In the ever-changing tapestry of life on Earth, evolution is the silent artist, constantly painting new patterns and forms. While it’s easy to think of evolution as a process that occurs over millennia, some species are showing remarkable changes in much shorter time frames. These rapid evolutions are not only fascinating but offer a glimpse into how adaptable life can be when faced with changing environments. Here, we explore eight species that are evolving right before our eyes, demonstrating nature’s incredible capacity for change.
1. Urban Coyotes: Navigating the Cityscape
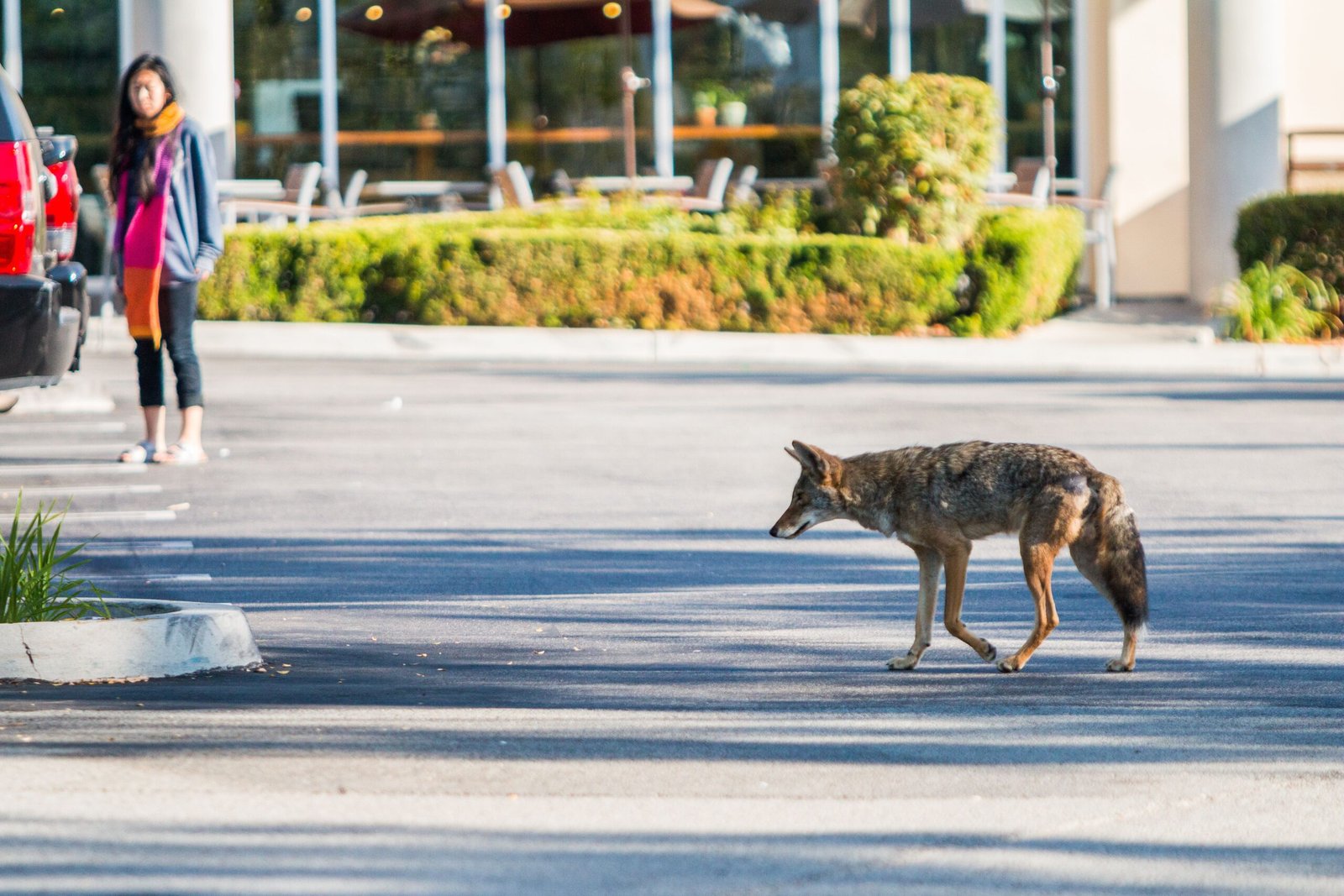

