In a world grappling with the dual challenges of food scarcity and energy shortages, the search for sustainable solutions has never been more urgent. Enter microalgae, an unassuming yet powerful organism that has the potential to revolutionize how we address these global crises. With their remarkable efficiency in converting sunlight into energy and nutrients, microalgae present a promising avenue for both food production and renewable energy sources. But how exactly do these tiny organisms work their magic, and can they truly live up to the hype? Let’s dive into the science behind algae farming and uncover the possibilities it holds for our future.
The Basics of Microalgae
Microalgae are microscopic organisms found in freshwater and marine systems. They are known for their ability to perform photosynthesis, a process in which they convert sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water into energy. Unlike their terrestrial counterparts, microalgae grow rapidly and can be cultivated on non-arable land, making them an environmentally friendly option. Their high efficiency in capturing solar energy and converting it into biomass is what sets them apart. In fact, microalgae can produce up to 50% of their weight in oil, a potential source of biofuel. This unique capability of microalgae positions them as a viable solution to some of the world’s most pressing issues.
Microalgae as a Food Source
The potential of microalgae as a food source is immense. Packed with proteins, carbohydrates, vitamins, and minerals, these organisms offer a nutrient-dense alternative to traditional crops. Spirulina and Chlorella are among the most well-known microalgae used in dietary supplements and health foods. They are not only a rich source of essential amino acids but also provide omega-3 fatty acids, which are vital for heart health. Moreover, microalgae can be grown in a variety of environments, including urban settings, thus reducing the burden on agricultural land. Their ability to thrive in diverse conditions makes them a sustainable option for food production, especially in regions facing food insecurity.
