In the intricate web of life on Earth, certain species play crucial roles in maintaining the balance and health of ecosystems. These vital organisms, often referred to as ‘key species,’ can significantly influence the environment, supporting diverse life forms and maintaining stability. Understanding these species’ roles helps us appreciate their importance and drives home the urgent need to protect them for the health of our planet.
1. Honey Bees: The Tireless Pollinators
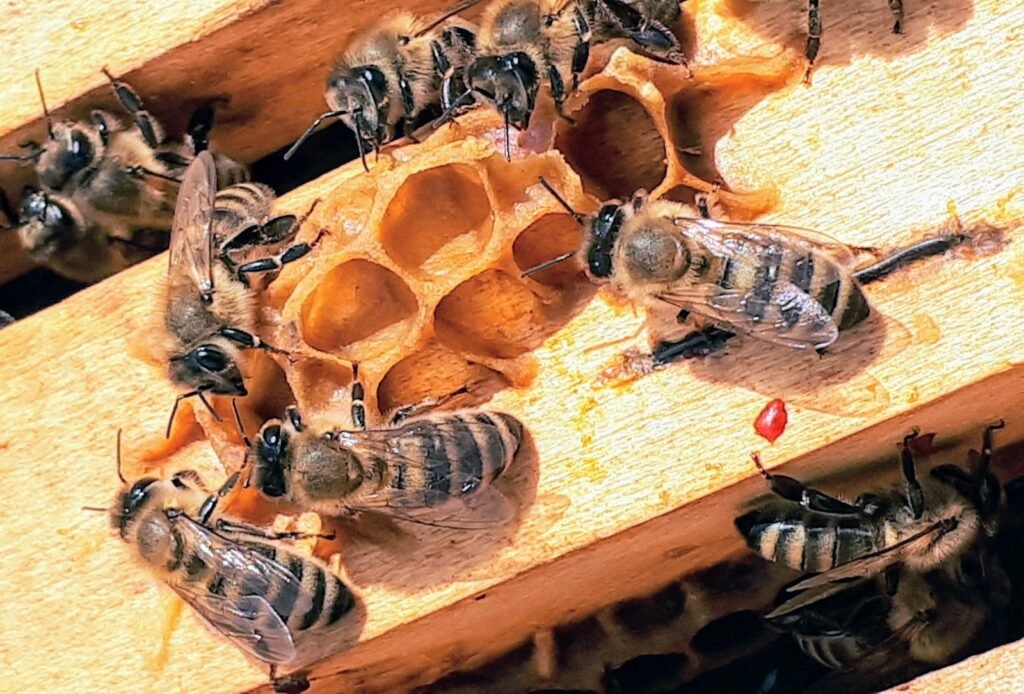

Honey bees are renowned for their crucial role in pollination, a process that enables the reproduction of flowering plants. They contribute to the growth of fruits, vegetables, and nuts, forming the foundation of many food chains. As they buzz from flower to flower, honey bees support not just agricultural industries but entire ecosystems by fostering plant diversity.
2. Wolves: Balancing Predator and Prey

