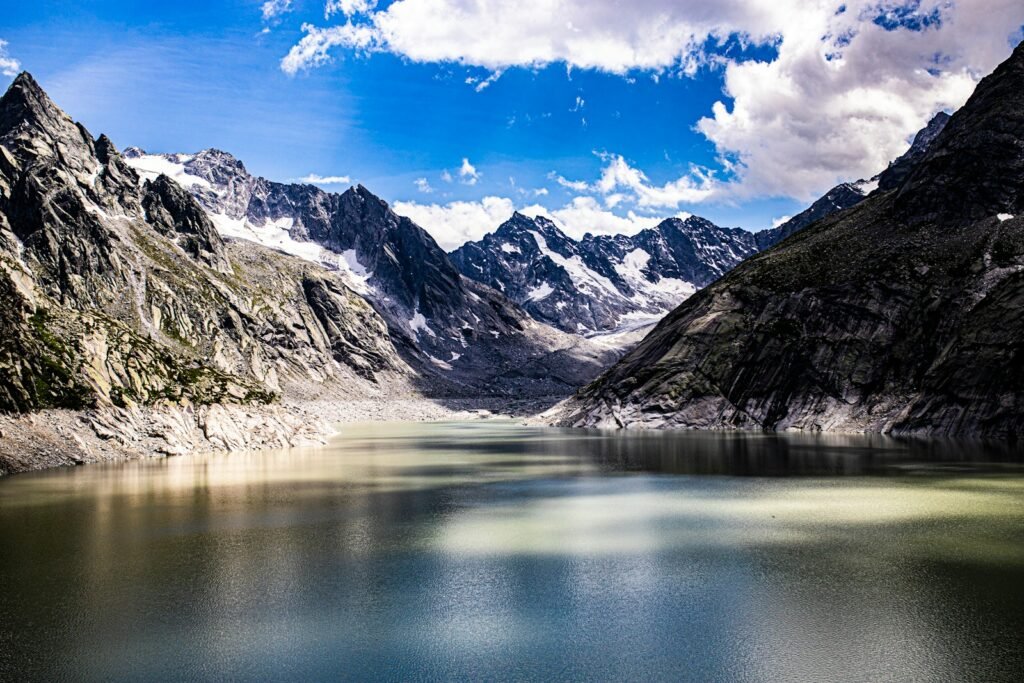
The breathtaking glaciers of the Alps, symbols of nature’s grandeur and resilience, are rapidly retreating. These natural wonders not only sculpt the landscape but also serve as pivotal freshwater reserves for vast regions. The vanishing glaciers signal not just environmental shifts but also profound implications for Europe’s freshwater supply. This article delves into the alarming retreat of the Alpine glaciers and explores what their disappearance means for the continent.
Glaciers: Europe’s Ancient Water Reservoirs

Glaciers in the Alps have long functioned as ancient reservoirs, holding water in frozen form and releasing it slowly over time. These icy structures are crucial in regulating Europe’s freshwater supply, feeding rivers and lakes, and sustaining communities, agriculture, and ecosystems across the continent. As such, they act as climate moderators and buffers against drought, ensuring water availability even in dry seasons.
The Accelerating Rate of Glacial Retreat

Scientific studies indicate that Alpine glaciers are retreating at an unprecedented pace, with some losing as much as one meter in thickness annually. This acceleration has been linked to rising global temperatures, with Europe experiencing some of its warmest years on record. The relentless retreat not only alters landscapes but also disrupts the natural water storage mechanism critical for maintaining the regional water cycle.
Impact on Europe’s Water Supply

As glaciers vanish, the immediate consequence is the reduced flow of freshwater into Europe’s river systems. This leads to lower water levels, which can significantly affect water availability for consumption, agriculture, and industry. With less water stored in glaciers, Europe’s dependency on seasonal and precipitation-based water sources will likely increase, introducing more variability and potential scarcity during dry spells.
Consequences for Wildlife and Biodiversity