As cities expand, coyotes have become a common sight in urban areas. These adaptable creatures are changing their behaviors to thrive in city environments. Unlike their rural counterparts, urban coyotes have developed a knack for navigating traffic and scavenging food from human sources. This evolution in behavior has allowed them to flourish in areas once deemed unsuitable. Researchers have observed that urban coyotes are becoming more nocturnal, likely to avoid human encounters. Their diets have also shifted, focusing more on human food waste, showcasing their incredible adaptability. This evolution highlights how wildlife can adjust to the sprawling human landscape.
2. The Peppered Moth: A Classic Tale of Adaptation
The story of the peppered moth is a textbook example of evolution in action. During the Industrial Revolution, these moths in England adapted to the soot-covered trees by developing darker wings, which provided better camouflage from predators. As pollution levels decreased and trees reverted to their lighter colors, the moths’ wings lightened again. This rapid shift in coloration is a clear demonstration of natural selection at work. The moth’s ability to change its appearance based on environmental conditions offers a profound insight into how species can respond to human-induced changes. It serves as a powerful reminder of nature’s resilience and adaptability.
3. Italian Wall Lizards: A Diet-Induced Transformation
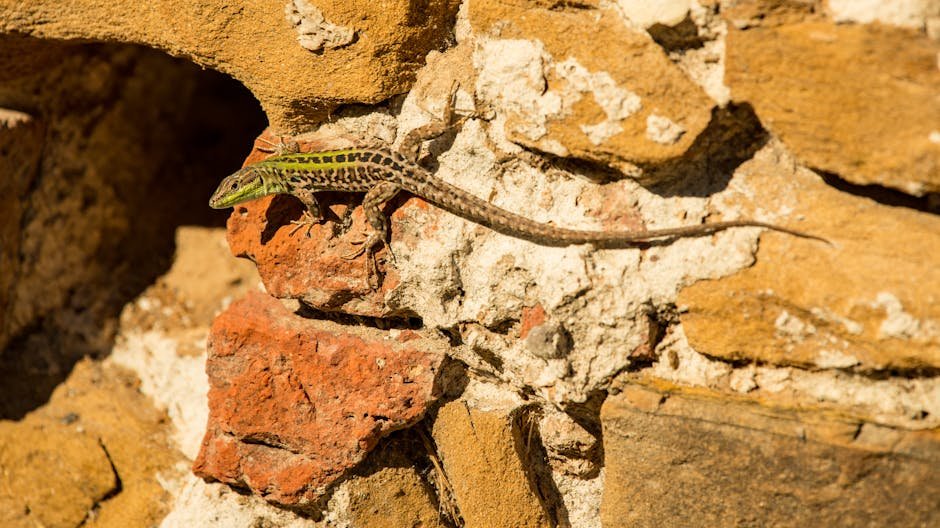

In the 1970s, a small population of Italian wall lizards was moved to a new island, resulting in a fascinating evolutionary experiment. Over a few decades, these lizards developed significant physical changes, including larger heads and stronger jaws. These adaptations were likely a response to a new diet of tough plants unavailable on their original island. The lizards also developed new digestive structures to process this fibrous diet, showcasing rapid evolutionary change. This transformation is a striking example of how a change in diet can drive evolutionary adaptations in a relatively short period.
4. Superbugs: The Antibiotic Arms Race
Bacteria are evolving at an alarming rate, particularly in response to the widespread use of antibiotics. These superbugs, like MRSA, have developed resistance to medications that once easily killed them. This rapid evolution is driven by the bacteria’s short life cycle and ability to share genetic material. The rise of antibiotic-resistant bacteria poses a significant challenge to modern medicine, highlighting the urgent need for new treatment strategies. This evolution serves as a stark reminder of the unintended consequences of human actions on microbial life. It underscores the importance of responsible antibiotic use and ongoing research into alternative treatments.
5. Cane Toads: Rapid Adaptation in Australia

Introduced in Australia to control pests, cane toads have become a notorious invasive species. In response to the harsh Australian environment, these toads are evolving longer legs, allowing them to cover more ground and spread rapidly. This physical change is accompanied by behavioral adaptations, such as increased aggression and altered feeding habits. The evolution of cane toads is a testament to how quickly species can adapt to new environments, even when introduced by human intervention. This rapid adaptation highlights the complex dynamics between invasive species and their new ecosystems.
6. Elephant Tusklessness: A Response to Poaching

The brutal reality of poaching has left a lasting impact on elephant populations. In some areas, there is a noticeable increase in tuskless elephants, a trait that offers a survival advantage in regions plagued by poaching. As poachers target elephants with tusks, those without them are more likely to survive and reproduce. This shift in genetics is a poignant example of evolution driven by human activity. While tusklessness provides protection against poachers, it also raises concerns about the long-term implications for elephant populations and their ecosystems.
7. Darwin’s Finches: A Living Laboratory of Evolution

