The Murray-Darling Basin, a vast area spanning over a million square kilometers in Australia, is a critical resource for the nation. Housing one of the world’s most productive agricultural regions, it is vital to both the environment and economy. However, water shortages have become an ever-growing concern, challenging states like New South Wales (NSW) and Victoria. This article delves into the strategies these regions are employing to address this pressing issue.
Background of the Murray-Darling Basin

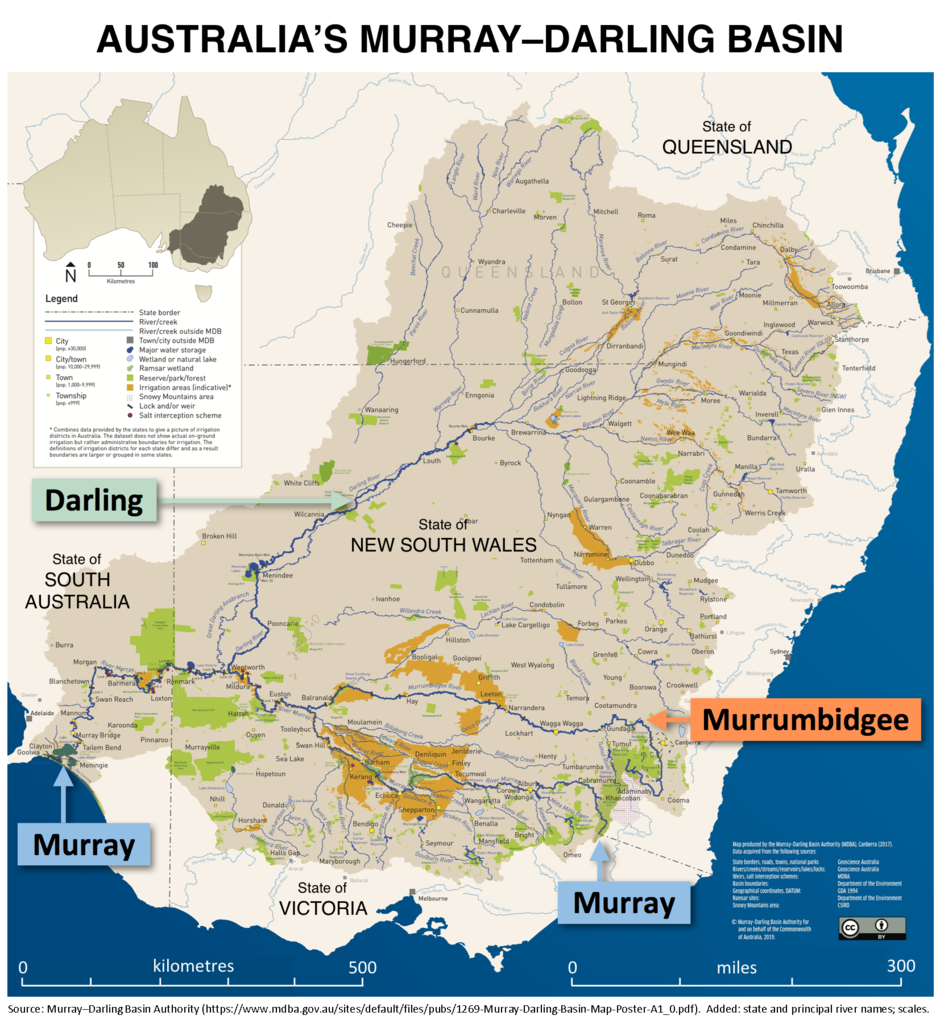
The Murray-Darling Basin covers parts of Queensland, New South Wales, the Australian Capital Territory, Victoria, and South Australia. Home to a network of rivers and rich biodiversity, it supports agriculture, wildlife, and the communities that live there. However, water management has been a contentious issue, given the competing needs of agriculture, environment, and urban use.
Water Shortages: A Growing Challenge

Over the past decade, water scarcity has intensified primarily due to prolonged droughts, over-allocation of water resources, and climate change. These shortages threaten the basin’s agriculture and ecosystems, prompting state governments to take action.
New South Wales: Policy and Plans
NSW has established comprehensive plans to manage water resources effectively. The state government is implementing policies focused on water conservation, efficiency improvements, and infrastructure development. Efforts include upgrading irrigation systems, promoting water-efficient farming practices, and constructing new water storage facilities.
Victoria’s Approach to Water Management

Victoria has adopted an integrated water management approach, which aims to balance environmental, social, and economic needs. The state promotes initiatives such as water recycling, stormwater harvesting, and improved catchment management. Victoria’s water corporations work closely with communities to ensure sustainable water use.
Environmental Water Allocations

Both NSW and Victoria have dedicated efforts to restore natural flows and support ecological health. Environmental water allocations are made to ensure that wetlands and other key ecosystems maintain their functions and biodiversity. These allocations are crucial for maintaining the health and resilience of the basin’s environment.
Technological Innovations

Innovations in technology play a significant role in managing water shortages. Both states are investing in advanced monitoring systems and data analytics to optimize water usage. Smart irrigation systems and remote sensing technologies are among the initiatives enhancing water management practices.
Community Engagement and Education

Public education and community engagement are central to water management strategies in both states. By involving local communities and raising awareness about water conservation, NSW and Victoria aim to foster a culture of sustainable water use. Community programs and educational campaigns highlight the importance of individual and collective action.
Economic Implications

Water shortages have significant economic implications, with agriculture being one of the hardest-hit sectors. NSW and Victoria are investing in research and development to mitigate these impacts. Developing water-efficient crops and encouraging alternative farming practices are pivotal to sustaining agricultural productivity.
Challenges in Policy Implementation

Despite efforts, policy implementation faces several challenges, including regulatory inconsistencies and insufficient funding. Inter-state coordination is necessary to ensure that policies are effective across the entire basin. Both NSW and Victoria continue to navigate these complexities as they refine their water management strategies.
Opportunities for Collaboration

Collaborative efforts between states, industries, and communities offer opportunities for more resilient water management. Joint initiatives can leverage resources, share best practices, and develop innovative solutions to address water shortages collectively. Partnerships with research institutions and private sectors enhance these collaborative efforts.
Future Outlook
Looking ahead, the future of the Murray-Darling Basin depends significantly on adaptive management and comprehensive planning. Continued investment in infrastructure, technology, and research is necessary to build resilience against water shortages. Climate change adaptation strategies will also play a critical role in safeguarding water resources for future generations.
Conclusion: A Path Forward

The future of the Murray-Darling Basin hinges on the effectiveness of water management strategies employed by NSW and Victoria. Through innovation, collaboration, and policy reform, these states are working to secure a sustainable water future. While challenges remain, the efforts underway offer hope for balancing environmental health and economic prosperity in this iconic region.