Algae Farming for Renewable Energy
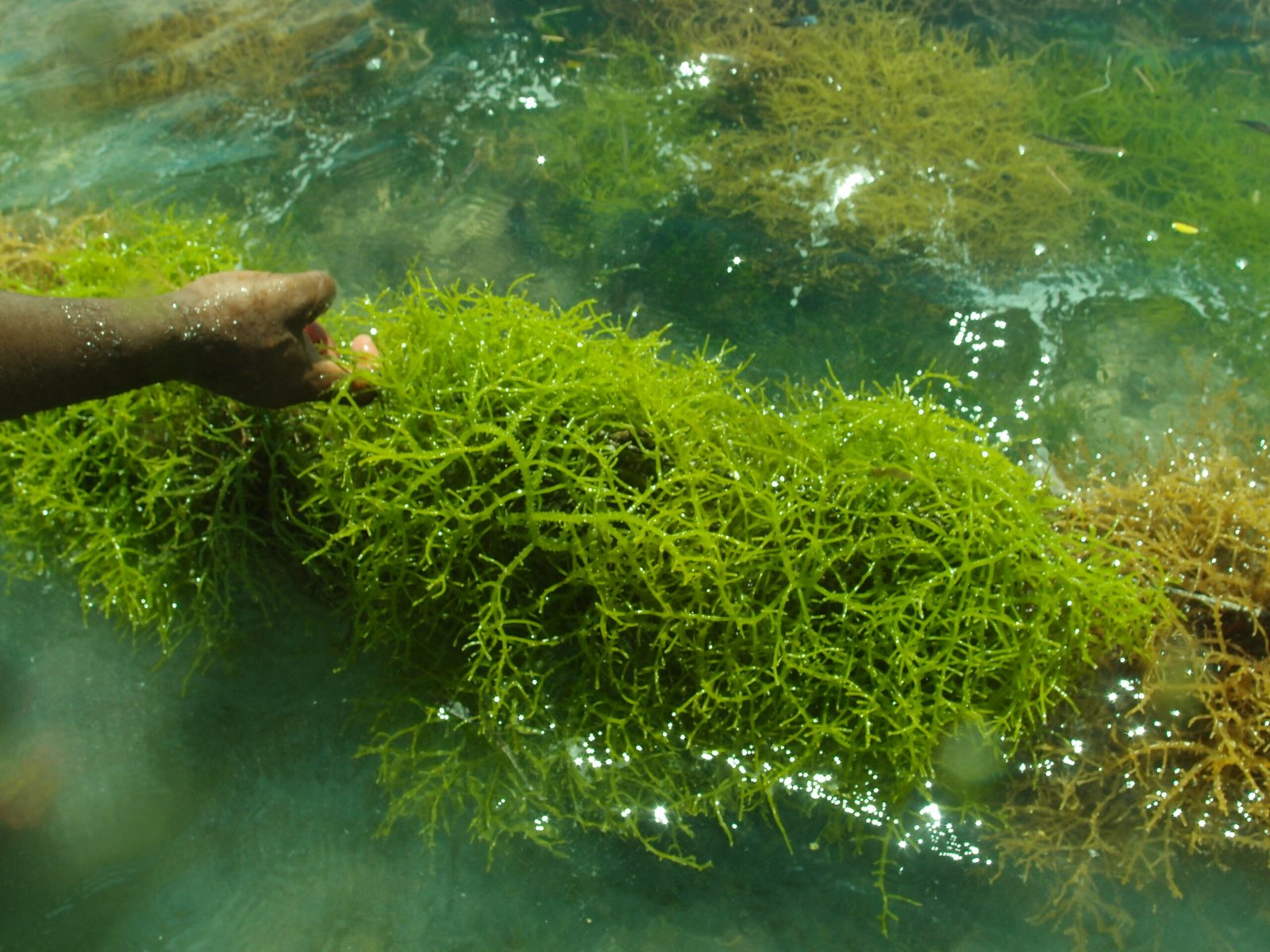

The energy potential of microalgae is equally significant. As the world seeks alternatives to fossil fuels, microalgae-based biofuels emerge as a promising solution. Algae farming involves cultivating these organisms in controlled environments, where they can be harvested for their oil content. This oil can then be converted into biodiesel, a renewable energy source that burns cleaner than conventional fossil fuels. The process of algae farming is not only efficient but also environmentally friendly, as it absorbs carbon dioxide during photosynthesis, thereby reducing greenhouse gas emissions. The scalability of algae farming makes it an attractive option for energy production on a global scale.
Environmental Benefits of Algae Cultivation
Beyond their role in food and energy, microalgae offer several environmental benefits. They play a crucial role in carbon sequestration, capturing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and converting it into biomass. This ability to absorb carbon makes algae cultivation a potential tool in mitigating climate change. Additionally, microalgae can be used in wastewater treatment, where they remove pollutants and produce oxygen as a byproduct. This dual function of cleaning waste and generating energy highlights the multifaceted advantages of algae farming. The integration of microalgae into existing systems could lead to more sustainable and eco-friendly practices across various industries.
Challenges in Algae Farming
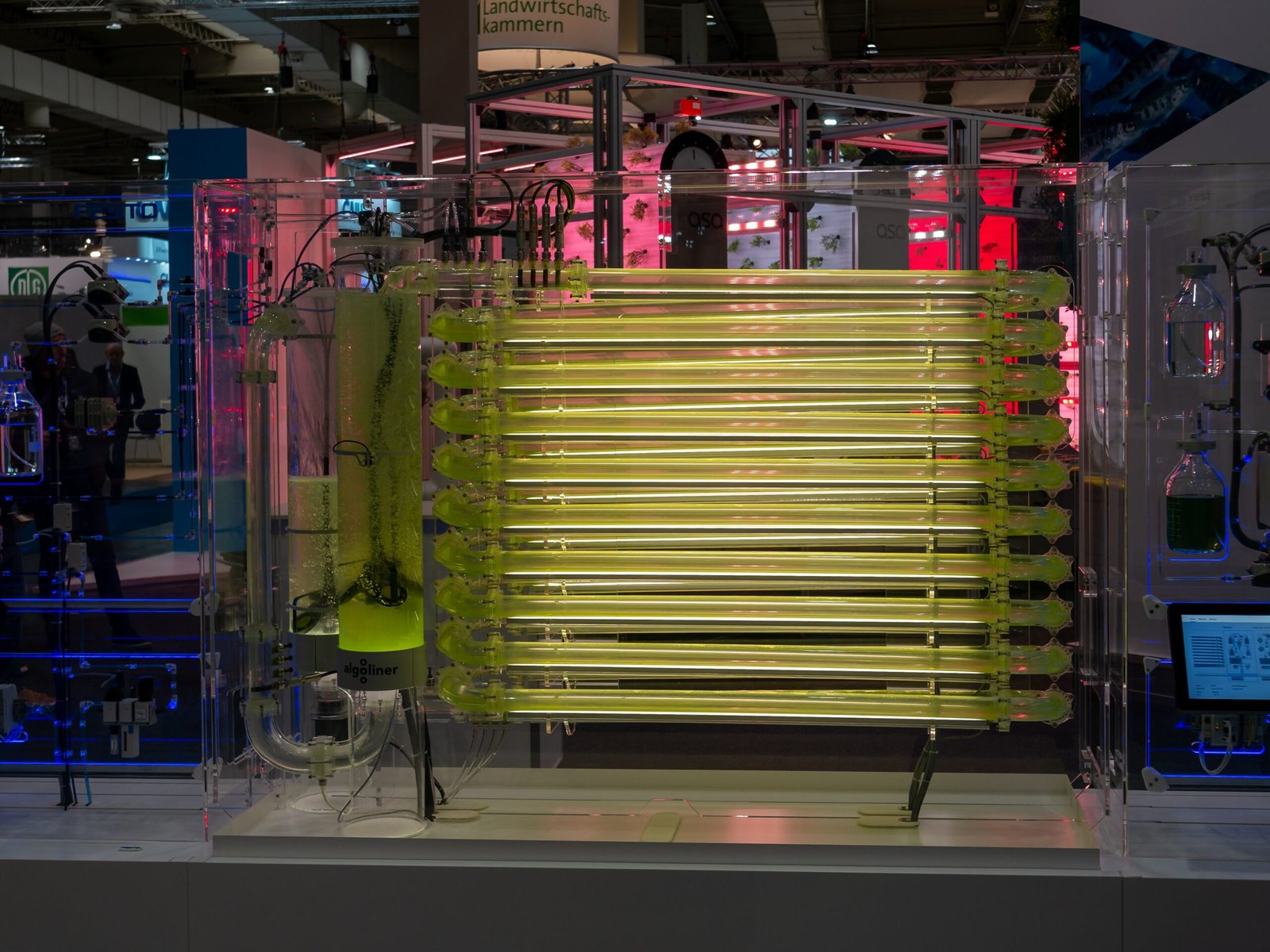
Despite the numerous benefits, algae farming is not without its challenges. One of the primary hurdles is the cost of production, which remains relatively high compared to traditional agricultural and energy sources. The cultivation of microalgae requires specific conditions, including light, temperature, and nutrient availability, which can be difficult to maintain on a large scale. Additionally, harvesting and processing microalgae efficiently is an area that requires further technological advancements. Addressing these challenges will be crucial for the widespread adoption of algae farming as a viable solution for food and energy production.
