Genetic engineering has been at the forefront of scientific innovation, offering groundbreaking solutions to some of the most complex problems in agriculture, medicine, and environmental sustainability. From enhancing crop yields to pioneering treatments for genetic disorders, this dynamic field constantly evolves, driven by an intersection of biology, technology, and ethical considerations. This article explores 13 intriguing advances in genetic engineering, highlighting how these innovations are reshaping our world.
Improved Crop Resistance

One of the most impactful applications of genetic engineering is the development of crops that can withstand environmental stressors. Through gene editing techniques, scientists have been able to enhance plant resistance to drought, pests, and diseases. For example, genetically modified (GM) maize and soybeans have been engineered for greater resilience, leading to increased food security and reduced reliance on chemical pesticides.
Golden Rice and Nutritional Enhancement
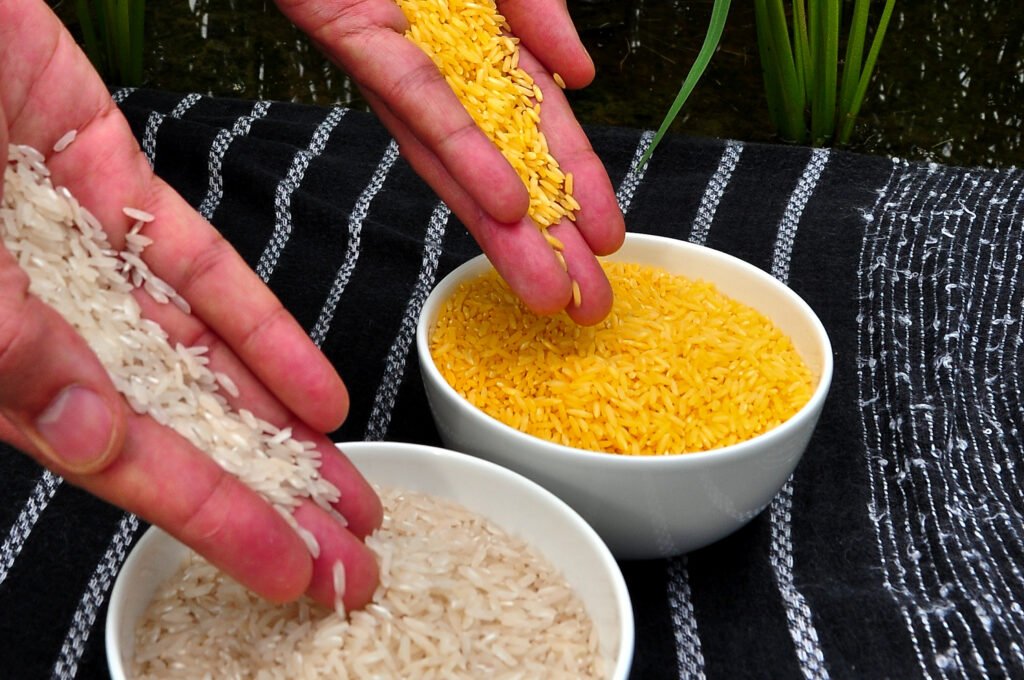

Golden Rice is a genetically modified variety of rice engineered to produce beta-carotene, a precursor of vitamin A. This innovation addresses vitamin A deficiency, a critical health issue affecting millions worldwide, particularly in developing countries. By integrating vital nutrients directly into staple crops, genetic engineering has the potential to combat malnutrition and associated health problems.
CRISPR Technology and Genome Editing
The advent of CRISPR-Cas9 technology has revolutionized the field of genetics, offering precise, efficient, and cost-effective methods for genome editing. This tool allows scientists to make specific changes to an organism’s DNA, opening doors to potential cures for genetic disorders, improvements in agricultural productivity, and advancements in personalized medicine.
Reprogramming Stem Cells

Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) are adult cells that have been genetically reprogrammed to an embryonic stem cell-like state. This breakthrough in regenerative medicine means that these cells can potentially develop into any cell type, offering hope for treating a wide range of conditions such as Parkinson’s disease, spinal cord injuries, and heart disease.
Targeted Cancer Therapies

Genetic engineering has paved the way for targeted cancer therapies, which are designed to attack cancer cells without harming normal cells. By identifying genetic mutations unique to an individual’s cancer, treatments can be personalized, improving efficacy and reducing side effects. This approach is transforming cancer care and improving survival rates worldwide.
Gene Therapy for Inherited Diseases

Gene therapy involves altering the genes inside a patient’s cells to treat or prevent disease. Successful applications include treatments for inherited conditions like cystic fibrosis, hemophilia, and more recently, spinal muscular atrophy. By targeting the root causes of genetic disorders, gene therapy offers a promising path to long-term solutions.
Biofortification of Staple Foods