Wolves are apex predators, meaning they are at the top of the food chain. Their presence regulates prey populations such as deer and elk, preventing overgrazing and helping to sustain healthy vegetative growth. This, in turn, supports a variety of other species, showcasing the wolf’s pivotal role in ecosystem balance.
3. Sea Otters: Guardians of Kelp Forests
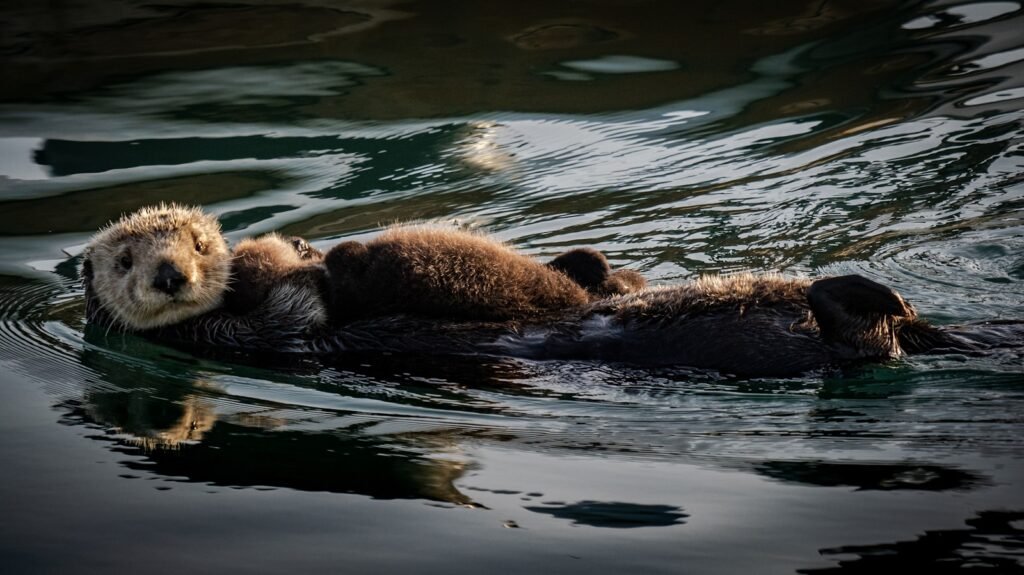

Sea otters play a significant role in marine environments by controlling sea urchin populations. Sea urchins, if left unchecked, can decimate kelp forests, which are crucial habitats for numerous marine organisms. By regulating the sea urchin population, sea otters help maintain these underwater forests, supporting species diversity and carbon sequestration.
4. Keystone Elephants: Landscape Architects

Elephants are known as ‘ecosystem engineers’ due to their ability to transform landscapes. Through activities such as tree felling and seed dispersal, they create clearings in densely wooded areas, encouraging plant diversity and providing habitats for other species. Their movements and behaviors are vital for maintaining ecological balance.
5. Prairie Dogs: Earth Movers
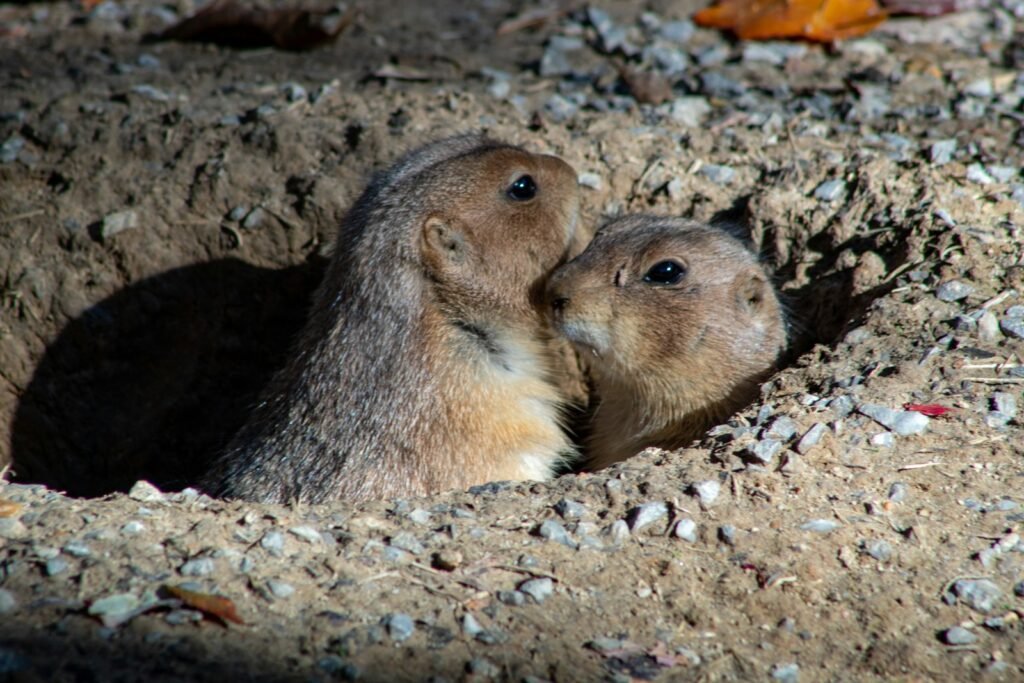

