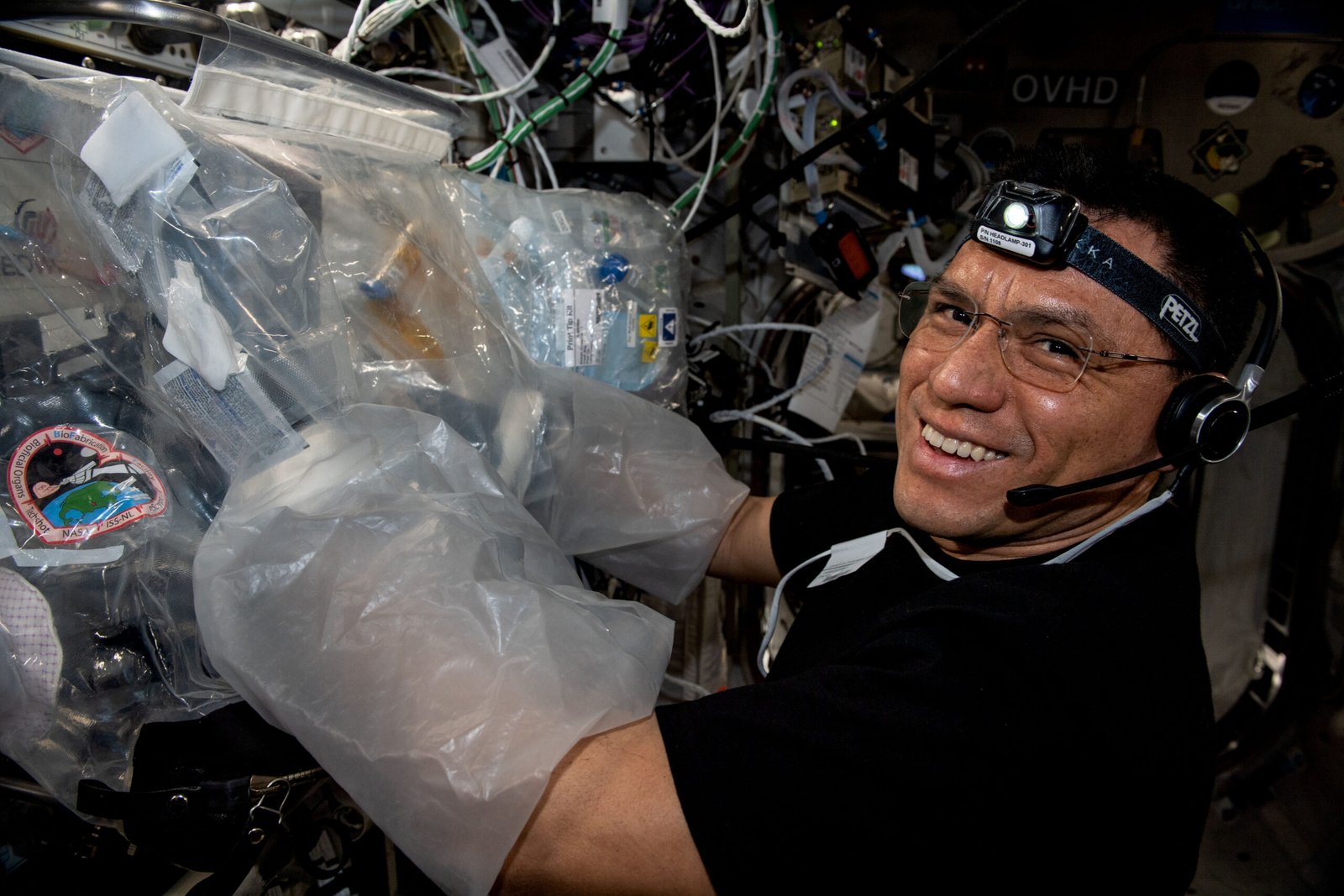

The future of 3D organ printing holds immense promise, with ongoing research paving the way for new breakthroughs. Researchers are exploring the potential of printing more complex organs such as kidneys, hearts, and lungs, each with its unique set of challenges. Collaborative efforts between scientists, engineers, and healthcare professionals are driving innovation and expanding the possibilities of what can be achieved. As technology continues to advance, the dream of a world where organ scarcity is a thing of the past becomes increasingly feasible. The journey toward fully functional 3D-printed organs is an ongoing adventure, filled with both challenges and exciting opportunities.
Conclusion
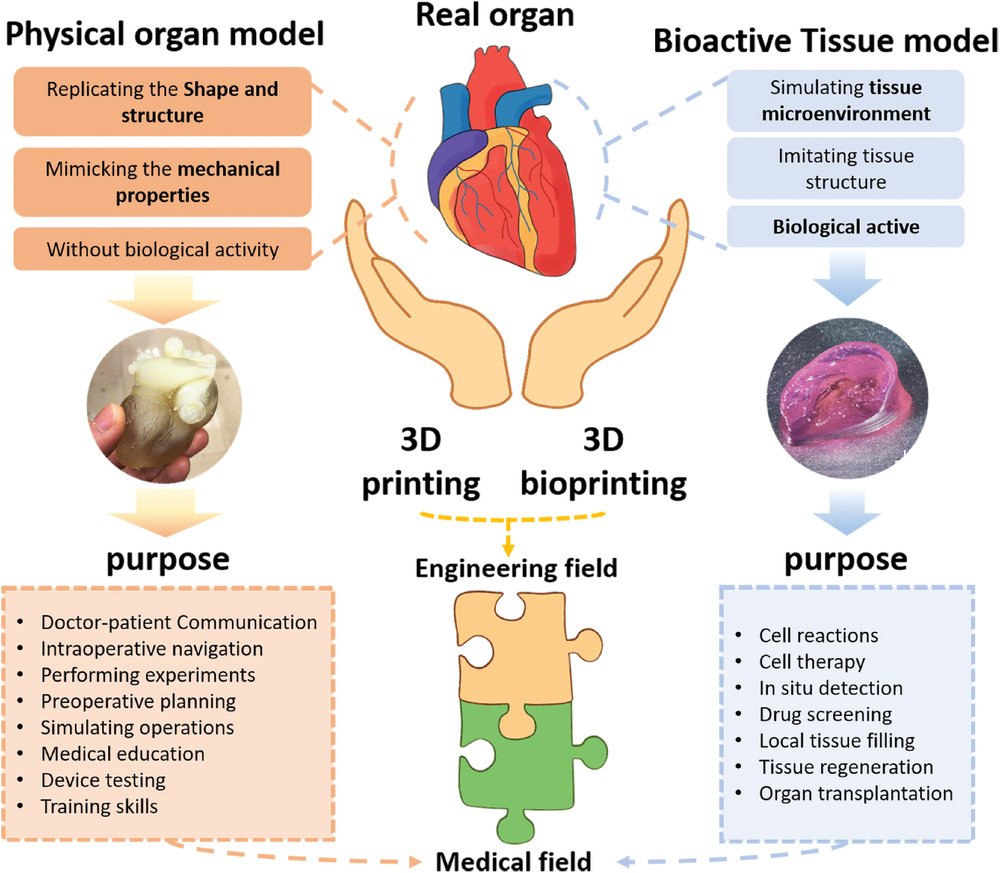
In conclusion, the field of 3D organ printing offers a glimpse into a future where organ scarcity is no longer a barrier to life-saving transplants. While challenges remain, the progress made so far is a testament to human ingenuity and the potential for transformative change. As researchers continue to push the boundaries of what is possible, the dream of 3D-printed organs may soon become a reality, offering hope and healing to millions around the world.