Innovations in Algae Technology

Recent advancements in technology have paved the way for more efficient algae farming practices. Researchers are exploring genetic engineering to enhance the growth rate and oil content of microalgae, making them more suitable for large-scale production. Innovations in photobioreactor design, which optimize light exposure and nutrient delivery, are also being developed to improve cultivation efficiency. Furthermore, integration with other renewable energy technologies, such as solar power, is being explored to reduce the operational costs of algae farming. These innovations hold the promise of making algae a more competitive and sustainable alternative in the global market.
Case Studies: Successful Algae Projects

Several successful algae farming projects around the world demonstrate the potential of these tiny organisms. In the United States, companies like Solazyme and Algenol have made significant strides in producing algae-based biofuels. Meanwhile, in Asia, countries like Japan and China are investing heavily in algae research for both energy and food applications. These projects showcase the versatility of microalgae and their ability to adapt to different environments and needs. By learning from these case studies, other regions can implement similar strategies to harness the power of algae for sustainable development.
The Future of Algae Farming
The future of algae farming looks promising, with ongoing research and innovation driving the industry forward. As the global population continues to grow, the demand for sustainable food and energy sources will only increase. Microalgae, with their unique properties and versatility, are well-positioned to meet these demands. By addressing the challenges and investing in technology, algae farming can become a cornerstone of sustainable development. The potential of microalgae to transform the way we approach food and energy production is immense, and the time to harness this potential is now.
