Kew Gardens, renowned for its vast botanical collections and contributions to global plant conservation, marks an exciting milestone with its largest expansion in a decade. Over 300 wild plant species are now under preservation, ensuring their survival amidst the growing threats of climate change and habitat destruction. This monumental effort not only strengthens conservation outreach but also enriches Kew’s renowned scientific research capabilities.
History and Mission of Kew Gardens

Founded in 1840, Kew Gardens has been at the forefront of botanical research and plant conservation for over a century. The organization is committed to safeguarding plant biodiversity and fostering sustainable relationships between plants and people. Its mission extends beyond preservation, aiming to educate the public and promote global conservation policies.
The Need for Seed Preservation

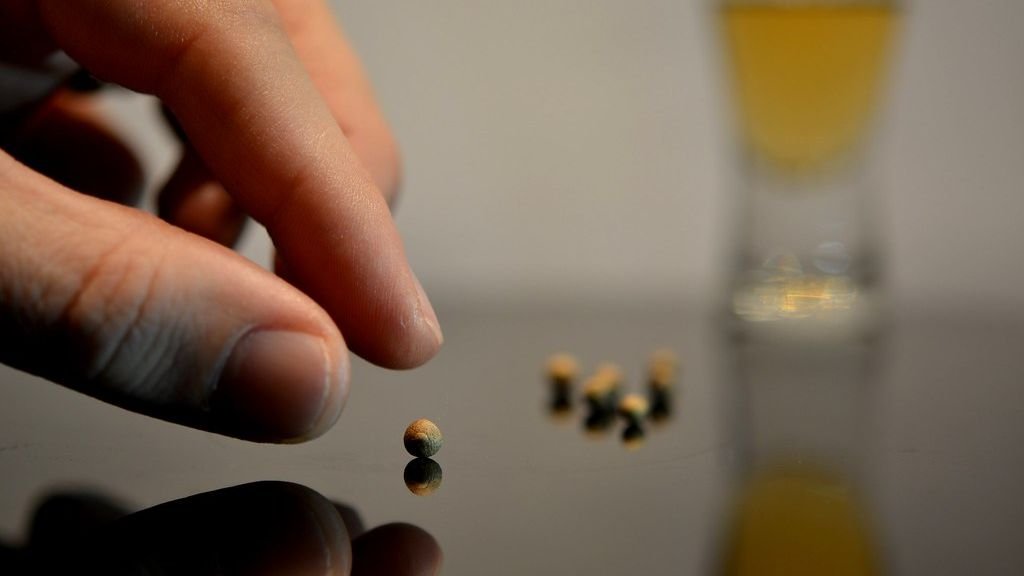
With ongoing environmental challenges, such as deforestation and climate change, the preservation of wild plant seeds becomes crucial. Kew Gardens’ initiative focuses on species that are at risk of extinction, ensuring their propagation for future generations. This initiative provides insurance against biodiversity loss, allowing these plants to potentially be reintroduced to their native environments if necessary.
Understanding the Science of Seed Banking

Seed banking involves the collection, drying, and storage of seeds to preserve plant genetic diversity. The process needs meticulous attention to ensure seed viability over time. Seeds are stored at low temperatures to slow down the natural aging process, preserving them for decades or even centuries. Kew Gardens is at the cutting edge of this technology, leveraging its expertise to expand its seed banks.
Target Species for Preservation