Prairie dogs are small yet mighty influencers of their ecosystems. Their burrowing activities aerate the soil, promote water penetration, and increase nutrient cycling. These actions enhance plant growth, support wildlife diversity, and contribute to a thriving ecosystem.
6. Bats: Night-time Pest Controllers
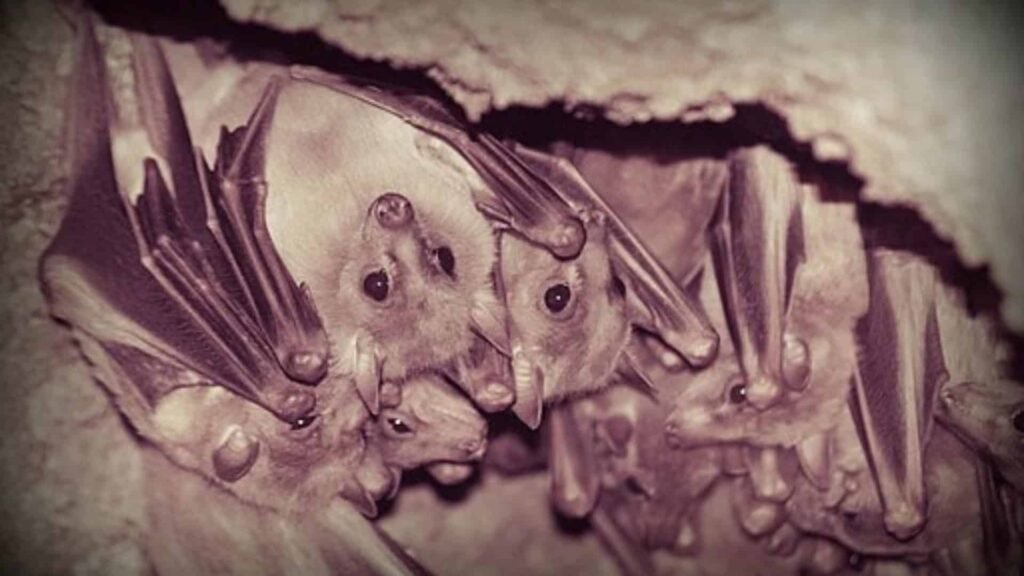
Bats serve as natural pest controllers, consuming vast quantities of insects each night. This predation helps protect crops and reduces the need for chemical pesticides, benefiting both agricultural landscapes and natural food webs. Furthermore, some bat species are also essential pollinators and seed dispersers in tropical regions.
7. Beavers: Natural Dam Builders

Beavers are another example of ecosystem engineers who dramatically alter their habitats through dam-building activities. These structures create wetlands, which are rich ecosystems that support a wide array of plant and animal life. Beaver activity promotes biodiversity and provides critical services like water filtration and flood control.
8. Sharks: Ocean Health Monitors

As top predators, sharks maintain the balance within marine ecosystems by controlling prey populations. Their presence ensures the health of fish communities, preventing any single species from dominating. Healthy shark populations indicate robust and balanced ocean environments.
9. African Cape Buffalo: Grassland Managers