Algae and the Circular Economy
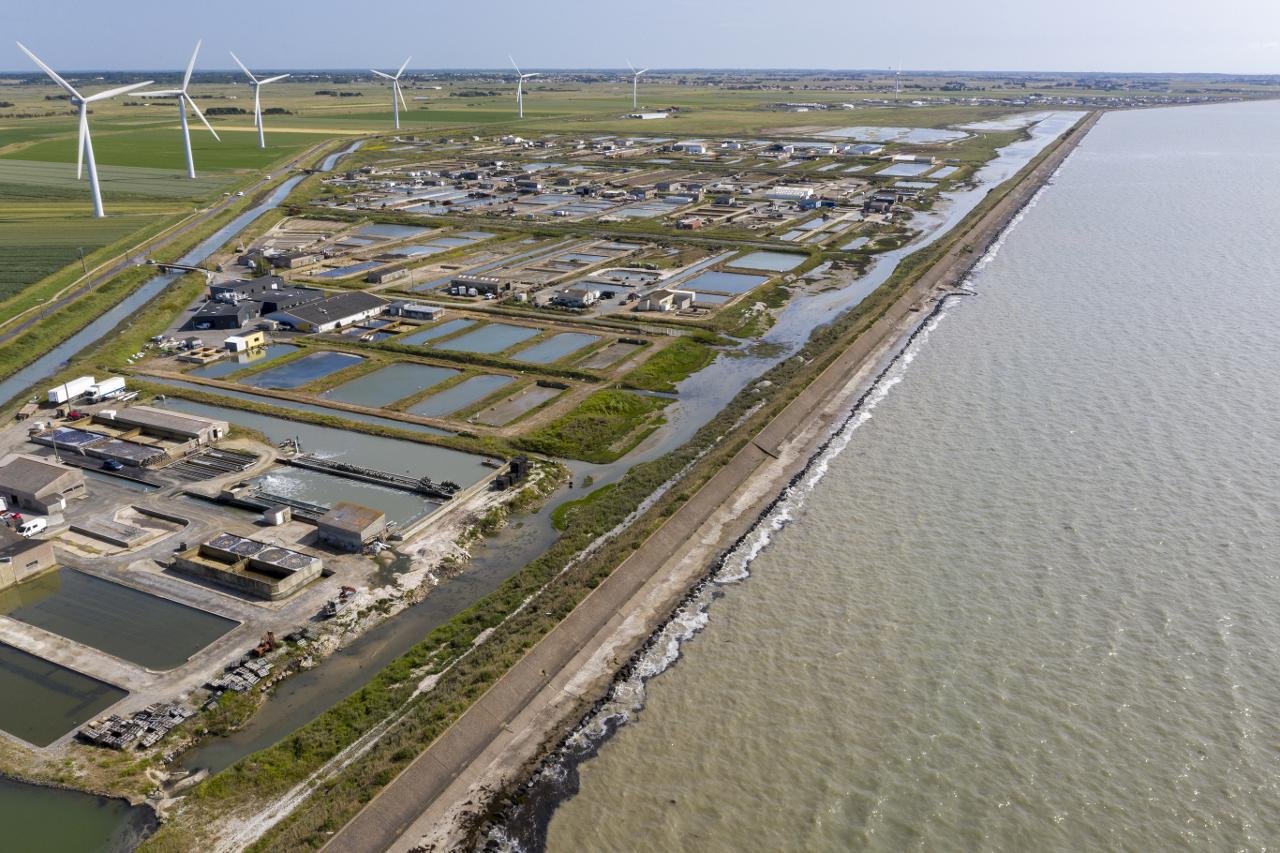

Microalgae farming aligns with the principles of a circular economy, where resources are used sustainably and waste is minimized. Algae cultivation can be integrated into various industries, creating a closed-loop system that recycles nutrients and energy. For instance, algae can be used to treat wastewater, which in turn provides nutrients for their growth. The biomass produced can then be converted into biofuel or animal feed, creating a sustainable cycle. This approach not only reduces waste but also maximizes resource efficiency, making it an attractive model for future development.
Conclusion: A Call to Action
The potential of microalgae to address the world’s food and energy challenges is undeniable. However, realizing this potential requires concerted efforts from governments, researchers, and industries. By investing in algae research and development, we can unlock new opportunities for sustainable growth. As we stand at the crossroads of a global crisis, the time to act is now. Embracing the power of microalgae could pave the way for a more sustainable and resilient future, where food and energy are abundant and accessible to all.




