Forests are often described as the lungs of our planet, playing a critical role in maintaining the delicate balance of our ecosystem. However, beneath the forest floor lies an unseen network that is just as crucial to the survival and health of these magnificent woodlands: mycorrhizal fungi. These underground fungal networks form symbiotic relationships with plant roots, providing essential nutrients and fostering communication between trees. Let’s delve into the fascinating world of mycorrhizal fungi and explore how they keep forests thriving.
The Symbiotic Relationship
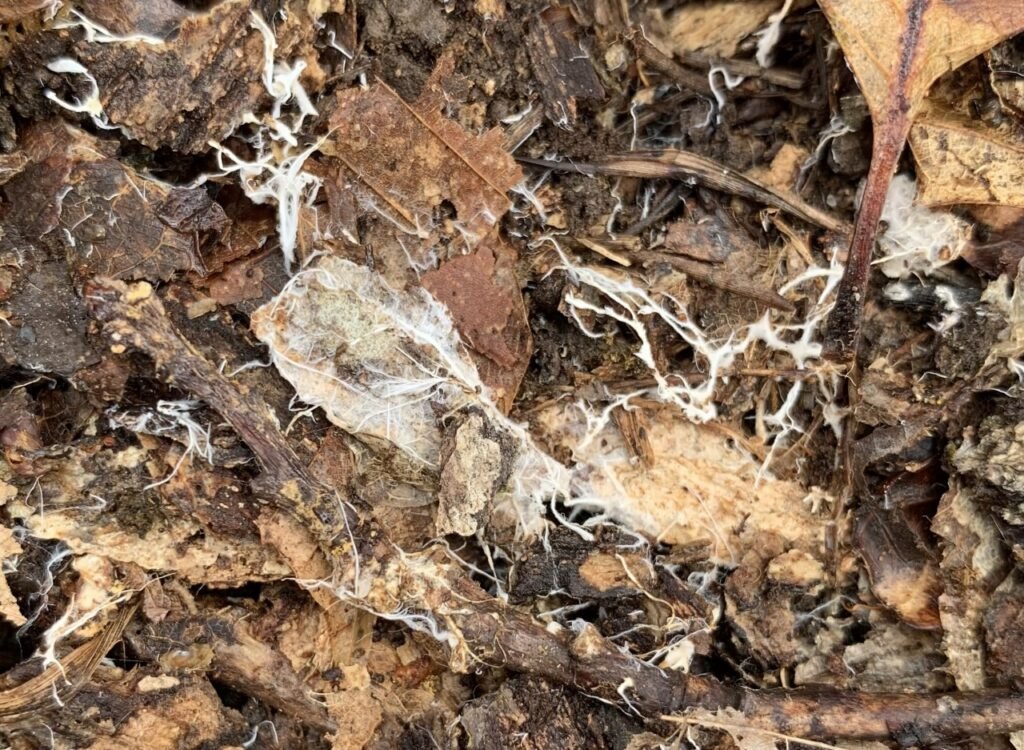

Mycorrhizal fungi and trees have a mutually beneficial relationship that has existed for millions of years. The fungi attach themselves to the roots of trees, forming an intricate network that extends far beyond the reach of the roots themselves. In return for sugars produced by the tree through photosynthesis, the fungi provide essential nutrients like phosphorus and nitrogen, which are often scarce in the soil. This relationship is akin to a barter system, where both parties benefit and thrive. Without this collaboration, trees would struggle to obtain the necessary nutrients to grow and sustain themselves.
A Boost to Nutrient Uptake
The secret to the success of mycorrhizal fungi lies in their ability to extend the root system of a tree far beyond its natural reach. The fine threads, or hyphae, of the fungi penetrate the soil, accessing nutrients and water that are otherwise unavailable to the tree. Imagine the fungi as a vast network of straws, sipping up vital nutrients and delivering them directly to the tree’s roots. This not only enhances the tree’s growth but also increases its resilience to environmental stresses, such as drought or poor soil conditions.