The selection of species for preservation centers around those most at risk. This includes endemic species with limited geographic distribution and others perceived as crucial for ecosystem restoration. Kew Gardens collaborates globally to assess conservation priorities and identify the species in dire need of protection.
Advanced Techniques in Seed Preservation
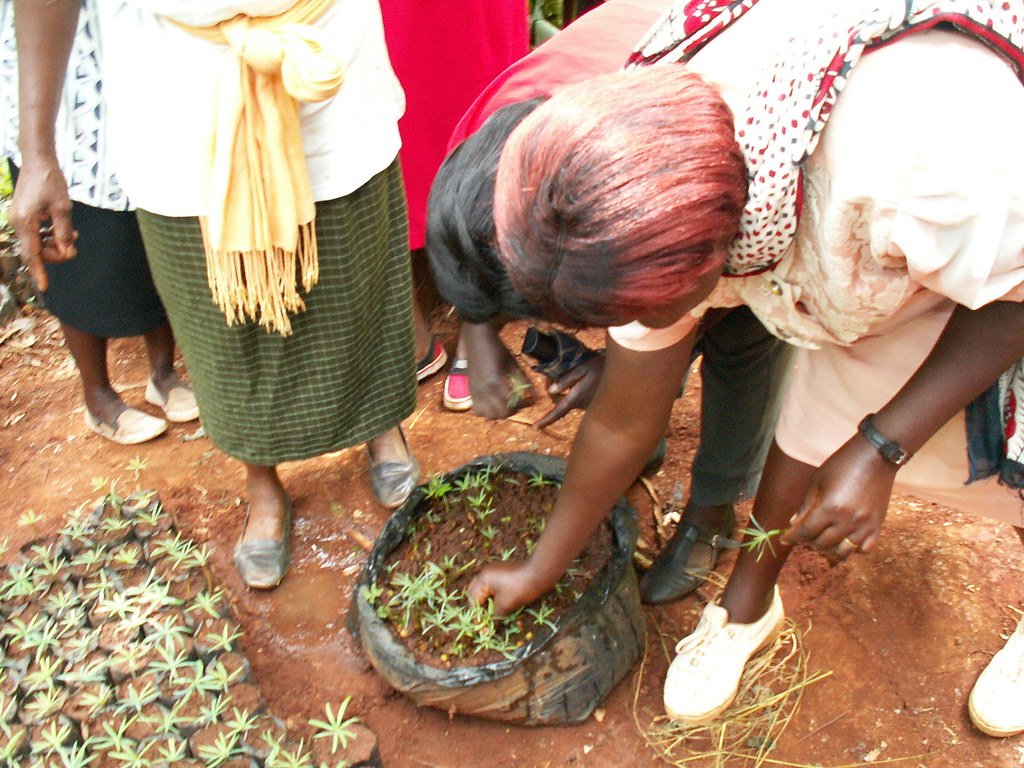

Kew Gardens employs advanced biotechnological methods to assess seed quality and improve germination rates. Techniques such as micropropagation and cryopreservation enable long-term storage while maintaining genetic integrity. These methods ensure that even the most challenging seeds can be preserved effectively.
Collaboration with Global Partners

This expansion is not a solitary endeavor; Kew Gardens collaborates with international conservation organizations and research institutes. These partnerships allow for the exchange of knowledge and resources, enhancing the global impact of seed preservation efforts and facilitating biodiversity restoration projects.
Public Education and Engagement

Educating the public about the importance of plant conservation is integral to Kew’s mission. Through workshops, exhibitions, and interactive sessions, visitors learn about the role of seed preservation and its significance to global ecosystems. This educational component fosters a deeper appreciation for nature and encourages public involvement in conservation efforts.
Innovations in Climate Adaptation Research

Preserving seeds provides critical data that helps researchers understand how plants adapt to changing climates. Kew Gardens uses this information to study plant resilience, offering insights that can inform restoration projects and guide conservation strategies in the face of environmental shifts.
The Role of Kew Gardens in Global Biodiversity Policies

In their efforts, the staff at Kew work closely with environmental policymakers. This collaboration ensures that the preservation strategies align with global biodiversity frameworks like the Convention on Biological Diversity. Such alignment facilitates synergies across various national and international conservation efforts.
Contributing to Sustainable Development Goals

Seed preservation at Kew Gardens contributes to the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals, particularly those related to life on land and climate action. By preserving plant diversity, Kew Gardens supports ecosystem sustainability, food security, and the mitigation of economic impact resulting from plant-based resource depletion.
Future Prospects and Expansion Goals

Kew Gardens plans to expand its seed bank capacity further, incorporating more species and enhancing its storage technologies. These efforts will require increased funding, research, and public support, aiming to establish the most comprehensive collection of preserved wild plant seeds in history.
The Importance of Volunteering and Community Involvement

Community volunteers play a pivotal role at Kew, assisting with both on-site activities and outreach programs. Their contribution enhances the garden’s ability to manage and sustain its expansive collection, offering a model of how community involvement can underpin large-scale conservation efforts.
Final Thoughts: A Green Legacy for Future Generations

Kew Gardens’ largest expansion in seed preservation marks an essential step towards safeguarding plant biodiversity. By protecting over 300 species from extinction, Kew provides a living vault of nature’s legacy that can inspire, educate, and benefit future generations. As the threats to our natural world intensify, such efforts underscore the critical importance of conserving plant life for both ecological balance and human prosperity.