The Cape buffalo is crucial for maintaining savanna ecosystems. Their grazing patterns clear tall grasses, which would otherwise suppress plant diversity. This grazing supports food availability for other species and contributes to a dynamic and balanced habitat.
10. Mycorrhizal Fungi: Underground Networkers
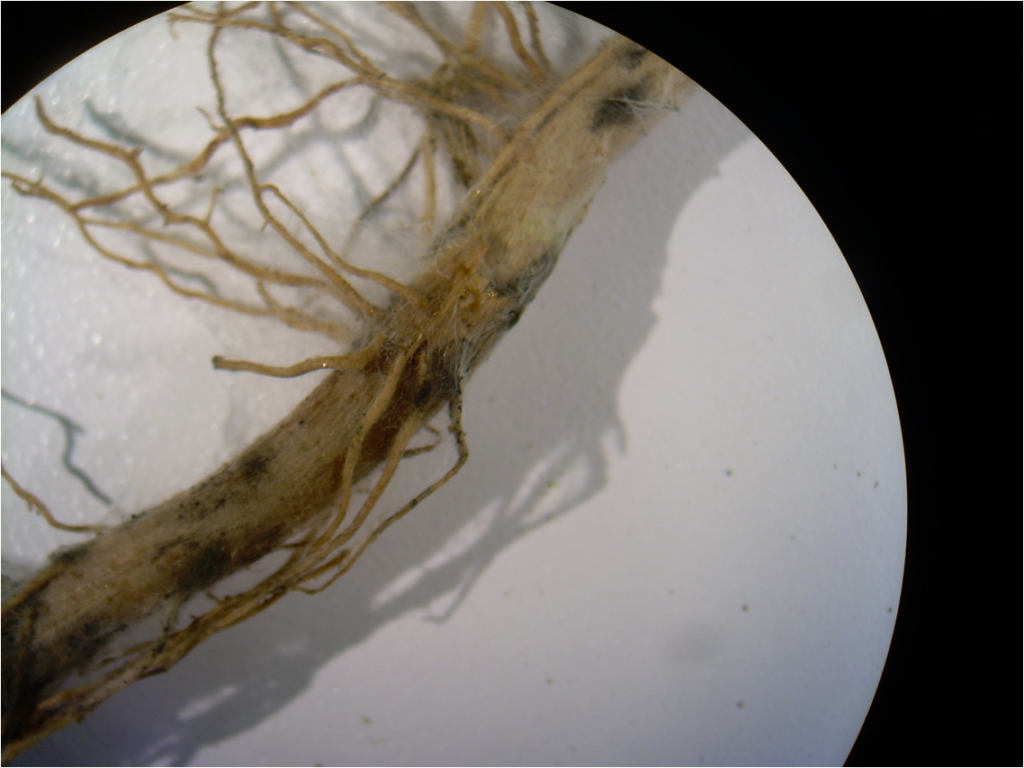
These fungi form symbiotic relationships with about 90% of plant species, extending their root systems and aiding in water and nutrient uptake. Mycorrhizal networks boost plant health, increase resistance to disease, and improve soil cohabitation, making them indispensable players in terrestrial ecosystems.
11. Horseshoe Crabs: Blue Blood Biochemists
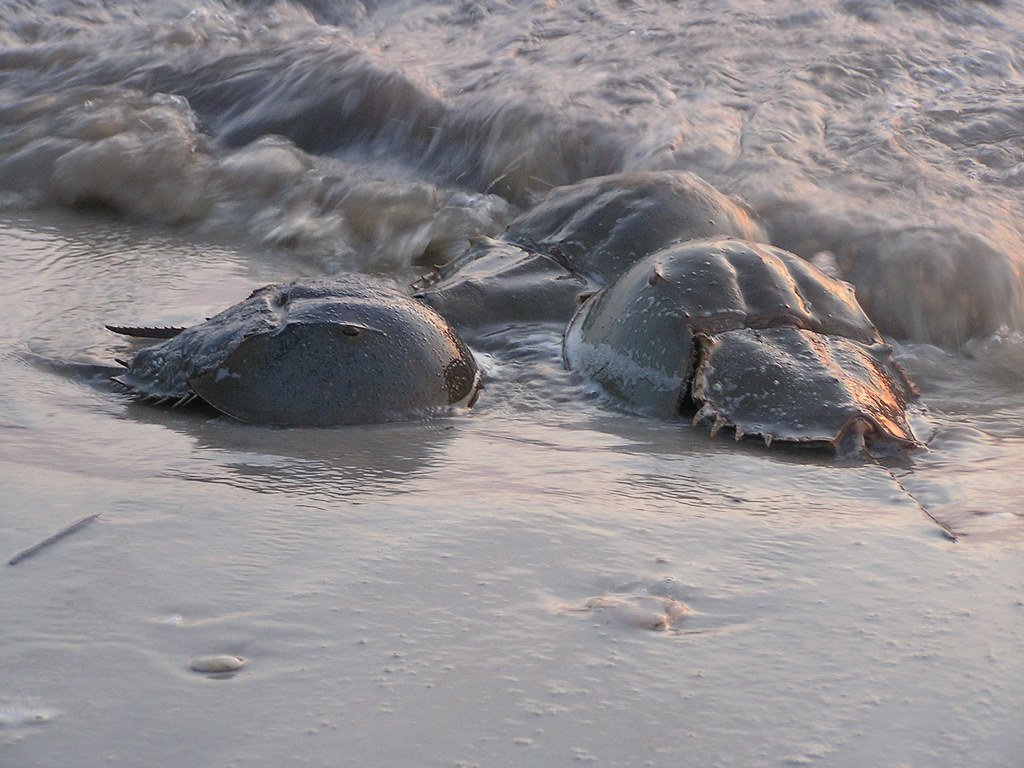