The ecosystem surrounding the Alps is highly diverse, hosting a range of flora and fauna that depend on glacial meltwater. As these sources dwindle, the ripple effect on biodiversity is profound. Aquatic species, mountain vegetation, and many animal populations may face severe stress, potentially leading to habitat loss and declines in biodiversity.
Impact on Agriculture and Economy

The agricultural sector, heavily reliant on consistent water supply, is directly affected by the changes in meltwater flow. Regions that once depended on glacial runoff for irrigation may face challenges in maintaining crop yields. Furthermore, industries including hydropower generation, renowned for its reliance on steady river flow, face uncertainties that could translate into economic challenges.
Challenges Faced by Alpine Communities

Alpine communities, historically built around the abundance of glaciers, are now confronting new realities. Water scarcity affects daily life, commercial activities, and future prospects. Traditional practices and local economies, such as tourism and agriculture, must adapt to the changing landscape and water availability.
Tourism and Its Ecological Footprint

The Alps draw millions of tourists each year, captivated by the stunning glacial scenery. However, the influx of visitors contributes to environmental deterioration. The impact of tourism includes increased greenhouse gas emissions, littering, and infrastructure strain, all of which exacerbate the glaciers’ swift decline.
Climate Change: The Driving Force

At the root of the glacier’s decline lies climate change. Rising temperatures caused by increased greenhouse gas emissions are the primary drivers of glacial retreat. It’s a global problem with local repercussions, necessitating coordinated international efforts to mitigate emissions and curb temperature rises.
Adaptation and Mitigation Strategies

To address these challenges, adaptation and mitigation strategies are essential. This includes enhancing water conservation practices, investing in alternative water sources, and implementing modern irrigation techniques. Additionally, embracing renewable energy sources and advocating for policies aimed at reducing carbon emissions can help slow the rate of climate change.
Preserving Alpine Heritage

Preserving the cultural and natural heritage of the Alps is imperative. Local traditions, closely tied to the presence of glaciers, need to be documented and conserved. This involves fostering sustainable tourism practices and engaging local communities in glacial and environmental conservation efforts.
The Role of Technology in Monitoring Changes

Advanced technologies play a crucial role in monitoring and understanding glacial dynamics. Satellites, drones, and climate modeling software provide valuable data that helps track glacier changes, predict future scenarios, and shape responsive strategies. Leveraging such technology is vital for informed decision-making and planning.
International Cooperation for Environmental Protection

Protecting the Alps and their glaciers requires international cooperation, as environmental concerns transcend borders. Policies and treaties focusing on green energy, emission reductions, and climate adaptation strategies are essential for a sustainable future. Shared responsibility can drive meaningful action and foster a collaborative approach to environmental stewardship.
Engaging the Public: Awareness and Education

Raising awareness about the issues surrounding glacial retreat is fundamental. Public education initiatives can highlight the importance of glaciers and their role in the water cycle, encouraging individuals to adopt sustainable practices. Awareness can drive collective action and build a community committed to preserving these critical natural resources.
A Call to Action

The urgency of the situation calls for immediate attention and action from all sectors. Governments, industries, communities, and individuals must commit to sustainable practices, climate-smart policies, and innovation to protect the Alps and secure Europe’s freshwater future. Together, we can tackle the challenges posed by the vanishing glaciers and ensure a resilient response to climate impacts.
Conclusion

The retreat of the Alpine glaciers presents a stark warning about the wider impacts of climate change. As ancient glaciers vanish, the implications for Europe’s freshwater supply are multifaceted, affecting ecosystems, economies, and communities alike. However, with proactive measures, collaborative efforts, and sustainable practices, there is still hope for preserving the bounty of the Alps for future generations. Recognizing the value of these natural treasures is the first step toward safeguarding them. By acting today, we secure water security and environmental health for the Europe of tomorrow.