Fungal Networks Facilitate Communication
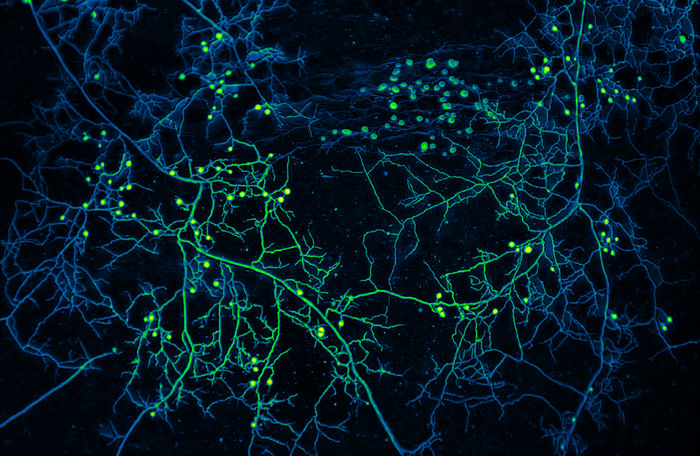
Beyond nutrient exchange, mycorrhizal fungi also play a crucial role in communication between trees. These underground networks allow trees to share information about environmental changes and threats, such as pest infestations or disease outbreaks. This communication system, often referred to as the “wood wide web,” enables trees to respond collectively to challenges, improving their chances of survival. It’s a bit like a forest-wide alarm system, alerting trees to danger and allowing them to mount a coordinated defense.
Enhancing Soil Structure
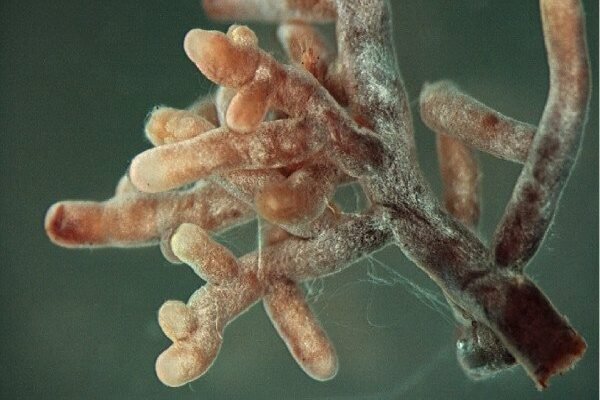
Mycorrhizal fungi contribute to the overall health of forest ecosystems by enhancing soil structure. As the fungi grow and spread, they bind soil particles together, creating aggregates that improve soil porosity and stability. This process not only aids in water retention but also reduces soil erosion, preserving the delicate balance of nutrients necessary for forest growth. In essence, these fungi act as nature’s engineers, continually reshaping and fortifying the soil beneath our feet.
Carbon Sequestration and Climate Change
Forests play a crucial role in mitigating climate change by sequestering carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. Mycorrhizal fungi contribute significantly to this process by enhancing the carbon storage capacity of trees. As trees absorb carbon dioxide during photosynthesis, a portion of this carbon is transferred to the fungi in exchange for nutrients. This carbon is then stored in the fungal network and soil, effectively locking it away and reducing the amount of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. In this way, mycorrhizal fungi are silent allies in the fight against climate change.