Horseshoe crabs play a dual role in ecosystems and in science. Their eggs provide essential food for migratory birds, while their blood, unique for its use in medical testing, highlights their biological importance. Maintaining horseshoe crab populations is crucial for both ecological and scientific reasons.
12. Coral Reefs: Biodiversity Hotspots

Coral reefs support an exceptional diversity of marine life. Hundreds of thousands of species rely on reefs for food and shelter, making corals a foundation for marine biodiversity. The health of coral reefs is directly linked to the overall wellness of ocean ecosystems.
13. Jaguars: Jungle Enforcers

As apex predators, jaguars help manage prey populations in rainforests. Their regulation of species such as capybara and deer helps maintain a balance that supports the vegetation diversity necessary for a thriving ecosystem.
14. Vultures: Nature’s Clean-up Crew
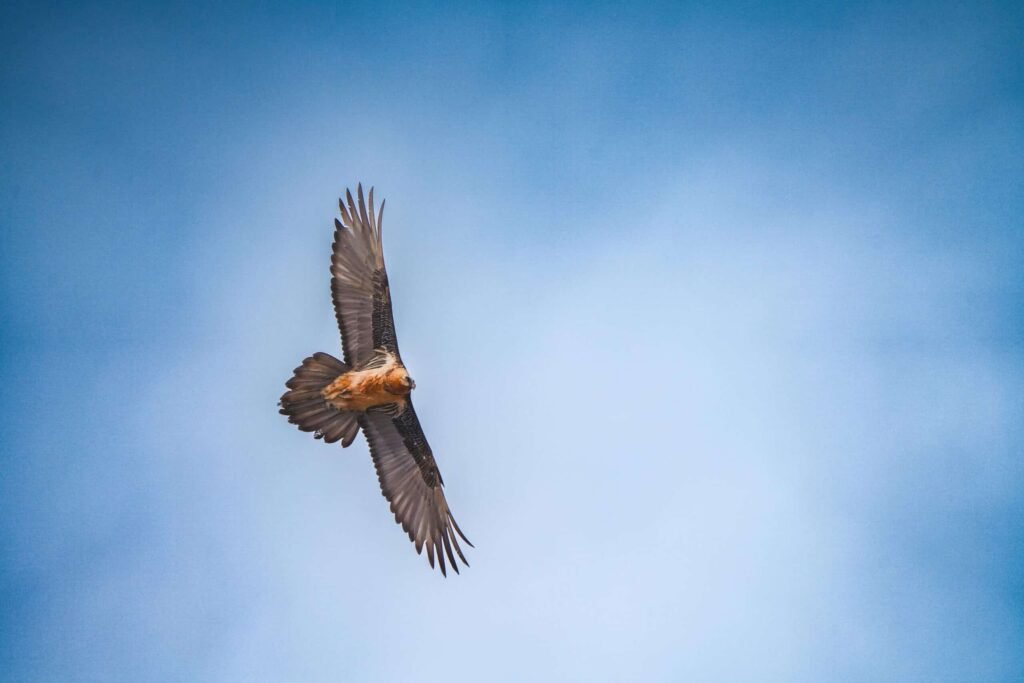