Beyond Golden Rice, genetic engineering is harnessed to biofortify other staple foods like cassava, sweet potatoes, and bananas. By introducing genes that boost their vitamin and mineral content, scientists aim to improve the nutritional profile of these foods, enhancing public health and reducing incidences of diet-related diseases.
Biodiversity Conservation and Genetic Rescue

Conservation efforts are increasingly relying on genetic engineering to protect endangered species. Techniques such as ‘genetic rescue’ involve increasing genetic diversity within small populations to improve their survival chances. This approach can help to counteract the effects of inbreeding and environmental changes threatening biodiversity.
Synthetic Biology and New Biofuels

Synthetic biology combines genetic engineering and bioinformatics to design and construct new biological entities. In the realm of energy, this innovation is being used to create biofuels from engineered microorganisms. These sustainable alternatives to fossil fuels could play a significant role in reducing carbon emissions and combating climate change.
Designer Probiotics for Gut Health

Genetic engineering is advancing our understanding and manipulation of the gut microbiome through the development of designer probiotics. These engineered microorganisms are tailored to promote gut health, aiding in digestion and boosting immunity. This approach could lead to new treatments for gastrointestinal disorders and metabolic diseases.
Enhancing Animal Welfare through Genetic Innovations
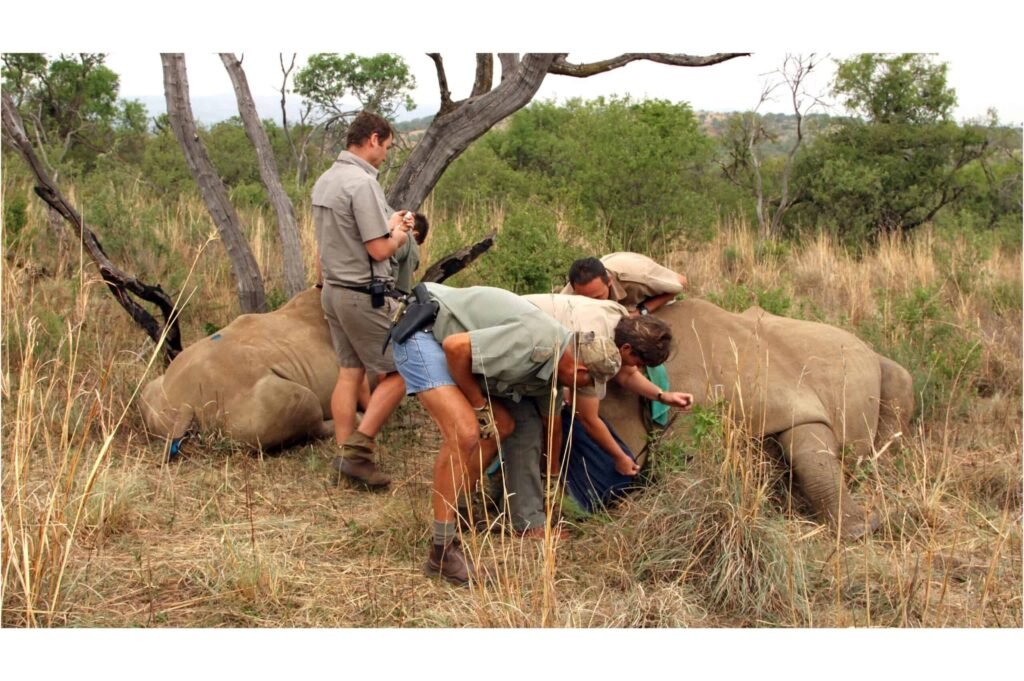

In the agricultural sector, genetic engineering is being used to improve animal welfare. For example, researchers have developed hornless cattle through genome editing, reducing the need for painful dehorning procedures. These efforts reflect a broader aim to create more humane and sustainable livestock farming practices.
Genome Sequencing and Personalized Medicine

The cost of genome sequencing has decreased dramatically, making it more accessible for personalized medicine. By understanding an individual’s genetic makeup, healthcare providers can tailor prevention, diagnostics, and treatments more effectively. This personalized approach promises improved patient outcomes and a new era in healthcare.
Therapeutic Cloning and Regenerative Medicine

Therapeutic cloning, which involves creating embryonic stem cells for medical treatments, is a pioneering area of genetic engineering. It holds the potential for regenerating damaged tissues and organs, offering solutions for patients suffering from degenerative diseases or traumatic injuries. While ethical considerations remain, the prospects for regenerative medicine are transforming healthcare possibilities.
Conclusion

Genetic engineering continues to break new ground, offering solutions that were once thought to belong only to the realm of science fiction. As we have explored, the advances span various domains from agriculture to medicine, delivering promising innovations to address pressing global challenges. While ethical considerations and regulatory frameworks will continue to evolve, the potential for positive impact on human health, food security, and environmental conservation is immense. As researchers push the boundaries of what’s possible, genetic engineering stands as a testament to human ingenuity and the relentless pursuit of progress.




