Mars has always captured human imagination with its striking red hues and mysterious landscapes. Recent images from NASA’s Mars Orbiter unveiled a peculiar geological feature that has intrigued scientists and space enthusiasts alike: kidney bean-shaped sand dunes. These fascinating formations provide new insights into the Martian climate and surface processes, enhancing our understanding of the Red Planet’s evolution.
Understanding Mars Orbiter’s Role

NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) plays a crucial role in exploring Mars, equipped with high-resolution cameras like the High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE). These instruments capture detailed images of Mars’ surface, aiding scientists in studying its topography, weather patterns, and potential landing sites for future missions. The recent images of the kidney bean-shaped dunes are another remarkable result of MRO’s ongoing observations.
The Formation of Kidney Bean-Shaped Dunes
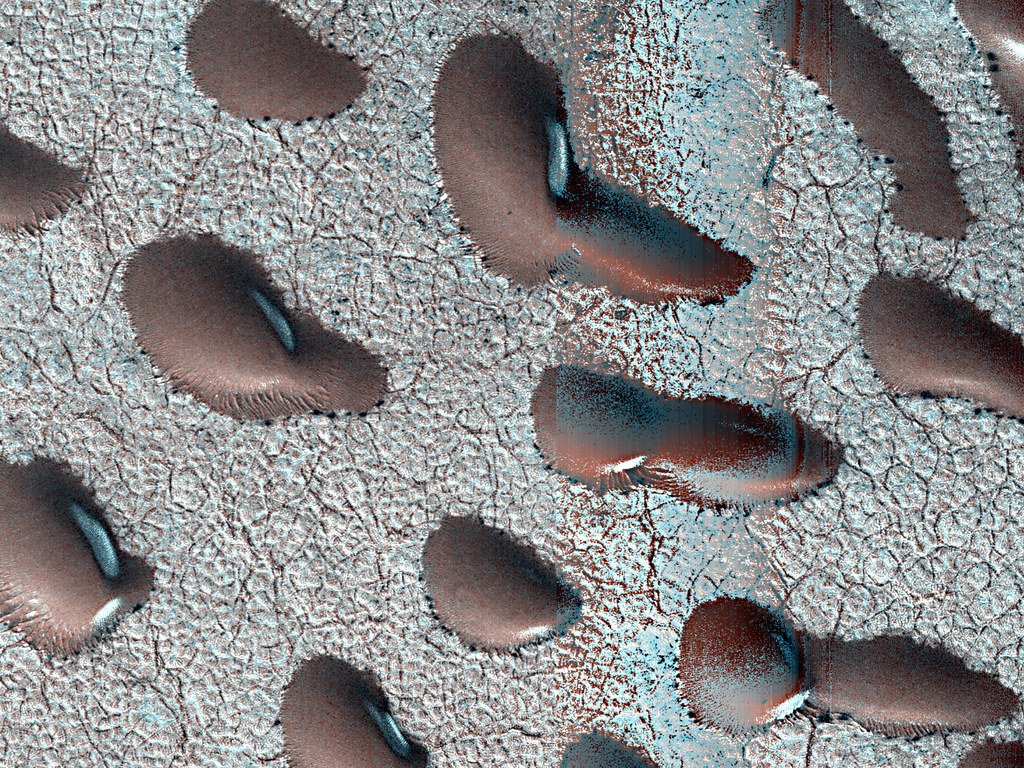
These unusual dunes are formed by the complex interplay of Martian winds and sand movement. Their shape is primarily influenced by bi-directional wind patterns, where wind blows from two different directions over time. This interaction causes the dunes to take on their distinctive kidney bean-like appearance, which is different from the more common crescent-shaped barchan dunes found on Mars.
Role of Wind in Shaping Martian Dunes

Wind plays a significant role in shaping the Martian landscape, much like it does on Earth. However, Mars’ less dense atmosphere means that wind speeds need to be higher to move sand particles. The study of these kidney bean dunes helps scientists understand wind directions, speeds, and seasonal changes on Mars, offering clues about the planet’s atmospheric conditions both in the present and past.
Implications for Martian Climate Studies

The discovery of these dunes is crucial for interpreting Mars’ climatic history. The formation patterns of these dunes suggest the presence of wet and dry cycles, indicating how the climate may have evolved over time. Understanding these cycles is pivotal in piecing together the planet’s environmental history and assessing its habitability.
Insights into Erosion and Sediment Transport

By analyzing the size, shape, and distribution of these dunes, researchers gain essential insights into erosion processes and sediment transport on Mars. This knowledge helps in unraveling the history of water and wind activity, which are key factors in shaping the planet’s surface environment, hinting at Mars’ dynamic geological past.
Comparative Studies with Earth

Studying Martian dunes also allows scientists to compare them with terrestrial dunes, enhancing our understanding of geological processes in different planetary environments. Such comparative analysis is essential for recognizing universal patterns in dune formation and evolution, offering broader insights into planetary science.
Technological Advancements in Mars Exploration
The capability to capture detailed images of Mars’ surface is a testament to the technological advancements in space exploration. Instruments like HiRISE empower scientists to conduct remote geological studies with unprecedented accuracy. As technology evolves, so too does our capacity to explore and understand distant worlds.
Future Exploration and Research Opportunities

The findings from MRO set the stage for future Mars missions and research. Understanding the Martian environment is crucial for preparing manned missions, as well as for selecting landing sites for robotic explorers. The study of kidney bean dunes will continue to be an integral part of these planning processes.
Conclusion: A New Chapter in Mars Exploration

The discovery of kidney bean-shaped sand dunes on Mars is more than just a fascinating visual; it’s a gateway to deeper scientific inquiry. These dunes offer a unique window into past and present weather patterns, climate conditions, and geological processes on Mars. As NASA and other space agencies continue to explore the Red Planet, each finding brings us one step closer to unraveling Mars’ secrets, paving the way for future discoveries and potential human exploration.