Supporting Biodiversity
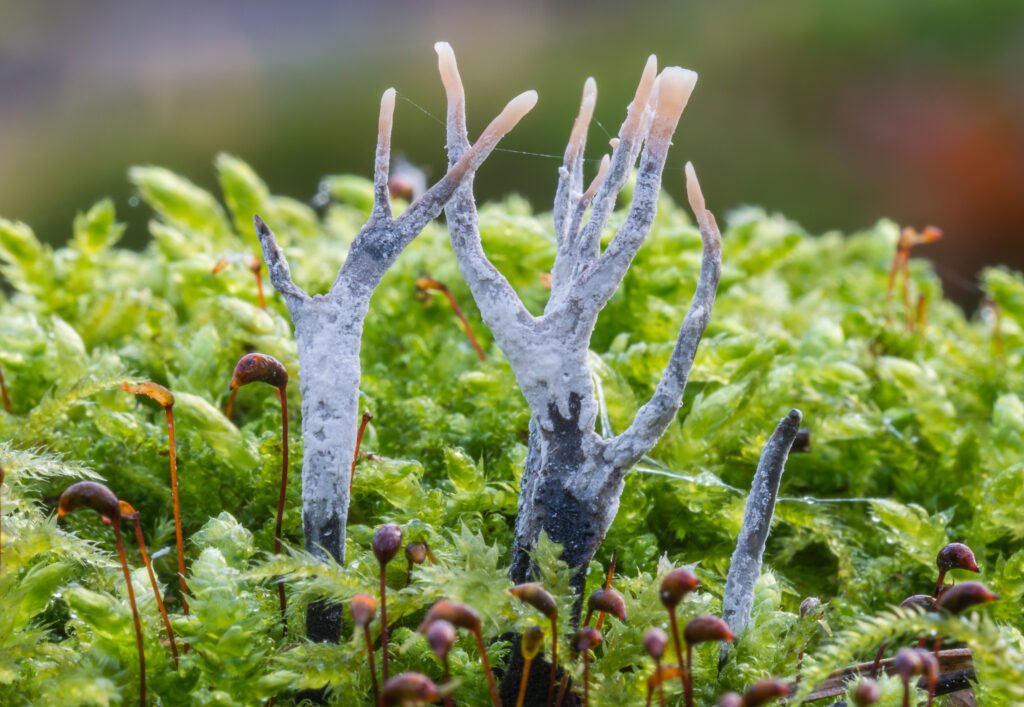

The presence of mycorrhizal fungi in forests promotes biodiversity by supporting a wide range of plant species. Different fungi form associations with different plant species, creating a complex web of interactions that fosters a diverse ecosystem. These fungi allow plant species that are less competitive for resources to thrive, maintaining a balance that supports a variety of organisms. By enhancing plant diversity, mycorrhizal fungi indirectly support insect, bird, and animal species, contributing to the rich tapestry of life found within forests.
Resilience Against Environmental Stress
Mycorrhizal fungi enhance the resilience of forests against environmental stressors such as drought, pollution, and disease. The fungi improve the water uptake efficiency of trees by accessing moisture from deeper soil layers, helping them survive during periods of drought. Additionally, the enhanced nutrient exchange provided by the fungi fortifies trees against pollutants and pathogens, reducing the likelihood of disease outbreaks. With the help of mycorrhizal fungi, forests can better withstand the challenges posed by a changing climate and human activities.
Restoring Degraded Ecosystems
In areas where forests have been degraded or destroyed, mycorrhizal fungi play a vital role in restoration efforts. By reintroducing these fungi into the soil, restoration projects can accelerate the recovery of plant communities and support the re-establishment of healthy ecosystems. The fungi enhance nutrient availability and soil structure, creating favorable conditions for plant growth and regeneration. As such, mycorrhizal fungi are indispensable allies in the fight to restore and preserve the world’s forests.
The Future of Forest Conservation
Understanding the role of mycorrhizal fungi in forest ecosystems opens up new avenues for conservation efforts. By prioritizing the protection and restoration of these underground networks, we can enhance the health and resilience of forests worldwide. Future research and conservation strategies must consider the importance of mycorrhizal fungi to ensure the long-term survival of forest ecosystems. By recognizing and harnessing the power of these fungi, we can work towards a more sustainable future for our planet’s forests.
In conclusion, mycorrhizal fungi are the unsung heroes of forest ecosystems, working tirelessly beneath the surface to support the health and vitality of trees. Through their intricate networks, these fungi provide essential nutrients, facilitate communication, and enhance resilience against environmental stressors. As we continue to explore the wonders of the natural world, let us not forget the vital role that mycorrhizal fungi play in keeping our forests alive and thriving.