Vultures play a critical role in maintaining ecosystem health by consuming carcasses. Their efficient scavenging helps prevent the spread of disease and fosters a cleaner environment. Vultures’ unique digestive systems neutralize dangerous pathogens, keeping ecosystems safe.
15. Native Pollinators: Unsung Heroes
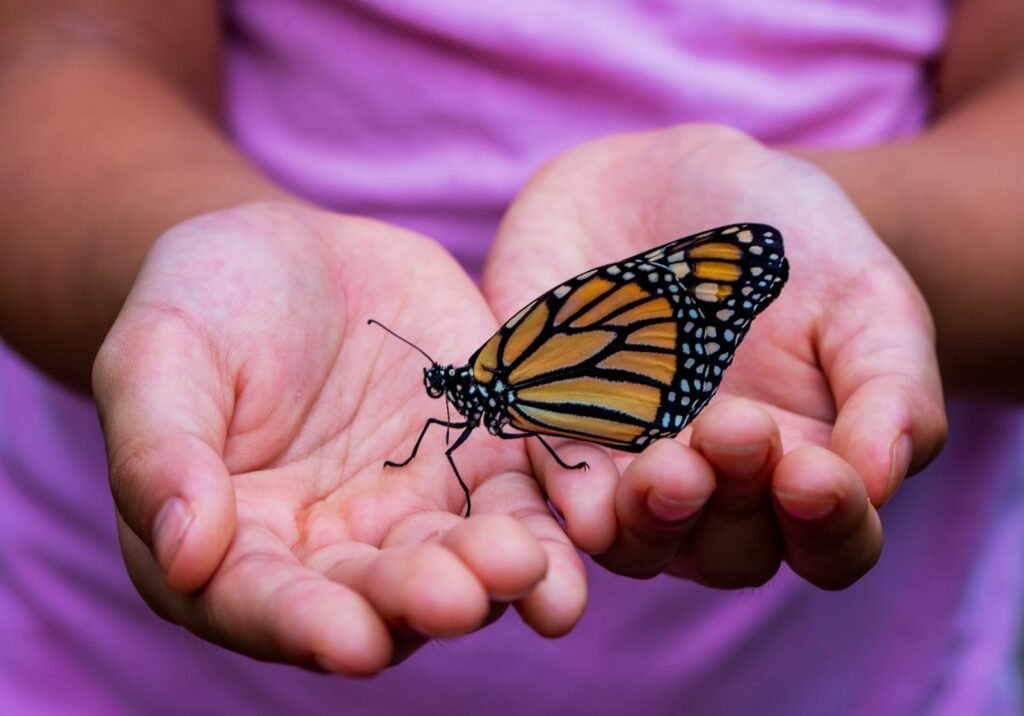

Beyond honey bees, many native pollinators like butterflies, moths, and solitary bees perform indispensable services in maintaining plant diversity. These species pollinate wild plants that form the basis of many food webs, supporting a multitude of other life forms.
Protecting Key Species for Our Future

In conclusion, each species plays a role in the vibrant tapestry of life, especially these key species that support ecosystem health and diversity. Their contributions underscore the interconnectedness of life and the importance of biodiversity to planetary health. As stewards of the Earth, it is imperative that we protect these species to sustain ecosystems and, ultimately, our own survival.




