In recent years, the concept of eco-villages has grown in prominence as individuals and communities seek sustainable alternatives to urban living. These intentionally designed communities aim to minimize environmental impact and promote a harmonious balance with nature. As we face pressing environmental challenges, the allure of eco-villages raises an important question: Are they the future of sustainable living?
Understanding Eco-Villages

Eco-villages are communities that employ sustainable practices in every aspect of life, from building homes and cultivating food to managing waste and energy. These communities are designed with the goal of minimizing negative environmental impacts, fostering social wellbeing, and often incorporating elements of permaculture and renewable energy sources. Each eco-village is unique, but they all share a common vision of living in harmony with the natural world.
The Historical Roots of Eco-Villages

The roots of the eco-village movement can be traced back to the 1960s and 1970s, when counter-culture movements began to question conventional living practices. As environmental awareness grew, so did the desire for alternative, sustainable ways of living. This led to the establishment of early eco-communities focused on self-sufficiency and ecological balance, sowing the seeds for modern eco-villages.
Community and Collaboration

At the heart of every eco-village is a strong sense of community and collaboration. Members of eco-villages work together to achieve common goals, whether it’s managing shared resources or organizing social activities. This collaborative spirit not only strengthens community bonds but also ensures the sustainable management of resources, leading to greater resilience and adaptability in the face of environmental changes.
Energy Efficiency and Renewable Resources

Eco-villages prioritize the use of renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and hydro power. By reducing reliance on non-renewable energy, these villages significantly lower their carbon footprints. Energy-efficient design principles, including passive heating and cooling, are often incorporated to optimize energy use, demonstrating that high-quality, comfortable living need not be energy-intensive.
Sustainable Agriculture and Food Production

Food production is a cornerstone of eco-village life, where emphasis is placed on organic farming methods and permaculture principles. Eco-villages often maintain community gardens, orchards, and farms, promoting biodiversity and reducing dependency on industrial agriculture. This local, sustainable approach to food production not only nurtures the environment but also enhances food security and resilience.
Innovative Building Practices
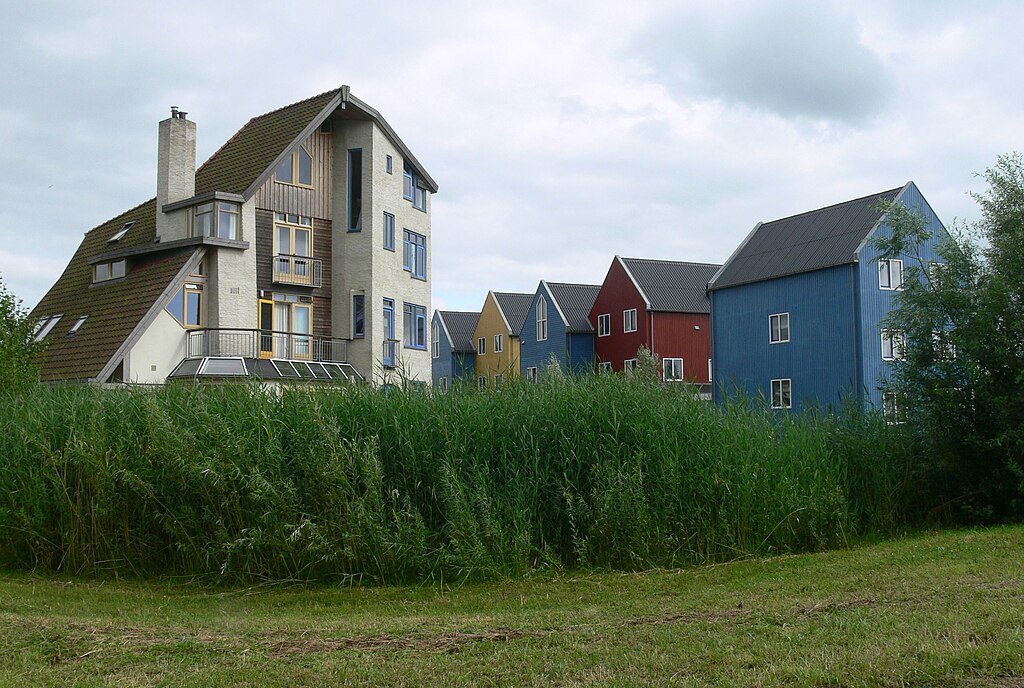

The architectural design in eco-villages typically features sustainable building materials like straw bales, cob, and reclaimed wood. These materials, combined with innovative building techniques, result in structures that are the epitome of sustainability and aesthetic appeal. The focus on energy conservation, insulation, and natural light further reduces environmental impact.
Waste Management and Recycling

Effective waste management systems are integral to eco-villages. Composting toilets, recycling programs, and resource recovery strategies are commonplace to minimize waste generation. Eco-villages champion the concept of a circular economy, where resources are reused and recycled, drastically reducing landfill contributions.
Social and Educational Impact