In the Galápagos Islands, Darwin’s finches continue to evolve, providing a living laboratory for scientists. Researchers have observed changes in beak size and shape in response to food availability and environmental conditions. These adaptations occur over relatively short periods, demonstrating natural selection in action. The finches’ ability to adapt to changing conditions underscores the dynamic nature of evolution. Their ongoing evolution offers invaluable insights into how species can respond to environmental pressures, contributing to our understanding of natural selection.
8. Human Evolution: The Ever-Changing Species
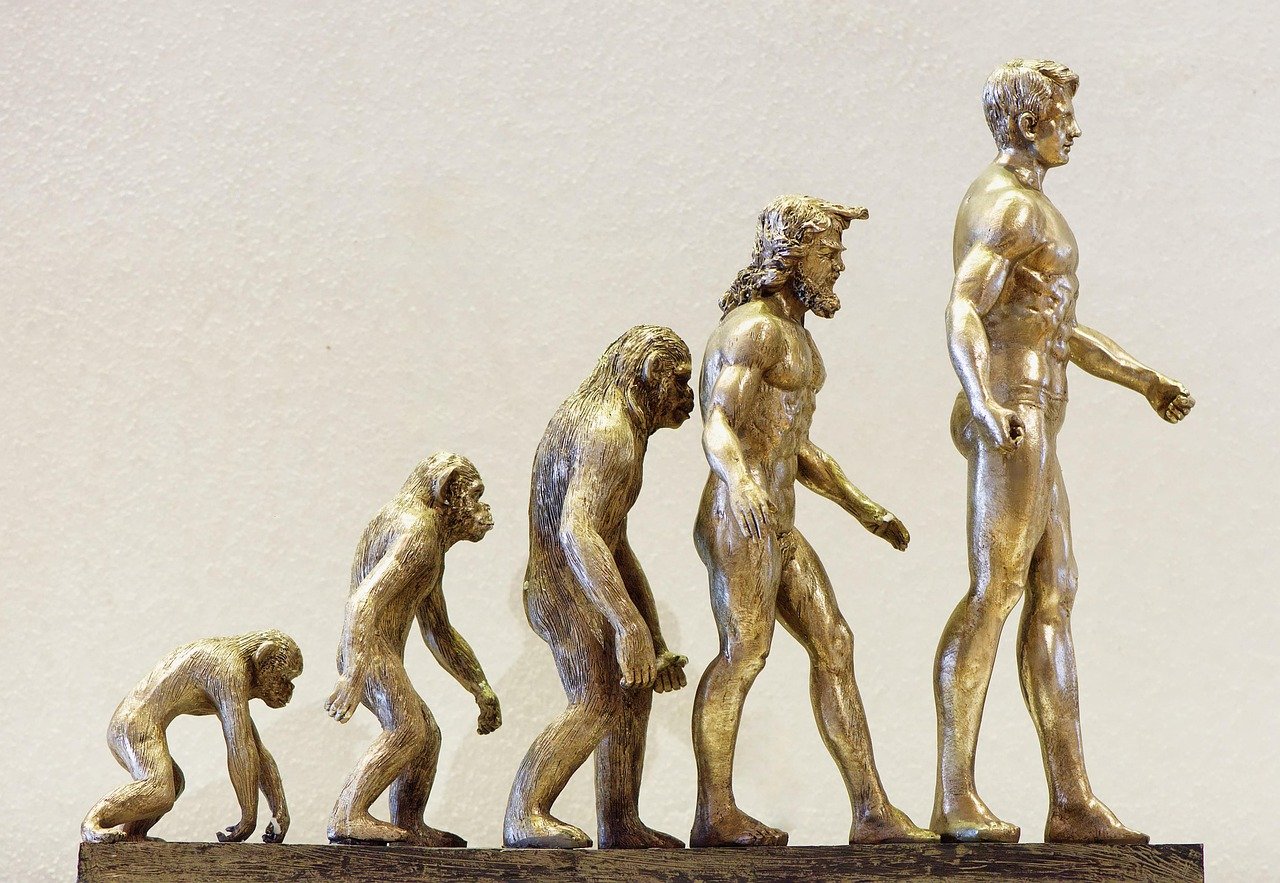

Humans are not exempt from the forces of evolution. While our evolution may not be as immediately visible as other species, it is happening nonetheless. Changes in diet, lifestyle, and environment continue to shape our physiology and genetics. For instance, some populations have developed lactose tolerance, an adaptation to dairy consumption. The rise of technology and modern medicine is also influencing human evolution, leading to new traits and adaptations. This ongoing evolution highlights our species’ ability to adapt to a rapidly changing world, offering a fascinating glimpse into our future.
Evolution is a continuous process, shaping life in response to an ever-changing world. The species discussed here are just a few examples of how life adapts and evolves right before our eyes. These stories remind us of the incredible resilience and adaptability of nature, encouraging us to appreciate and protect the diverse tapestry of life on Earth.