Beyond environmental benefits, eco-villages foster social interaction and offer educational opportunities. Workshops in sustainable practices and community events encourage knowledge sharing, collaboration, and personal growth. These interactions foster a deep connection with nature and empower individuals to live sustainably even outside the eco-village setting.
Challenges and Criticisms

Despite their benefits, eco-villages face several challenges, including initial financial investments, regulatory hurdles, and social dynamics. Critics also argue that eco-villages might be limited in scale and struggle to exert broader influence. However, as ecological and technological innovations advance, these challenges become increasingly surmountable.
The Role of Technology
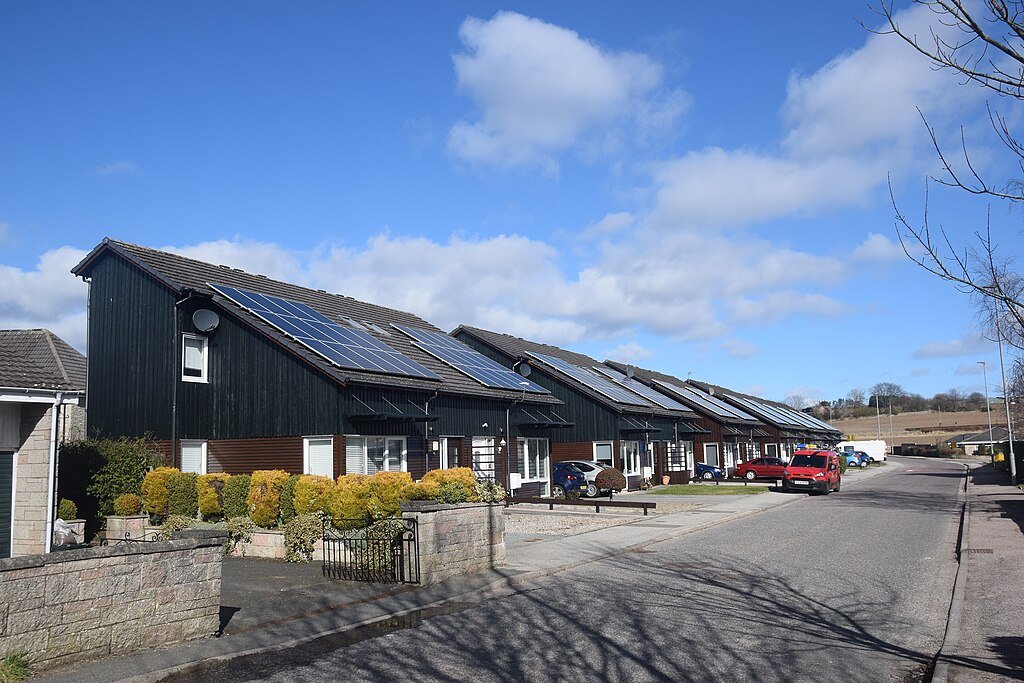

Technology plays a pivotal role in the success of eco-villages. Smart technologies, such as digital energy management systems and water-saving devices, facilitate efficient resource use. These innovations not only enhance sustainability but also demonstrate how modern technologies can be harmoniously integrated into sustainable living.
Eco-Villages Around the World

Globally, eco-villages exist in diverse forms, from the urban eco-districts of Berlin to rural initiatives in Thailand. Each reflects local traditions, environment, and resources, showcasing the adaptability of the eco-village model. These communities serve as living laboratories for sustainable innovation and offer valuable insights into sustainable practices adaptable to various contexts.
Are Eco-Villages the Future?
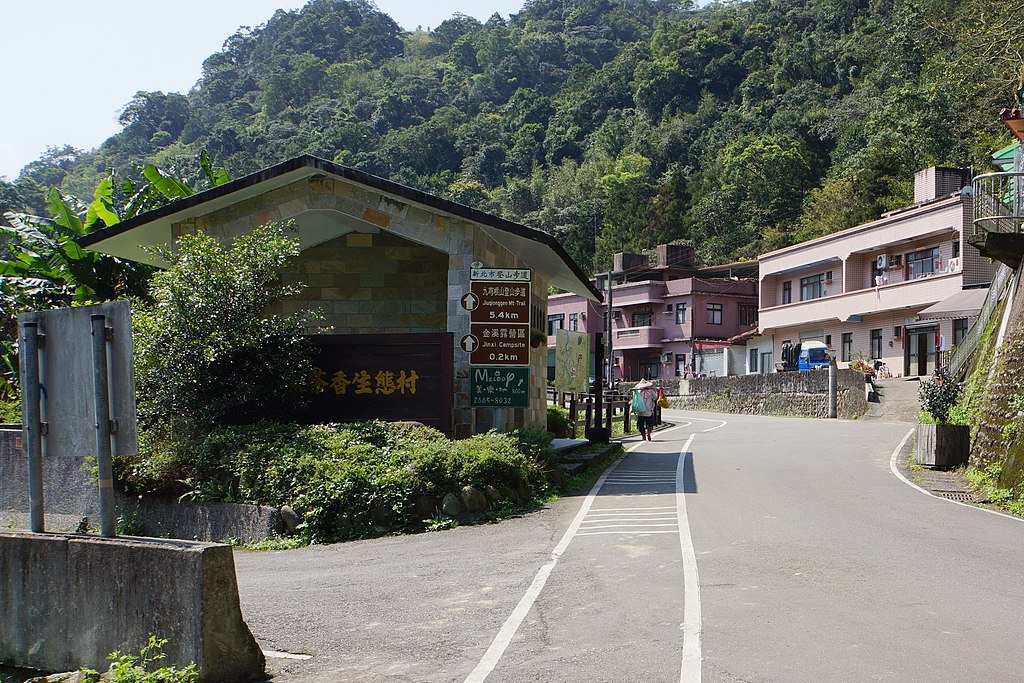

While eco-villages may not replace urban environments en masse, they offer a viable blueprint for sustainable living. They embody principles that can be scaled and integrated into existing cities, influencing urban planning, policy, and individual lifestyles. As awareness grows, the eco-village model will likely inspire widespread adoption of sustainable practices.
Conclusion: Embracing a Sustainable Future
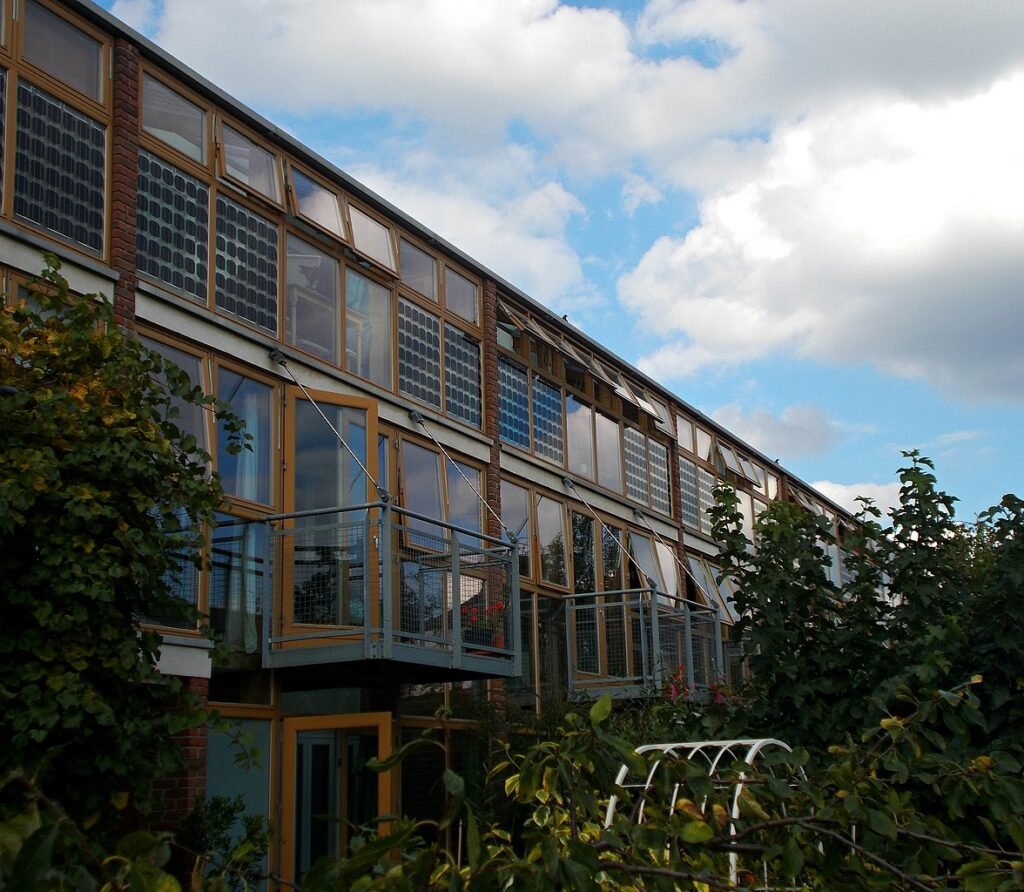

Eco-villages illustrate a path forward amid environmental challenges, demonstrating that sustainable living is not only possible but also desirable. While they may not be the sole future of sustainable living, they offer a compelling vision for how communities can align with ecological principles. As environmental urgency increases, the lessons and innovations from eco-villages will be invaluable in guiding society towards a more sustainable future.